Deliberative politics emphasizes reasoned discussion and inclusive dialogue to make collective decisions that reflect diverse perspectives. It fosters transparency, mutual respect, and accountability, enabling communities to deliberate on complex issues effectively. Explore the rest of the article to understand how deliberative practices can enhance Your political engagement.
Table of Comparison
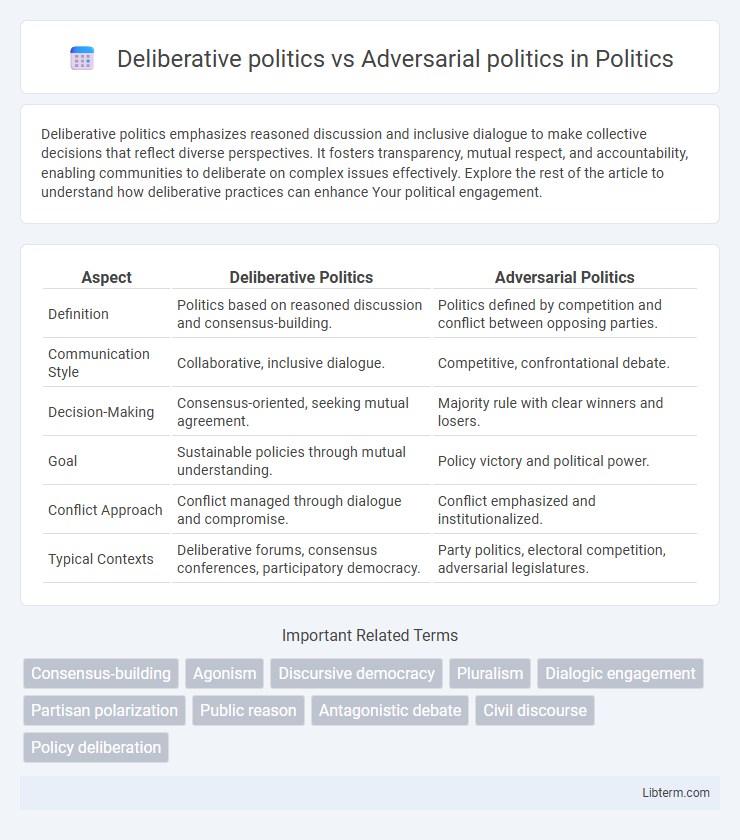
| Aspect | Deliberative Politics | Adversarial Politics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Politics based on reasoned discussion and consensus-building. | Politics defined by competition and conflict between opposing parties. |
| Communication Style | Collaborative, inclusive dialogue. | Competitive, confrontational debate. |
| Decision-Making | Consensus-oriented, seeking mutual agreement. | Majority rule with clear winners and losers. |
| Goal | Sustainable policies through mutual understanding. | Policy victory and political power. |
| Conflict Approach | Conflict managed through dialogue and compromise. | Conflict emphasized and institutionalized. |
| Typical Contexts | Deliberative forums, consensus conferences, participatory democracy. | Party politics, electoral competition, adversarial legislatures. |
Introduction to Deliberative and Adversarial Politics
Deliberative politics centers on reasoned discussion and consensus-building among diverse participants to arrive at well-informed decisions, emphasizing transparency and mutual respect. Adversarial politics involves competing parties or individuals engaging in strategic debate and conflict to advance their interests and secure power, often highlighting division and opposition. Understanding these contrasting approaches clarifies how democratic processes function through cooperation or contestation in policymaking.
Core Principles of Deliberative Politics
Deliberative politics centers on inclusive dialogue, reasoned debate, and mutual respect to achieve consensus-driven decisions that reflect the common good. It emphasizes transparency, equal participation, and the thorough consideration of diverse viewpoints to foster informed and legitimate policy outcomes. This approach contrasts with adversarial politics, which often prioritizes competition and winning over collaborative problem-solving.
Fundamental Tenets of Adversarial Politics
Adversarial politics is founded on the principle of structured competition between opposing parties aiming to assert their interests and values within a political system. It emphasizes conflict, debate, and the pursuit of power through electoral victories and negotiation tactics. Central to this model are partisan loyalty, strategic opposition, and the prioritization of political advantage over consensus-building.
Key Differences Between Deliberative and Adversarial Approaches
Deliberative politics emphasizes consensus-building through reasoned dialogue and inclusive participation, fostering mutual understanding and collaborative decision-making. Adversarial politics centers on competition and conflict between opposing parties or interests, often prioritizing winning over consensus. Key differences include the deliberative approach's focus on thoughtful debate and shared solutions, contrasted with the adversarial approach's reliance on confrontation and strategic advantage.
Historical Evolution of Political Debate Styles
The historical evolution of political debate styles reveals a transition from adversarial politics, characterized by confrontational and competitive dialogue rooted in ancient Greek democracy, to deliberative politics, emphasizing reasoned discussion and consensus-building traced to Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke and Jurgen Habermas. Adversarial politics dominated early parliamentary systems, promoting clear divisions between parties to foster accountability, while deliberative politics gained traction in modern democracies seeking inclusive, reflective dialogue to address complex societal challenges. This shift underscores the increasing recognition of dialogue quality and participatory engagement as essential components of effective political decision-making.
Impact on Policy Making and Governance
Deliberative politics fosters inclusive dialogue and consensus-building, leading to more transparent and well-informed policy decisions that enhance governance legitimacy and public trust. In contrast, adversarial politics emphasizes competition and conflict, often resulting in polarized outcomes and gridlock that impede effective policy implementation. The impact on governance is significant, as deliberative approaches promote collaborative problem-solving, while adversarial methods can undermine cooperative policymaking and reduce governmental efficiency.
Public Participation and Civic Engagement
Deliberative politics emphasizes inclusive public participation by fostering open dialogue and reasoned debate among citizens to reach consensus on policy issues. Civic engagement in this model involves collaborative problem-solving and active listening, encouraging diverse viewpoints to shape collective decisions. In contrast, adversarial politics prioritizes competitive debate and partisan conflict, often mobilizing public participation through rallies, protests, and electoral campaigns that highlight opposing interests rather than consensus-building.
Media Influence on Political Styles
Media influence shapes deliberative politics by promoting reasoned debate and in-depth discussion through public forums and fact-based reporting, encouraging citizens to engage constructively. In adversarial politics, media often amplifies conflict and polarization by highlighting sensationalism and dramatic confrontations, fostering a competitive and divisive political climate. The contrasting media portrayals significantly affect public perception, political accountability, and the overall democratic process.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Deliberative politics, exemplified by the Oregon Citizens' Initiative Review, demonstrates success in fostering informed public decisions through inclusive dialogue and expert input, leading to higher voter satisfaction and more nuanced policies. Conversely, adversarial politics, as seen in the 2016 US Presidential Election, often results in polarization and gridlock, undermining legislative productivity and public trust. Case studies reveal that deliberative approaches enhance democratic legitimacy, while adversarial tactics frequently exacerbate societal divisions and reduce government effectiveness.
Future Trends in Political Discourse
Future trends in political discourse emphasize a shift toward deliberative politics, promoting inclusive dialogue and consensus-building to address complex societal issues. Advancements in digital platforms are facilitating more participatory and reflective citizen engagement, contrasting with traditional adversarial politics characterized by competition and polarized debate. This evolution aims to reduce division and foster more collaborative governance models responsive to diverse stakeholder perspectives.
Deliberative politics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com