Rule by decree allows governments to enact laws and policies without the usual legislative approval, speeding decision-making in times of crisis or urgency. This approach can enhance executive power but may also reduce parliamentary oversight and democratic accountability. Explore how rule by decree impacts governance and your rights in the full article.
Table of Comparison
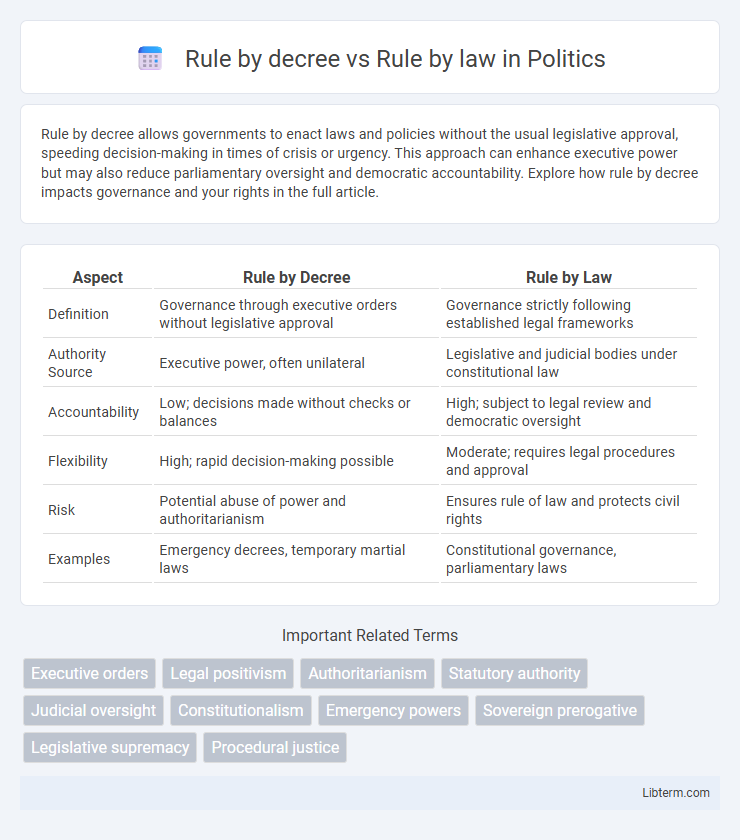
| Aspect | Rule by Decree | Rule by Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance through executive orders without legislative approval | Governance strictly following established legal frameworks |
| Authority Source | Executive power, often unilateral | Legislative and judicial bodies under constitutional law |
| Accountability | Low; decisions made without checks or balances | High; subject to legal review and democratic oversight |
| Flexibility | High; rapid decision-making possible | Moderate; requires legal procedures and approval |
| Risk | Potential abuse of power and authoritarianism | Ensures rule of law and protects civil rights |
| Examples | Emergency decrees, temporary martial laws | Constitutional governance, parliamentary laws |
Understanding Rule by Decree
Rule by decree involves decisions made directly by an authority without requiring legislative approval, allowing swift and sometimes unilateral governance. This approach contrasts with rule by law, where laws are established through formal legislative processes and must be followed consistently. Understanding rule by decree highlights how it can centralize power, often used in emergencies but potentially bypassing democratic checks and balances.
Defining Rule by Law
Rule by law refers to a governance system where laws are clearly defined, publicly promulgated, and apply equally to all individuals, ensuring legal predictability and fairness. Unlike rule by decree, which involves decisions made unilaterally by authorities without legislative process, rule by law emphasizes adherence to established legal frameworks and judicial oversight. This concept underpins constitutional democracies, promoting accountability and limiting arbitrary power by rooting authority in codified statutes.
Historical Contexts: Decrees vs Laws
Rule by decree historically emerges in autocratic regimes where leaders bypass legislative bodies, enabling swift decisions without legal scrutiny, often seen in wartime or emergency contexts. Rule by law develops from democratic traditions, establishing a framework where laws are created through representative institutions and apply equally to all, ensuring accountability and predictability. Historical shifts from decree-based rule to law-based governance mark transitions from absolutist monarchies or dictatorships to constitutional states emphasizing legal norms.
Characteristics of Rule by Decree
Rule by decree is characterized by the concentration of legislative, executive, and sometimes judicial powers in the hands of a single authority or ruler, enabling rapid decision-making without the need for parliamentary approval or legal procedures. It often results in temporary or emergency laws that bypass established legal frameworks, allowing for swift implementation but limited checks and balances. This form of governance prioritizes efficiency and control, frequently at the expense of transparency, accountability, and civil liberties.
Principles Underpinning Rule by Law
The principles underpinning rule by law emphasize accountability, predictability, and equality before the law, ensuring that laws govern a nation rather than arbitrary decisions by rulers. Rule by law mandates that laws are publicly promulgated, equally enforced, and independently adjudicated, protecting individual rights and limiting government power. In contrast, rule by decree often bypasses these principles, allowing leaders to enact decisions unilaterally without legal constraints or judicial oversight.
Political Implications and Power Dynamics
Rule by decree centralizes power in the hands of a single authority or executive, often bypassing legislative oversight and undermining democratic processes. Rule by law establishes a legal framework where laws apply equally to all, distributing power through institutional checks and balances that limit arbitrary decision-making. The political implications revolve around accountability, where rule by decree risks authoritarianism, while rule by law promotes transparency and protection of civil liberties.
Impact on Civil Liberties and Human Rights
Rule by decree often concentrates power in the hands of a single ruler or executive body, leading to arbitrary decision-making that can severely restrict civil liberties and human rights. In contrast, rule by law establishes a transparent legal framework that protects individual freedoms through consistent application of laws and judicial oversight. Societies governed by rule of law typically experience stronger safeguards against abuses of power and better enforcement of human rights standards.
Case Studies: Global Examples
Rule by decree is exemplified by authoritarian regimes such as Nazi Germany and Soviet Russia, where leaders issued unilateral executive orders bypassing legislative processes to consolidate power rapidly. In contrast, Rule by law is observed in democratic nations like the United States and Germany, where legal frameworks and independent courts limit government authority and ensure accountability through transparent legislative procedures. Comparative case studies reveal that rule by decree often leads to unchecked power and human rights abuses, whereas rule by law promotes stability, fairness, and the protection of civil liberties.
Risks and Consequences of Decree-Based Governance
Decree-based governance concentrates power in the hands of executives, bypassing legislative oversight and increasing the risk of authoritarianism and arbitrary decision-making. Without the constraints of rule by law, which ensures transparent, stable, and codified legal frameworks, decree-based rule often leads to legal uncertainty, abuse of power, and erosion of democratic institutions. The absence of checks and balances in decree governance undermines public trust and can trigger social unrest and economic instability due to unpredictable policy shifts.
Pathways to Upholding the Rule of Law
Rule by decree centralizes decision-making in executive authorities issuing orders without legislative oversight, often bypassing established legal frameworks and undermining checks and balances. In contrast, rule by law emphasizes adherence to codified statutes and constitutional principles, ensuring that all government actions are subject to legal scrutiny and judicial review. Effective pathways to upholding the rule of law involve strengthening independent judiciaries, promoting transparent legislative processes, and enforcing accountability mechanisms that prevent arbitrary governance.
Rule by decree Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com