E-participation enhances democratic engagement by enabling citizens to contribute to decision-making through digital platforms. This approach increases transparency, encourages diverse viewpoints, and fosters greater accountability within governance processes. Discover how e-participation can empower Your voice and transform public involvement in the full article.
Table of Comparison
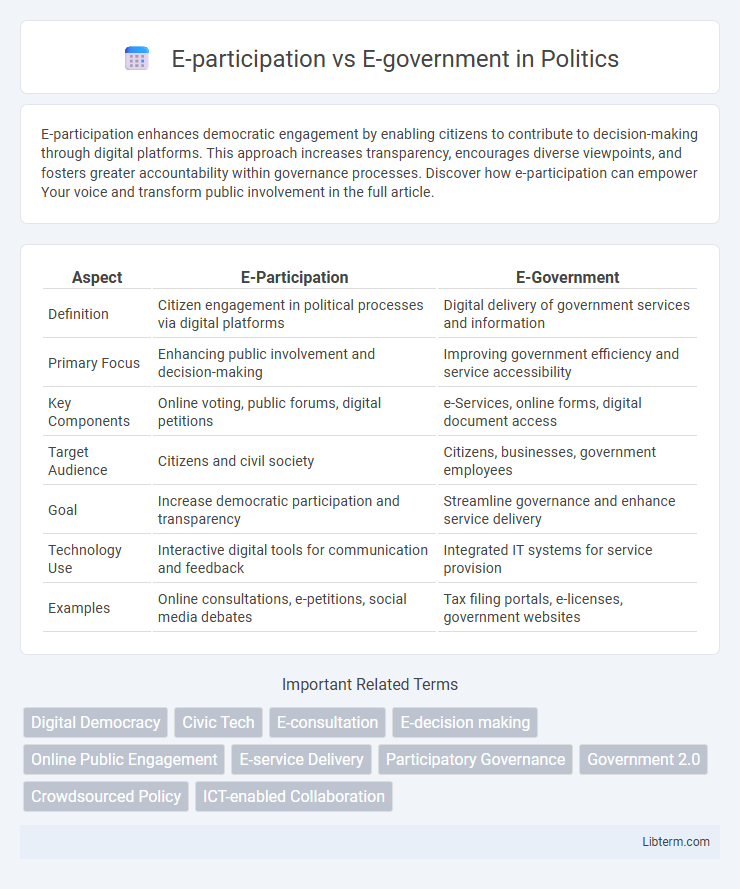
| Aspect | E-Participation | E-Government |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Citizen engagement in political processes via digital platforms | Digital delivery of government services and information |
| Primary Focus | Enhancing public involvement and decision-making | Improving government efficiency and service accessibility |
| Key Components | Online voting, public forums, digital petitions | e-Services, online forms, digital document access |
| Target Audience | Citizens and civil society | Citizens, businesses, government employees |
| Goal | Increase democratic participation and transparency | Streamline governance and enhance service delivery |
| Technology Use | Interactive digital tools for communication and feedback | Integrated IT systems for service provision |
| Examples | Online consultations, e-petitions, social media debates | Tax filing portals, e-licenses, government websites |
Introduction to E-participation and E-government
E-government refers to the use of digital technologies by government agencies to deliver public services, improve administrative efficiency, and enhance information access for citizens. E-participation specifically focuses on enabling citizens to engage actively in the decision-making processes through online platforms, facilitating transparency, consultation, and collaboration. Both concepts leverage ICT tools but differ in scope; e-government centers on service delivery, while e-participation emphasizes citizen involvement in governance.
Defining E-participation
E-participation refers to the use of digital tools and platforms to enable citizens' direct involvement in decision-making processes, policy formulation, and public discourse. It emphasizes active engagement, transparency, and collaboration between government entities and the public, fostering democratic participation beyond traditional voting mechanisms. Distinct from e-government, which primarily focuses on the digital delivery of public services and administrative functions, e-participation centers on interactive communication and civic empowerment through technology.
Defining E-government
E-government refers to the use of digital technologies by government agencies to deliver public services, enhance administrative efficiency, and facilitate communication with citizens. It encompasses online platforms for service delivery, digital management of internal processes, and transparent information dissemination to promote accountability. Unlike e-participation, which focuses on citizen engagement and input in governance, e-government primarily centers on the digital transformation of public sector operations.
Key Differences Between E-participation and E-government
E-participation emphasizes citizen engagement and interaction through digital platforms, enabling public input in policymaking and decision processes. E-government centers on the digital delivery of government services and administration, streamlining operations and improving accessibility. Key differences include the focus on participatory democracy in e-participation versus service efficiency and transparency in e-government initiatives.
Core Benefits of E-participation
E-participation enhances democratic engagement by enabling citizens to actively contribute to decision-making processes through digital platforms, increasing transparency and accountability in governance. It fosters inclusive dialogue, allowing diverse groups to voice opinions and collaborate on policy development, which strengthens social trust and community empowerment. These core benefits support more responsive and effective public services within the broader framework of e-government initiatives.
Advantages of E-government Implementation
E-government implementation enhances public service accessibility by providing digital platforms that facilitate efficient communication between citizens and governmental agencies while reducing bureaucratic delays. It improves transparency and accountability through online portals that allow real-time monitoring of government activities and public expenditure. Cost savings result from automated processes and reduced reliance on physical documentation, enabling governments to allocate resources more effectively.
Challenges Facing E-participation Initiatives
E-participation initiatives face significant challenges including digital divide issues, limited public awareness, and inadequate technological infrastructure that hinder widespread citizen engagement. Privacy and security concerns also deter participation, alongside the lack of legal frameworks and transparency in the digital decision-making process. Addressing these obstacles is critical to enhancing the effectiveness of e-participation within broader e-government strategies.
Obstacles in E-government Adoption
E-government adoption faces significant obstacles such as digital divide, lack of trust in online services, and inadequate legal frameworks. Limited internet access and low digital literacy hinder citizen engagement, while concerns over data privacy and cybersecurity reduce confidence in government platforms. Furthermore, bureaucratic resistance and insufficient infrastructure delay the implementation of effective e-government solutions, contrasting with the more flexible and participatory nature of e-participation initiatives.
Case Studies: Global Success Stories
E-participation empowers citizens to actively engage in decision-making processes through digital platforms, enhancing transparency and accountability in governance. Case studies from countries like Estonia highlight how e-participation tools have increased voter turnout and public consultation, while South Korea's E-government initiatives demonstrate streamlined service delivery and reduced bureaucratic inefficiencies. These global success stories emphasize the complementary roles of e-participation and e-government in fostering inclusive, efficient, and responsive governance ecosystems.
Future Trends in Digital Governance
E-participation enhances digital governance by enabling citizens to actively engage in policy-making through online platforms, increasing transparency and inclusivity. Future trends emphasize the integration of AI-driven analytics and blockchain technology to secure citizen data and streamline decision-making processes. E-government initiatives are evolving to prioritize real-time feedback systems and personalized public services, fostering a more collaborative and responsive governance model.
E-participation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com