Suspension plays a crucial role in vehicle performance, ensuring a smooth ride by absorbing shocks from uneven road surfaces and maintaining tire contact with the ground. Proper suspension tuning enhances handling, stability, and comfort, directly impacting your driving safety and experience. Explore the rest of the article to understand how suspension systems work and how to optimize them for your vehicle.
Table of Comparison
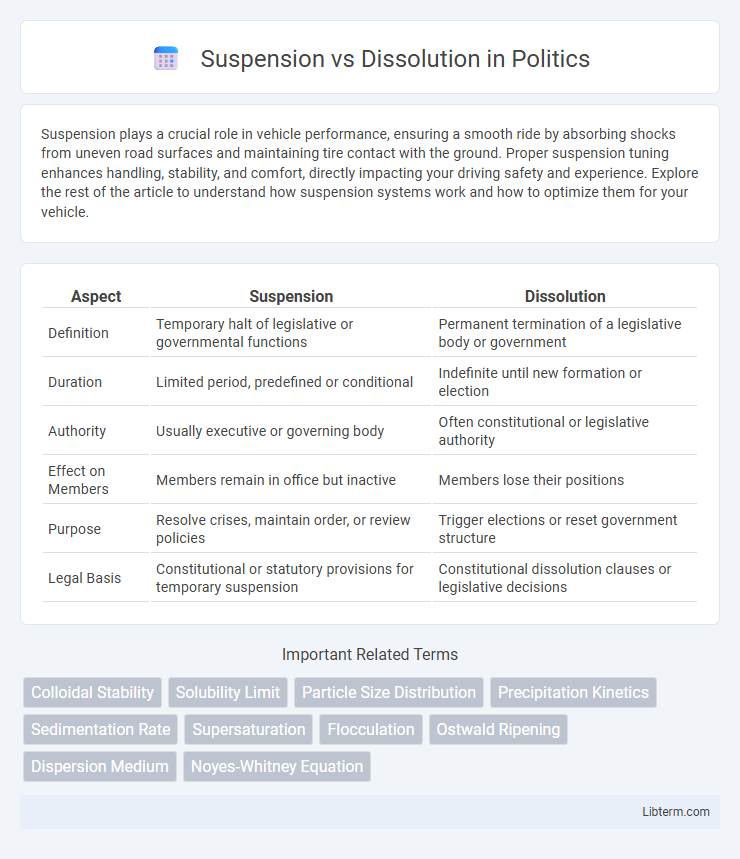
| Aspect | Suspension | Dissolution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary halt of legislative or governmental functions | Permanent termination of a legislative body or government |
| Duration | Limited period, predefined or conditional | Indefinite until new formation or election |
| Authority | Usually executive or governing body | Often constitutional or legislative authority |
| Effect on Members | Members remain in office but inactive | Members lose their positions |
| Purpose | Resolve crises, maintain order, or review policies | Trigger elections or reset government structure |
| Legal Basis | Constitutional or statutory provisions for temporary suspension | Constitutional dissolution clauses or legislative decisions |
Introduction to Suspension and Dissolution
Suspension refers to the temporary halt of a company's operations or legal status without ending its existence, often used to resolve specific issues or comply with regulatory requirements. Dissolution denotes the formal termination and complete closure of a company, leading to the liquidation of assets and removal from the business registry. Understanding the distinctions between suspension and dissolution is crucial for effective corporate governance and compliance management.
Defining Business Suspension
Business suspension refers to the temporary halt of a company's operations without terminating its legal existence, allowing the business to resume activities later. This status often involves pausing all commercial transactions to address internal issues such as financial restructuring or regulatory compliance. Unlike dissolution, suspension does not dissolve the corporate entity, preserving its rights, obligations, and registration while preventing new business conduct during the inactive period.
Defining Business Dissolution
Business dissolution refers to the formal process of closing a company, terminating its legal existence, and distributing its assets to creditors and shareholders. Unlike suspension, which temporarily halts business operations without ending the company's legal status, dissolution permanently ends the business entity. Legal requirements for dissolution often include filing specific documents with state authorities and settling outstanding liabilities.
Key Legal Differences
Suspension temporarily halts a company's operations or legal rights without terminating its existence, while dissolution permanently ends the company's legal existence and initiates the process of winding up assets. Suspension often occurs due to regulatory non-compliance or administrative reasons and can be reversed upon rectifying issues, whereas dissolution requires formal liquidation of assets and settling of liabilities before the company is officially closed. Key legal differences include the continuity of the company's legal entity during suspension versus complete termination in dissolution, affecting contractual obligations and creditor claims.
Impact on Operations
Suspension temporarily halts a company's operations while maintaining its legal status, allowing resumption without lengthy re-registration. Dissolution permanently terminates the business, leading to asset liquidation and cessation of all activities. Operational impact of suspension is reversible downtime; dissolution results in complete closure and removal from official registers.
Financial and Tax Implications
Suspension temporarily halts business operations while keeping the legal entity active, allowing tax obligations such as VAT registration and payroll taxes to remain in effect, which requires continued compliance and reporting. Dissolution permanently terminates the business entity, resulting in the cessation of all tax responsibilities, the need to file final tax returns, and the cancellation of business registrations with tax authorities. Financially, suspension minimizes ongoing operational costs without liquidating assets, whereas dissolution mandates asset liquidation, debt settlement, and potential distribution of remaining funds to shareholders.
Common Reasons for Suspension
Common reasons for suspension include regulatory non-compliance, failure to meet contractual obligations, and temporary financial difficulties impacting operational capacity. Suspension is often enacted to allow corrective measures without permanently ending the relationship, unlike dissolution which signifies formal termination. Regulatory bodies frequently impose suspensions to enforce compliance and protect stakeholder interests.
Common Reasons for Dissolution
Common reasons for dissolution include prolonged financial insolvency, violation of corporate laws, or unanimous shareholder agreement. Business inactivity, failure to file necessary documents with government authorities, and disputes among partners often prompt legal termination of a company. Unlike suspension, which is temporary and reversible, dissolution signifies the permanent end of a company's legal existence.
Process and Documentation Required
Suspension involves temporarily halting a company's operations through board resolutions and filing specific forms with regulatory bodies, requiring documentation such as a suspension application, financial statements, and compliance certificates. Dissolution is the formal process of permanently closing a business, necessitating submission of liquidation reports, settlement of debts, and approval from shareholders and regulatory authorities. Both processes demand detailed statutory filings with government agencies like the Registrar of Companies, ensuring legal compliance and proper record-keeping.
Choosing Between Suspension and Dissolution
Choosing between suspension and dissolution hinges on the company's long-term goals and financial health. Suspension temporarily halts business operations while preserving the company's legal status, allowing for potential reactivation without losing its corporate identity. Dissolution entails the complete termination of the business entity, involving asset liquidation and legal closure, suitable when the company intends to cease operations permanently.
Suspension Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com