Prospective voting occurs when voters make decisions based on anticipated future policies and the potential impact on their lives. This approach emphasizes evaluating candidates' promises and plans rather than past performance. Discover how prospective voting shapes elections and influences Your political engagement in the following article.
Table of Comparison
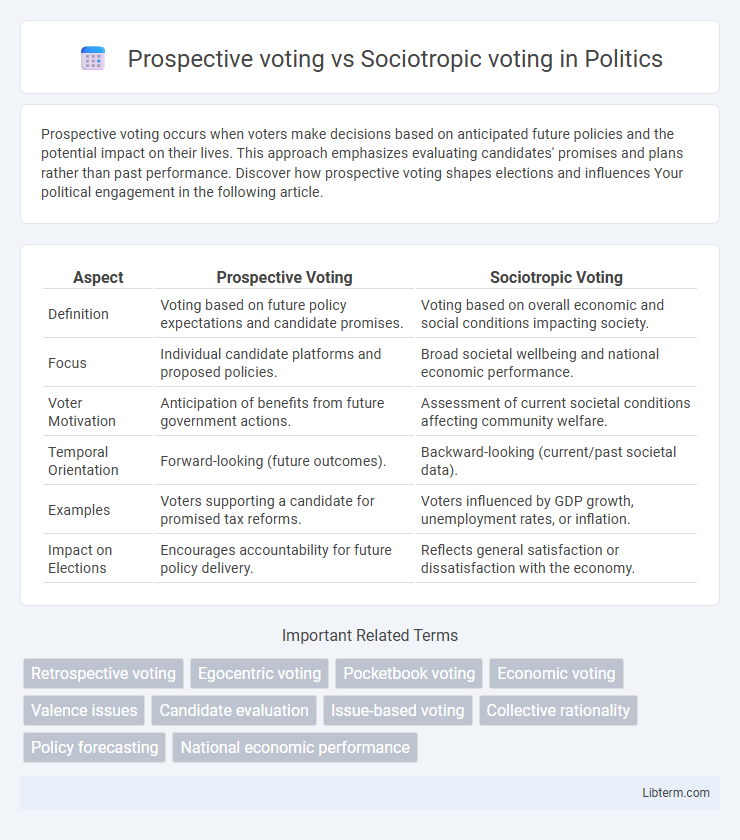
| Aspect | Prospective Voting | Sociotropic Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voting based on future policy expectations and candidate promises. | Voting based on overall economic and social conditions impacting society. |
| Focus | Individual candidate platforms and proposed policies. | Broad societal wellbeing and national economic performance. |
| Voter Motivation | Anticipation of benefits from future government actions. | Assessment of current societal conditions affecting community welfare. |
| Temporal Orientation | Forward-looking (future outcomes). | Backward-looking (current/past societal data). |
| Examples | Voters supporting a candidate for promised tax reforms. | Voters influenced by GDP growth, unemployment rates, or inflation. |
| Impact on Elections | Encourages accountability for future policy delivery. | Reflects general satisfaction or dissatisfaction with the economy. |
Understanding Prospective Voting
Prospective voting involves making electoral decisions based on expectations about a candidate's future policies and their anticipated impact on issues like the economy and social programs. Voters assess proposed plans and campaign promises to predict how these policies will improve their personal welfare or societal outcomes. This contrasts with sociotropic voting, where decisions hinge on evaluations of current national conditions rather than future projections.
Defining Sociotropic Voting
Sociotropic voting refers to casting ballots based on voters' perceptions of the overall economic and social conditions affecting their community or nation, rather than personal circumstances. This behavior contrasts with prospective voting, where decisions are influenced by expectations of future policies and candidate promises. Studies show sociotropic voters prioritize national economic indicators such as unemployment rates and inflation when evaluating incumbent performance.
Key Differences: Prospective vs Sociotropic Voting
Prospective voting centers on voters making decisions based on anticipated future policies and outcomes proposed by candidates or parties, emphasizing individual expectations and promises. In contrast, sociotropic voting relies on assessments of the overall economic and social conditions of society, where voters prioritize collective wellbeing and current economic indicators over personal interests. The key difference lies in prospective voting's forward-looking stance compared to sociotropic voting's focus on the present societal state.
Theoretical Foundations of Voting Behavior
Prospective voting theory posits that voters make decisions based on anticipated future policies and government performance, emphasizing rational evaluations of candidates' platforms and expected benefits. Sociotropic voting centers on the broader economic conditions and societal well-being, where voters assess the national economy's impact on their personal lives and collective prosperity when casting ballots. Both frameworks contribute to understanding voting behavior by highlighting individual forecasts versus macroeconomic perceptions as key determinants in electoral choices.
How Voters Assess Future Outcomes
Prospective voting involves voters making electoral decisions based on predictions about future policy outcomes and personal or national benefits. Sociotropic voting emphasizes evaluations of the overall economic and social conditions affecting society rather than individual circumstances. Voters using a sociotropic approach assess the broader impact of policies on community well-being, while prospective voters focus more on anticipated changes that directly influence their lives.
The Role of National Economic Perceptions
National economic perceptions play a crucial role in differentiating prospective and sociotropic voting behaviors. Prospective voters emphasize personal economic expectations and forecast future economic conditions when deciding their vote. Sociotropic voters prioritize the overall national economic climate, basing their decisions on perceptions of broader economic health rather than personal financial situations.
Psychological Drivers Behind Voting Choices
Prospective voting is driven by voters' expectations about future policies and their psychological need for hope and control over political outcomes. Sociotropic voting stems from voters' perceptions of the national economic and social conditions, reflecting a psychological emphasis on collective well-being rather than personal benefit. Both voting behaviors engage cognitive evaluations, but prospective voting prioritizes future-oriented optimism while sociotropic voting relies on assessments of current societal health.
Real-World Examples of Each Voting Type
Prospective voting is exemplified by voters in the 2008 U.S. presidential election who supported Barack Obama based on his proposed future healthcare reforms and economic policies. Sociotropic voting can be seen in the 2016 Brexit referendum where many voters prioritized the perceived overall economic and social impact on the United Kingdom rather than personal gain. These voting types illustrate distinct decision-making processes: prospective voters emphasize specific future policy promises, while sociotropic voters focus on broader societal outcomes.
Impacts on Election Results and Democracy
Prospective voting, which relies on voters' evaluation of future policy promises, encourages accountability by incentivizing candidates to present clear platforms, leading to more informed and policy-driven election results. Sociotropic voting, where voters consider the overall economic and social conditions of their country, often reflects collective well-being and can stabilize democratic governance by aligning electoral outcomes with national interests rather than personal gain. Both voting behaviors shape election results by influencing voter turnout and candidate success, thereby impacting the quality of democracy through responsiveness and legitimacy.
Policy Implications and Future Trends
Prospective voting emphasizes individual expectations about future policy outcomes, driving candidates to present clear, detailed plans to attract voters interested in long-term impacts. Sociotropic voting focuses on collective economic and social conditions, compelling policymakers to align proposals with broader community well-being and immediate social indicators. Future trends suggest a hybrid approach where data analytics personalize campaigns, integrating prospective promises with sociotropic concerns to better address diverse voter priorities and enhance democratic responsiveness.
Prospective voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com