A subcommittee is a smaller, specialized group formed within a larger committee to focus on specific tasks or issues. It allows for detailed analysis and efficient decision-making by dividing responsibilities among experts. Explore the full article to understand how subcommittees enhance organizational effectiveness and your role within them.
Table of Comparison
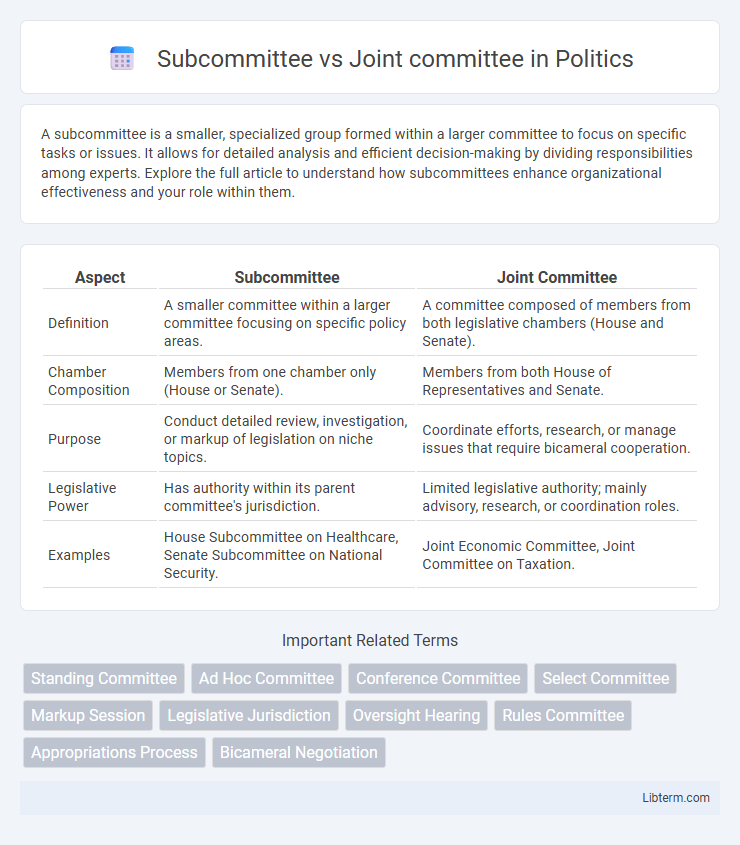
| Aspect | Subcommittee | Joint Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A smaller committee within a larger committee focusing on specific policy areas. | A committee composed of members from both legislative chambers (House and Senate). |
| Chamber Composition | Members from one chamber only (House or Senate). | Members from both House of Representatives and Senate. |
| Purpose | Conduct detailed review, investigation, or markup of legislation on niche topics. | Coordinate efforts, research, or manage issues that require bicameral cooperation. |
| Legislative Power | Has authority within its parent committee's jurisdiction. | Limited legislative authority; mainly advisory, research, or coordination roles. |
| Examples | House Subcommittee on Healthcare, Senate Subcommittee on National Security. | Joint Economic Committee, Joint Committee on Taxation. |
Introduction to Congressional Committees
Subcommittees are specialized groups within larger Congressional committees that focus on specific areas of legislation, allowing for detailed examination and expertise on particular issues. Joint committees consist of members from both the House of Representatives and the Senate, facilitating coordination and addressing shared topics such as taxation or the library of Congress. Understanding the distinctions between subcommittees and joint committees enhances comprehension of the legislative process and committee roles in Congress.
Definition of Subcommittee
A subcommittee is a smaller, specialized group formed within a larger committee to focus on specific tasks or issues, enabling more detailed examination and efficient decision-making. Unlike joint committees, which comprise members from both Houses of Congress to address common concerns, subcommittees operate under the authority of a standing committee and are limited to particular subject areas. Subcommittees play a critical role in legislation by conducting hearings, gathering information, and reporting findings to their parent committees.
Definition of Joint Committee
A joint committee is a legislative committee comprised of members from both chambers, such as the House and the Senate, created to address specific issues requiring collaboration. Unlike a subcommittee, which is a smaller subset of a single standing committee focusing on specialized topics, joint committees facilitate coordination and communication between the two chambers. Joint committees often handle administrative tasks, conduct studies, or oversee certain functions needing bipartisan and bicameral cooperation.
Composition and Membership Differences
Subcommittees consist of a smaller, specialized group of members from a single standing committee, allowing focused review and expertise on specific issues within the committee's jurisdiction. Joint committees include members from both the House of Representatives and the Senate, enabling collaboration across both chambers on legislative matters or investigations. Membership in subcommittees is limited to one chamber, while joint committee membership is drawn from both chambers, reflecting broader representation.
Key Functions and Responsibilities
Subcommittees focus on specialized areas within a larger committee, conducting detailed examination of bills, holding hearings, and making recommendations for the full committee's consideration. Joint committees consist of members from both the House and Senate, primarily tasked with administrative functions, oversight, and conducting studies on specific issues without legislative authority. Key responsibilities of subcommittees include drafting legislation and policy analysis, while joint committees emphasize coordination between chambers and managing shared legislative concerns.
Formation and Structure
A subcommittee is formed as a smaller, specialized group within a standing committee, comprising select members to focus on specific tasks or issues. Joint committees consist of members from both the House and Senate and are established for purposes that require coordination between the two chambers. The structure of a subcommittee is narrower with fewer members, while a joint committee has a broader composition representing both legislative bodies.
Legislative Process Involvement
Subcommittees play a crucial role in the legislative process by conducting detailed reviews, hearings, and markups on specific aspects of a bill before it reaches the full committee. Joint committees consist of members from both the House and Senate and primarily focus on conducting studies or overseeing certain governmental functions without directly drafting legislation. Subcommittees directly influence the progression of bills through targeted examination, whereas joint committees serve more advisory and investigatory roles in the legislative framework.
Advantages of Subcommittees
Subcommittees offer specialized expertise by focusing on specific issues within a larger committee's jurisdiction, enabling more detailed and efficient analysis. Their smaller size facilitates quicker decision-making and more effective oversight of complex legislative matters. This specialization promotes thorough vetting of bills and increased accountability in the legislative process.
Advantages of Joint Committees
Joint committees combine members from multiple standing committees, enhancing collaboration and resource sharing for complex legislative issues. They streamline decision-making by consolidating expertise and avoiding duplication of efforts, leading to more comprehensive and cohesive policy outcomes. This structure increases efficiency in handling topics requiring multidisciplinary insights, benefiting the legislative process through coordinated oversight and unified recommendations.
Key Differences Between Subcommittees and Joint Committees
Subcommittees are specialized groups within a single legislative chamber created to handle specific tasks or areas, allowing for detailed examination and expertise building. Joint committees consist of members from both the House and Senate, formed primarily to conduct studies or perform administrative functions rather than draft legislation. Key differences include their composition--single chamber versus bicameral--and their primary functions, with subcommittees focusing on legislative development and joint committees emphasizing coordination and oversight.
Subcommittee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com