Citizen diplomacy empowers individuals to build bridges between cultures through personal interactions and grassroots initiatives, fostering mutual understanding and peace beyond formal government channels. By engaging directly with people from diverse backgrounds, you can contribute to global harmony and challenge stereotypes. Discover how your role in citizen diplomacy can make a meaningful impact by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
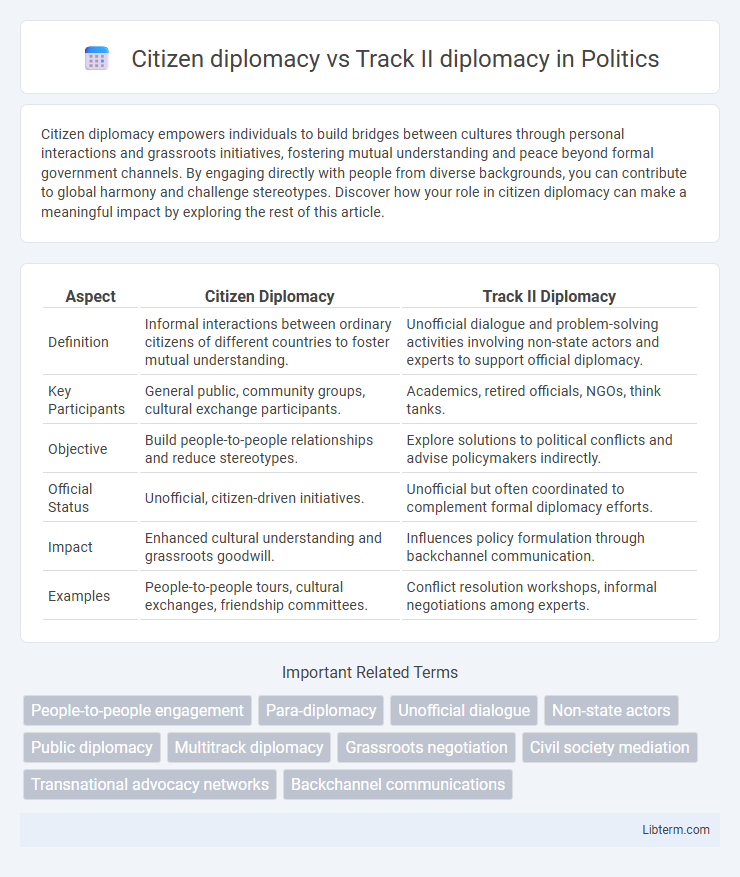
| Aspect | Citizen Diplomacy | Track II Diplomacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal interactions between ordinary citizens of different countries to foster mutual understanding. | Unofficial dialogue and problem-solving activities involving non-state actors and experts to support official diplomacy. |
| Key Participants | General public, community groups, cultural exchange participants. | Academics, retired officials, NGOs, think tanks. |
| Objective | Build people-to-people relationships and reduce stereotypes. | Explore solutions to political conflicts and advise policymakers indirectly. |
| Official Status | Unofficial, citizen-driven initiatives. | Unofficial but often coordinated to complement formal diplomacy efforts. |
| Impact | Enhanced cultural understanding and grassroots goodwill. | Influences policy formulation through backchannel communication. |
| Examples | People-to-people tours, cultural exchanges, friendship committees. | Conflict resolution workshops, informal negotiations among experts. |
Understanding Citizen Diplomacy: Definition and Scope
Citizen diplomacy involves individuals engaging informally in international relations to foster mutual understanding and peace, operating outside official government channels. It encompasses cultural exchanges, grassroots initiatives, and people-to-people interactions that build trust between societies. Unlike Track II diplomacy, which involves unofficial dialogues among former officials or experts, citizen diplomacy emphasizes ordinary citizens' direct participation in global dialogue.
Track II Diplomacy Explained: Origins and Evolution
Track II diplomacy originated during the Cold War as an informal negotiation channel involving non-governmental actors such as academics, retired officials, and civil society leaders. Its evolution reflects a shift from secretive back-channel communications to more structured dialogues aimed at building trust and understanding in conflicts where official diplomatic efforts face stalemates. Today, Track II diplomacy complements formal state negotiations by fostering people-to-people connections and creating environments conducive to conflict resolution.
Key Differences Between Citizen and Track II Diplomacy
Citizen diplomacy involves ordinary individuals engaging in international dialogue to foster mutual understanding, emphasizing grassroots-level influence and people-to-people connections. Track II diplomacy is conducted by non-governmental, often expert actors who facilitate unofficial dialogue and conflict resolution between conflicting parties outside formal government channels. The key difference lies in citizen diplomacy's broad public participation versus Track II diplomacy's strategic, expert-driven approach to complement official diplomatic efforts.
Roles of Non-State Actors in Modern Diplomacy
Citizen diplomacy empowers individual non-state actors to foster international understanding and cultural exchange, facilitating grassroots-level conflict resolution outside formal government channels. Track II diplomacy involves unofficial, informal dialogues typically led by non-governmental organizations and private experts to complement official diplomacy efforts by addressing sensitive issues with flexibility and confidentiality. Both forms leverage the unique capacities of non-state actors to influence peacebuilding, negotiation processes, and intercultural communication in a multipolar global landscape.
Main Objectives: Citizen Diplomats vs Track II Negotiators
Citizen diplomacy primarily aims to foster mutual understanding and build interpersonal relationships between ordinary citizens of different countries, promoting peace and cultural exchange at the grassroots level. Track II diplomacy focuses on facilitating informal dialogue between non-governmental actors such as academics, former officials, and experts to resolve conflicts and influence official foreign policy indirectly. Both approaches seek to complement formal diplomatic efforts, with citizen diplomacy emphasizing people-to-people connections and Track II diplomacy targeting strategic problem-solving in international relations.
Tools and Methods Used in Both Diplomacy Forms
Citizen diplomacy employs grassroots engagement methods such as cultural exchanges, social media campaigns, and community dialogues to foster mutual understanding and build informal international relationships. Track II diplomacy relies on confidential, non-governmental interactions including expert workshops, back-channel negotiations, and facilitated dialogues to resolve conflicts and complement official diplomatic efforts. Both approaches utilize communication platforms and interpersonal connections but differ in formality, scale, and the actors involved, with citizen diplomacy emphasizing public participation and Track II focusing on discreet problem-solving by experienced intermediaries.
Case Studies: Successful Citizen Diplomacy Initiatives
Citizen diplomacy initiatives like the Ping-Pong Diplomacy between the United States and China in the 1970s showcase how grassroots cultural exchanges can break governmental stalemates and foster mutual understanding. Another significant example includes the Seeds of Peace program, which brings together youth from conflict regions such as Israel and Palestine to participate in dialogue and leadership training, contributing to long-term peacebuilding efforts. These case studies highlight the unique impact of Citizen diplomacy by directly involving individuals outside official government channels to influence international relations positively.
Case Studies: Impactful Track II Diplomacy Efforts
Track II diplomacy, involving non-governmental actors such as academics and civil society representatives, has demonstrated significant impact in conflict resolution through case studies like the Oslo Accords between Israel and Palestine and the Dayton Agreement ending the Bosnian War. Citizen diplomacy, a form of Track II engagement, empowers individuals to foster mutual understanding and influence public opinion, evident in grassroots exchanges between American and Cuban communities that softened Cold War animosities. These efforts highlight how unofficial diplomatic initiatives complement formal negotiations by building trust and facilitating dialogue in polarized environments.
Challenges and Limitations in Citizen and Track II Diplomacy
Citizen diplomacy faces challenges such as lack of formal authority and limited access to official channels, which can hinder its influence on governmental policy. Track II diplomacy often encounters limitations related to legitimacy, as unofficial actors struggle to gain recognition and support from formal institutions or governments. Both approaches may face difficulties in ensuring sustained impact due to resource constraints, varying agendas, and inconsistent communication with official diplomatic efforts.
Future Trends: Integrating Citizen Diplomacy and Track II Approaches
Future trends in diplomacy indicate a growing integration of citizen diplomacy and Track II diplomacy, leveraging the unique strengths of both to address global challenges. Citizen diplomacy empowers individuals and grassroots organizations to foster mutual understanding and cultural exchange, while Track II diplomacy involves non-governmental actors engaging in informal dialogue to complement official negotiations. The fusion of these approaches enhances conflict resolution, promotes sustainable peacebuilding, and adapts to the complexities of 21st-century international relations by increasing inclusivity and local ownership in diplomatic processes.
Citizen diplomacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com