Preventive policy focuses on proactive measures designed to reduce risks and prevent adverse outcomes before they occur. Implementing such policies can improve societal health, safety, and economic stability by addressing potential issues early on. Discover how adopting effective preventive policies can benefit you and your community by reading the full article.
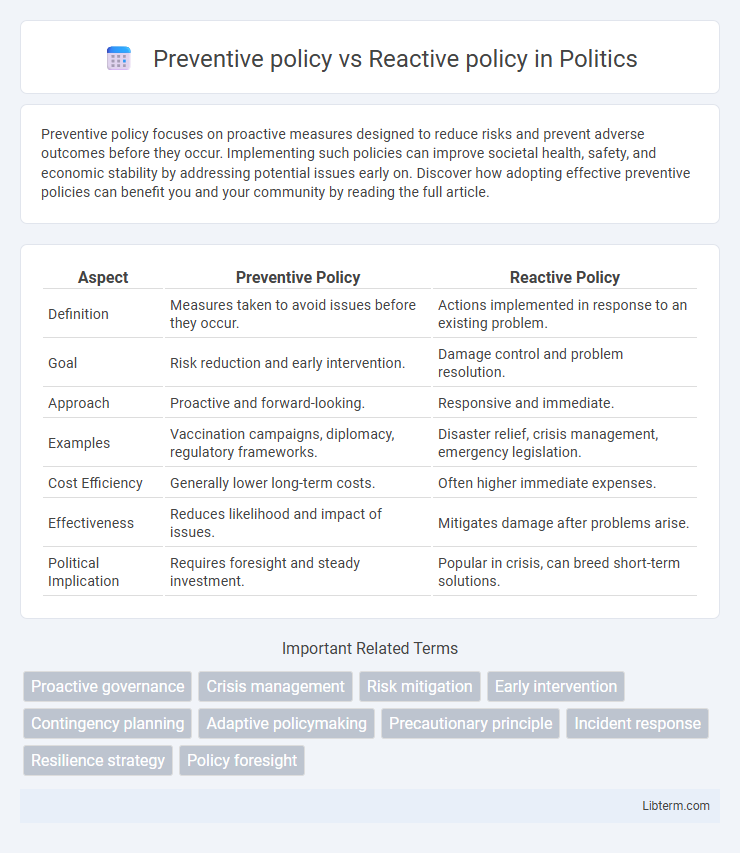
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Preventive Policy | Reactive Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures taken to avoid issues before they occur. | Actions implemented in response to an existing problem. |
| Goal | Risk reduction and early intervention. | Damage control and problem resolution. |
| Approach | Proactive and forward-looking. | Responsive and immediate. |
| Examples | Vaccination campaigns, diplomacy, regulatory frameworks. | Disaster relief, crisis management, emergency legislation. |
| Cost Efficiency | Generally lower long-term costs. | Often higher immediate expenses. |
| Effectiveness | Reduces likelihood and impact of issues. | Mitigates damage after problems arise. |
| Political Implication | Requires foresight and steady investment. | Popular in crisis, can breed short-term solutions. |
Introduction to Preventive and Reactive Policies
Preventive policies are designed to anticipate and mitigate potential problems before they occur, emphasizing risk assessment and proactive measures to ensure stability and avoid crises. Reactive policies, on the other hand, respond to events after they happen, focusing on damage control and recovery strategies to manage and resolve existing issues. Understanding the distinction between preventive and reactive policies is crucial for effective governance, resource allocation, and long-term strategic planning.
Defining Preventive Policy: Concepts and Goals
Preventive policy aims to identify and address potential risks and challenges before they escalate into significant problems, focusing on proactive measures such as early detection, risk assessment, and resource allocation. The core goal of preventive policy is to minimize negative outcomes by implementing strategies that promote sustainability, resilience, and long-term stability within social, economic, and environmental systems. Effective preventive policies rely on data-driven analysis, stakeholder collaboration, and continuous monitoring to anticipate and mitigate future threats.
Understanding Reactive Policy: Scope and Implications
Reactive policy addresses issues after they have occurred, focusing on immediate resolution rather than anticipating future problems. This approach often leads to increased costs and resource allocation due to the need to manage crises or emergencies. Understanding the scope of reactive policy highlights its role in damage control and the implications of delayed intervention on overall policy effectiveness.
Key Differences Between Preventive and Reactive Approaches
Preventive policies emphasize anticipation and mitigation of risks before issues arise, prioritizing proactive measures such as risk assessments, safety protocols, and compliance audits. Reactive policies focus on response and damage control after an event occurs, implementing corrective actions and crisis management strategies to minimize impact. The key difference lies in timing and approach: prevention aims to avoid problems entirely, while reaction deals with consequences post-incident.
Benefits of Preventive Policy Implementation
Preventive policy implementation reduces long-term costs by addressing issues before they escalate into more serious problems, enhancing overall societal stability and well-being. It improves public health outcomes through early intervention, decreasing the burden on healthcare systems and increasing productivity. By fostering proactive risk management, preventive policies promote sustainable development and resilience against future challenges.
Challenges and Limitations of Reactive Policy
Reactive policy often faces challenges such as delayed response times that exacerbate issues before intervention occurs. Limitations include insufficient data for accurate decision-making and higher costs associated with addressing problems after they have escalated. This approach can lead to inefficiencies and reduced public trust due to perceived lack of foresight and preparedness.
Cost-Effectiveness: Prevention vs Reaction
Preventive policies demonstrate greater cost-effectiveness by addressing potential issues before they escalate, significantly reducing long-term expenses associated with damage control and crisis management. Reactionary policies often incur higher immediate costs due to emergency responses and remediation efforts that could have been mitigated through early intervention. Investing in prevention not only minimizes financial burdens but also enhances overall system resilience and sustainability.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures in Policy Strategies
Case studies reveal that preventive policies, such as Sweden's proactive climate action, significantly reduce long-term environmental damage by addressing root causes early, while reactive policies often lead to higher costs and crisis management, exemplified by the delayed response to Hurricane Katrina. Successes in preventive policy include Singapore's water management strategies that anticipate shortages, contrasting with reactive failures seen in the opioid crisis response in the United States, where delayed interventions exacerbated public health impacts. Analysis of these cases underscores the importance of foresight and early investment in policy frameworks to mitigate risks effectively and avoid costly consequences.
Best Practices for Balancing Prevention and Reaction
Effective preventive policies emphasize risk assessment, early intervention, and consistent monitoring to minimize vulnerabilities before issues arise. Reactive policies prioritize rapid response, damage control, and adaptive learning to address incidents promptly and reduce long-term impact. Best practices balance these approaches by integrating real-time data analytics, cross-functional collaboration, and continuous feedback loops to ensure proactive measures are reinforced by efficient response strategies.
Future Trends in Policy Development and Governance
Future trends in policy development increasingly emphasize preventive policies that leverage data analytics and AI to anticipate societal challenges before they escalate, ensuring sustainable governance. Reactive policies often address immediate issues but may incur higher costs and inefficiencies, whereas preventive approaches foster resilience by integrating cross-sector collaboration and real-time monitoring systems. Emerging governance models prioritize adaptive frameworks that balance proactive intervention with responsive adjustments to dynamic global risks such as climate change and cybersecurity threats.
Preventive policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com