Legislation forms the foundation of legal systems, establishing rules that govern behavior and protect rights within society. Understanding how laws are created, interpreted, and enforced is essential for navigating legal responsibilities and ensuring compliance. Explore the full article to discover how legislation impacts your daily life and the justice system.
Table of Comparison
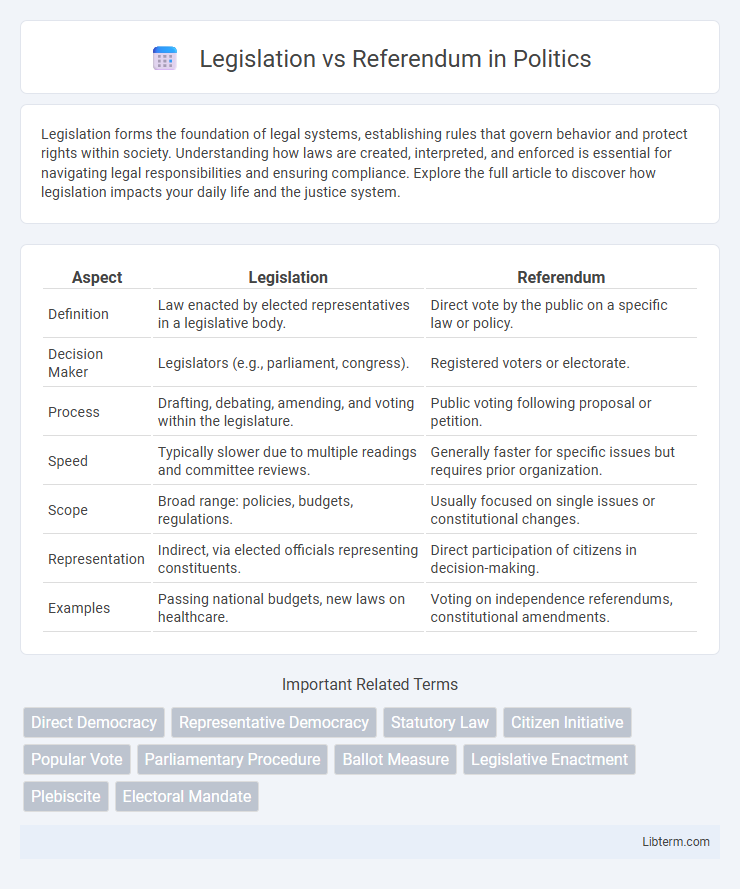
| Aspect | Legislation | Referendum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Law enacted by elected representatives in a legislative body. | Direct vote by the public on a specific law or policy. |
| Decision Maker | Legislators (e.g., parliament, congress). | Registered voters or electorate. |
| Process | Drafting, debating, amending, and voting within the legislature. | Public voting following proposal or petition. |
| Speed | Typically slower due to multiple readings and committee reviews. | Generally faster for specific issues but requires prior organization. |
| Scope | Broad range: policies, budgets, regulations. | Usually focused on single issues or constitutional changes. |
| Representation | Indirect, via elected officials representing constituents. | Direct participation of citizens in decision-making. |
| Examples | Passing national budgets, new laws on healthcare. | Voting on independence referendums, constitutional amendments. |
Understanding Legislation: Definition and Process
Legislation refers to the process by which legislative bodies, such as parliaments or congresses, create, amend, or repeal laws through formal procedures that include proposal, debate, committee review, and voting. This structured process ensures laws reflect representative decision-making and adhere to constitutional frameworks, involving multiple readings and potential executive approval or veto. Understanding legislation is fundamental to grasping how legal norms are established and enforced within a jurisdiction, contrasting with referendums where laws are decided directly by the electorate.
What is a Referendum? Meaning and Mechanisms
A referendum is a direct democratic tool allowing citizens to vote on specific legislative proposals or constitutional amendments, bypassing the traditional legislative process. It enables the public to accept or reject laws, often initiated by government authorities or through citizen petitions, ensuring popular involvement in decision-making. Mechanisms of referendums include binding votes, where outcomes are legally enforceable, or advisory votes, which guide legislative bodies without obligatory compliance.
Key Differences Between Legislation and Referendum
Legislation involves laws proposed, debated, and enacted by a legislative body, while a referendum is a direct vote by the electorate on a specific issue or law. Key differences include the source of decision-making authority--legislation is decided by elected representatives, whereas referendums empower citizens to make decisions directly. Furthermore, legislation can cover a wide range of policies, whereas referendums typically address specific, singular issues requiring public approval.
Advantages of the Legislative Process
The legislative process allows for comprehensive debate, expert testimony, and multiple readings, ensuring laws are thoroughly vetted before enactment. It provides opportunities for amendments and revisions, enabling lawmakers to address complexities and unintended consequences effectively. This structured approach promotes accountability, transparency, and consistency within the legal framework.
Benefits of the Referendum Approach
The referendum approach empowers citizens by allowing direct participation in the decision-making process, enhancing democratic legitimacy and accountability. It facilitates transparent policymaking by reflecting the popular will on specific issues without the filtering effects of legislative negotiations. This method often increases public engagement and trust in government by providing a clear mandate on contentious or significant legislative matters.
Limitations and Criticisms of Legislation
Legislation often faces limitations such as slow adaptation to public needs and susceptibility to influence by special interest groups, which can result in laws that may not reflect the broader public interest. Critics argue that legislative processes can be opaque, lacking direct citizen input, unlike referendums which allow for more direct democracy and public participation. Furthermore, legislation may create complex legal frameworks that are difficult for the average citizen to understand, leading to decreased transparency and accountability.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Referendums
Referendums often face challenges such as voter misinformation, which can lead to decisions based on incomplete or misleading data instead of informed judgment. The simplicity of a yes/no vote fails to capture the complexity of legislative issues, resulting in outcomes that may not align with nuanced policy needs. Additionally, referendums can be influenced by populist sentiments and short-term emotions, undermining the stability and thoroughness typically associated with legislative processes.
Examples of Legislation vs Referendum in Practice
Legislation involves laws enacted by parliamentary bodies, such as the Affordable Care Act passed by the United States Congress, whereas referendums allow citizens to directly vote on specific issues, exemplified by the 2016 Brexit referendum in the United Kingdom. Switzerland frequently utilizes referendums for constitutional amendments and policy decisions, reflecting direct democracy in action, while countries like Canada rely predominantly on legislative processes through elected representatives. The key distinction lies in decision-making authority: legislation is crafted by lawmakers, while referendums empower the electorate to approve or reject proposals.
Impact on Democracy: Legislation vs Referendum
Legislation enables elected representatives to craft detailed policies reflecting diverse interests, promoting stability and expertise within democratic governance. Referendums offer direct citizen participation, enhancing democratic legitimacy by allowing voters to decide on specific issues, but may oversimplify complex policy matters. The balance between legislation and referendums shapes democratic responsiveness and accountability, influencing how public will is translated into actionable laws.
Choosing the Best Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between legislation and referendum depends on factors such as the complexity of the issue, public engagement level, and decision-making speed. Legislation allows expert-driven, detailed policy crafting often suited for technical or nuanced matters, while referendums provide direct democratic involvement on clear, high-impact issues. Consider potential voter knowledge, cost implications, and the need for swift implementation when determining the best approach.
Legislation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com