A caucus is a meeting of members of a specific political party or group to discuss policy, select candidates, or make decisions on legislative matters. This process often plays a critical role in shaping political strategy and determining leadership within legislatures or party organizations. Explore the article to understand how caucuses influence elections and governance.
Table of Comparison
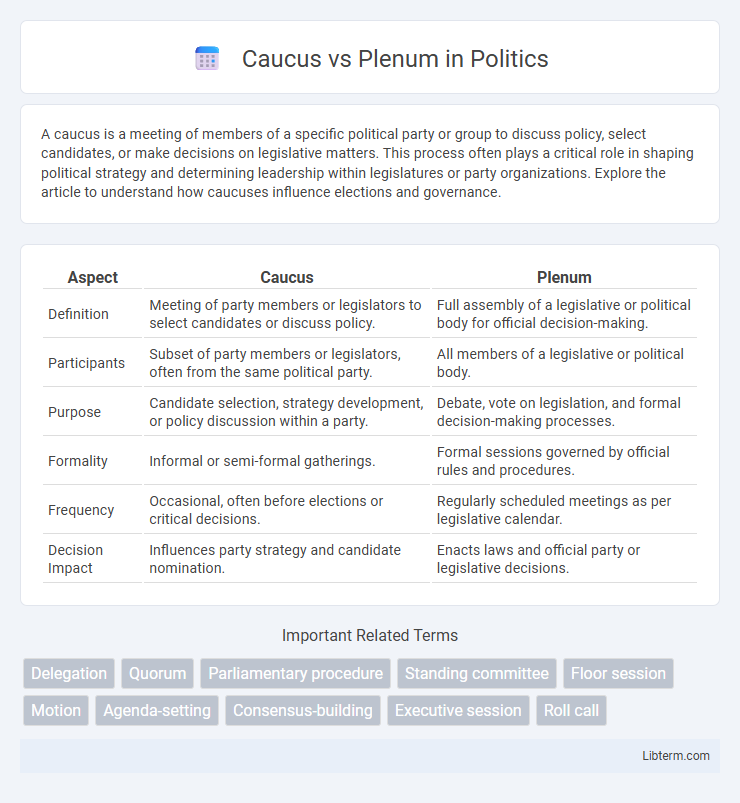
| Aspect | Caucus | Plenum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Meeting of party members or legislators to select candidates or discuss policy. | Full assembly of a legislative or political body for official decision-making. |
| Participants | Subset of party members or legislators, often from the same political party. | All members of a legislative or political body. |
| Purpose | Candidate selection, strategy development, or policy discussion within a party. | Debate, vote on legislation, and formal decision-making processes. |
| Formality | Informal or semi-formal gatherings. | Formal sessions governed by official rules and procedures. |
| Frequency | Occasional, often before elections or critical decisions. | Regularly scheduled meetings as per legislative calendar. |
| Decision Impact | Influences party strategy and candidate nomination. | Enacts laws and official party or legislative decisions. |
Understanding Caucus: Definition and Function
A caucus is a meeting of members within a specific political party or group to discuss policies, select candidates, and coordinate strategies. Its primary function is to enable concentrated decision-making and foster unity among members by facilitating open debate and consensus-building. Unlike a plenum, which includes all members of a legislative body, a caucus operates within a smaller subset, ensuring focused and ideologically aligned deliberations.
What Is a Plenum? An Overview
A plenum is a formal assembly where all members of a legislative or decision-making body gather to discuss, debate, and vote on important issues or policies. It serves as the highest authoritative meeting, ensuring inclusive participation and collective decision-making, distinct from smaller, specialized groups like caucuses. Plenums facilitate transparency and comprehensive deliberation, making them critical in democratic governance and organizational processes.
Key Differences Between Caucus and Plenum
A caucus is a smaller, private meeting of members within a specific political party or group to discuss strategies and select candidates, whereas a plenum refers to a full assembly of all members of a legislative body or organization to debate and make decisions. Caucus sessions emphasize internal consensus-building and party alignment, while plenums focus on formal, official policymaking and voting processes. The key differences lie in their scope, purpose, and participant composition, with caucuses being more exclusive and strategic, versus plenums being inclusive and authoritative.
Historical Origins of Caucus and Plenum
The historical origins of the caucus trace back to early American colonial assemblies where small groups of influential leaders met to select candidates and shape policy decisions. In contrast, the plenum originated in parliamentary settings as a formal session where all members of a legislative body convene to deliberate and vote on issues collectively. Both terms reflect distinct political practices: caucus emphasizes internal group consensus-building, while plenum underscores full assembly participation.
Roles in Political and Organizational Settings
Caucuses serve as smaller, focused groups within larger political parties or organizations, enabling members to align on specific interests, strategies, or policy goals to influence broader decision-making processes. Plenums convene all members of a political body or organization, providing a platform for comprehensive debate, collective voting, and final decision approval. Caucuses drive agenda-setting and coalition-building, while plenums ensure democratic legitimacy and authoritative resolutions in political and organizational settings.
Decision-Making Processes: Comparing Methods
Caucus meetings facilitate decision-making through smaller, focused group discussions, enabling quicker consensus on specific issues or candidate selections. Plenums involve the entire membership or assembly, promoting broad participation and collective deliberation to reach decisions, often resulting in more comprehensive but time-consuming outcomes. The choice between caucus and plenum methods impacts organizational dynamics, with caucuses favoring efficiency and plenums prioritizing inclusivity in decision-making processes.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Caucuses
Caucuses offer the benefit of fostering in-depth discussion and consensus-building among members with shared interests, promoting more engaged and informed decision-making. However, they can be less inclusive, limiting participation to active or influential members, which may reduce transparency and broader representation. The informal nature of caucuses may also lead to less structured debate compared to plenums, potentially affecting the consistency and clarity of outcomes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plenums
Plenums allow for comprehensive discussion and decision-making among all members, enhancing transparency and inclusivity in organizational or legislative processes. However, plenums can be time-consuming and inefficient due to the large number of participants, often leading to prolonged debates and difficulty reaching consensus. The broad participation may also dilute individual contributions and limit focused, strategic planning compared to smaller, more specialized groups like caucuses.
Real-World Examples of Caucus and Plenum Usage
Caucus and plenum serve distinct functions in political and legislative contexts, with caucuses often acting as smaller, issue-focused groups within larger assemblies, such as the Congressional Black Caucus in the U.S. House of Representatives advocating for minority interests. Plenums, on the other hand, involve the full membership of a legislative body or organization, exemplified by the German Bundestag plenary sessions where all elected representatives debate and vote on national legislation. These real-world examples highlight how caucuses drive specialized agendas within broader political frameworks while plenums address comprehensive policy decisions through collective participation.
Choosing Between Caucus and Plenum: Which Is Best?
Choosing between a caucus and a plenum depends on the decision-making context and desired level of inclusivity; caucuses allow smaller, more focused groups to deliberate, fostering detailed discussion and consensus among like-minded members. Plenums involve the entire membership, promoting transparency and broader representation but may lead to slower decision processes due to larger participant numbers. Evaluating the complexity of issues and the need for rapid versus comprehensive input guides whether a caucus or plenum is best suited for effective decision-making.
Caucus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com