Executive privilege allows government officials to withhold sensitive information from the public and other branches of government to protect national interests and confidential communications. Understanding its scope and limitations is essential for recognizing how it balances transparency with executive confidentiality. Explore the full article to learn how executive privilege impacts governance and your right to information.
Table of Comparison
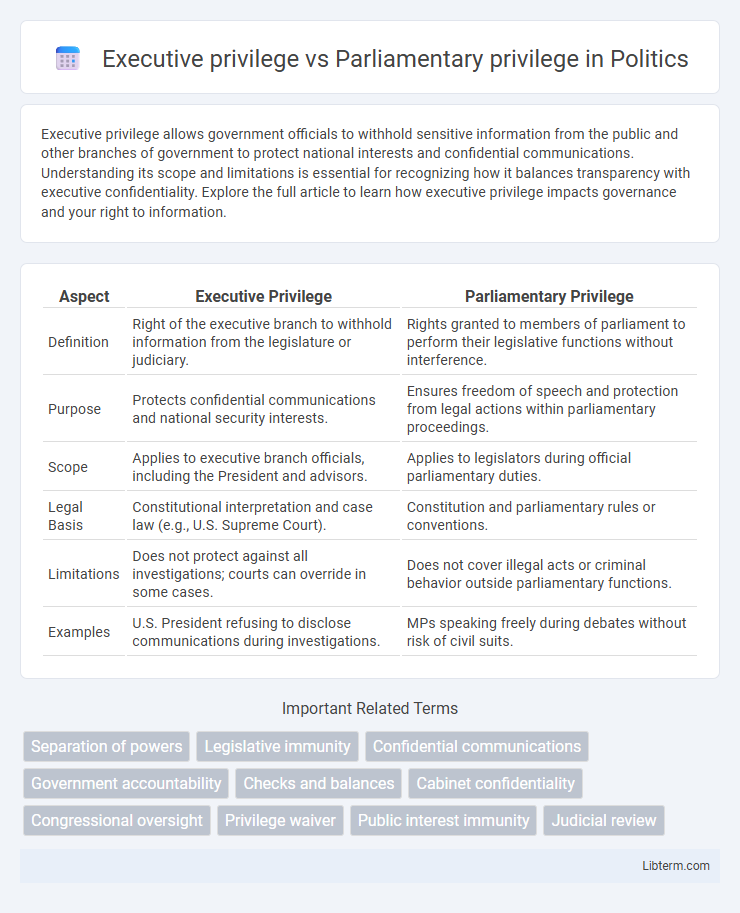
| Aspect | Executive Privilege | Parliamentary Privilege |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Right of the executive branch to withhold information from the legislature or judiciary. | Rights granted to members of parliament to perform their legislative functions without interference. |
| Purpose | Protects confidential communications and national security interests. | Ensures freedom of speech and protection from legal actions within parliamentary proceedings. |
| Scope | Applies to executive branch officials, including the President and advisors. | Applies to legislators during official parliamentary duties. |
| Legal Basis | Constitutional interpretation and case law (e.g., U.S. Supreme Court). | Constitution and parliamentary rules or conventions. |
| Limitations | Does not protect against all investigations; courts can override in some cases. | Does not cover illegal acts or criminal behavior outside parliamentary functions. |
| Examples | U.S. President refusing to disclose communications during investigations. | MPs speaking freely during debates without risk of civil suits. |
Understanding Executive Privilege: Definition and Scope
Executive privilege is the right claimed by the executive branch to withhold information from the legislature or judiciary, primarily to protect sensitive communications and national security interests. This privilege covers presidential communications, including internal deliberations and advice from advisors, ensuring candid decision-making without external pressure. However, its scope is not absolute and can be challenged when balanced against the needs of judicial review or legislative oversight.
Defining Parliamentary Privilege: Core Principles
Parliamentary privilege refers to the legal immunities and rights granted to members of Parliament to ensure the effective functioning of the legislative body, including freedom of speech during debates and protection from civil or criminal liability for actions within parliamentary proceedings. Core principles of parliamentary privilege include freedom of speech, exclusive cognizance, and freedom from arrest in civil cases, all designed to safeguard legislative independence from executive or judicial interference. These privileges enable Parliament to perform its functions without external pressures or constraints, maintaining the separation of powers essential to democratic governance.
Historical Origins of Both Privileges
Executive privilege originated in the early United States to protect the confidentiality of presidential communications, rooted in the separation of powers doctrine established during the late 18th century. Parliamentary privilege traces back to the English Parliament in the 17th century, designed to safeguard legislators from external interference, ensuring free debate and immunity within parliamentary proceedings. Both privileges serve as legal immunities but evolved from distinct historical contexts tied to executive authority and legislative independence.
Legal Basis and Constitutional Foundations
Executive privilege is grounded in the constitutional principle of separation of powers, allowing the executive branch to withhold information to protect national security and confidential deliberations, often justified under Article II of the U.S. Constitution. Parliamentary privilege stems from the need to ensure legislative independence and effectiveness, legally based on common law and codified in statutes like the Speech or Debate Clause in Article I, Section 6 of the U.S. Constitution, which protects legislators from external interference. Both privileges serve distinct constitutional functions: executive privilege safeguards executive confidentiality, while parliamentary privilege ensures legislative autonomy and free debate.
Key Differences: Executive vs Parliamentary Privilege
Executive privilege allows the President and executive branch officials to withhold information from Congress, courts, and the public to protect confidential communications and national security. Parliamentary privilege grants members of a legislature immunity from legal action for actions performed and statements made in the course of their legislative duties. The key difference lies in the scope and purpose: executive privilege safeguards executive branch confidentiality, while parliamentary privilege ensures legislative independence and freedom of speech within the legislature.
Practical Applications in Government
Executive privilege allows government executives, such as the President, to withhold confidential communications from legislative or judicial scrutiny to protect national security or sensitive decision-making processes. Parliamentary privilege grants legislators immunity from legal action or interference regarding their official duties, enabling open debate and effective lawmaking without fear of external repercussions. Both privileges serve essential roles in maintaining the balance of power by safeguarding confidential government functions and ensuring legislative independence.
Limitations and Checks on Executive Privilege
Executive privilege allows the president and executive branch to withhold information from Congress, courts, and the public, but it is limited by judicial review, especially when claims obstruct congressional investigations or judicial proceedings. Courts have ruled that executive privilege is not absolute and must yield when there is a demonstrated need for evidence in criminal cases or oversight functions. Congressional oversight serves as a key check, using subpoenas and hearings to challenge claims of executive privilege and enforce transparency and accountability in government operations.
Restrictions and Oversight of Parliamentary Privilege
Parliamentary privilege grants legislators immunity from certain legal actions to ensure independent lawmaking, but it is restricted by rules within parliamentary procedures and subject to internal oversight mechanisms such as ethics committees. These privileges do not exempt members from criminal laws outside legislative activities, and courts may intervene if privileges conflict with constitutional rights or public interest. Oversight includes maintaining transparency and accountability while balancing the need for legislative independence against potential abuses of power.
Landmark Cases and Precedents
Executive privilege is exemplified in landmark cases such as United States v. Nixon (1974), where the Supreme Court limited presidential immunity by ordering the release of Oval Office tapes during the Watergate scandal. Parliamentary privilege, rooted in British constitutional law, gained clarity through the Case of Prohibitions (1607) and later the Pepper v. Hart (1993), which affirmed the privilege protects speeches and debates in Parliament from court scrutiny. These precedents delineate the boundaries of state powers and immunities, establishing key frameworks for balancing governmental accountability and institutional autonomy.
Impact on Transparency and Governance
Executive privilege allows government executives to withhold information from the public and legislative bodies, impacting transparency by limiting oversight of executive actions. Parliamentary privilege protects legislators' freedom of speech and actions within parliament, promoting open debate but sometimes shielding misconduct from external scrutiny. Both privileges influence governance by balancing the need for confidentiality and accountability, often sparking debates over the appropriate limits to ensure transparent democratic processes.
Executive privilege Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com