The actual parliament operates as the central legislative body responsible for enacting laws, shaping national policies, and representing the interests of the public. Its structure, functions, and powers vary by country but typically include debating bills, approving budgets, and overseeing the government. Discover essential insights into how your parliament influences everyday governance in the rest of this article.
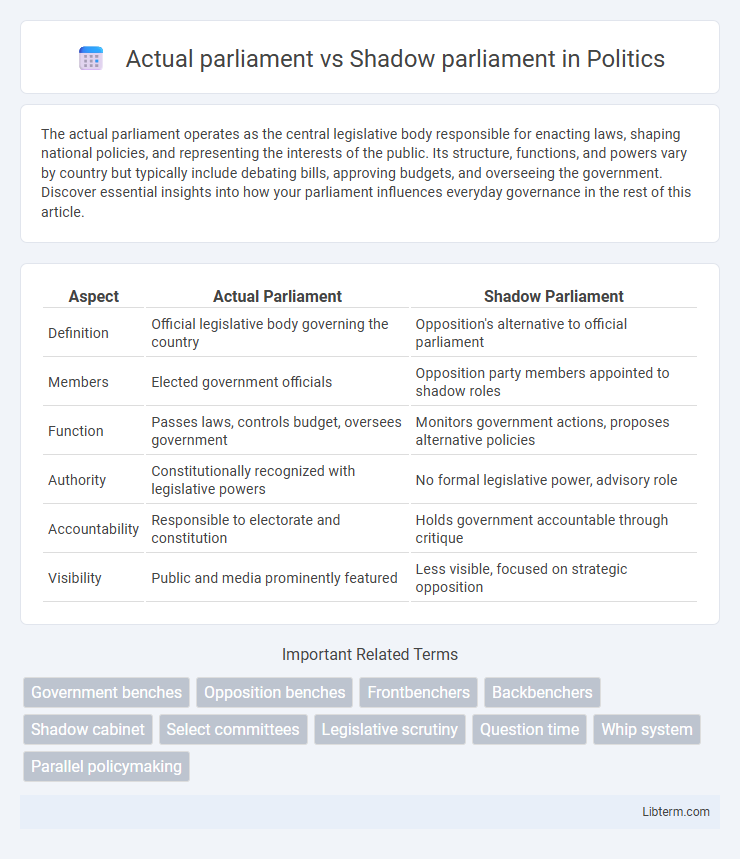
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Actual Parliament | Shadow Parliament |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official legislative body governing the country | Opposition's alternative to official parliament |
| Members | Elected government officials | Opposition party members appointed to shadow roles |
| Function | Passes laws, controls budget, oversees government | Monitors government actions, proposes alternative policies |
| Authority | Constitutionally recognized with legislative powers | No formal legislative power, advisory role |
| Accountability | Responsible to electorate and constitution | Holds government accountable through critique |
| Visibility | Public and media prominently featured | Less visible, focused on strategic opposition |
Introduction to Parliamentary Systems
The actual parliament serves as the primary legislative body in a parliamentary system, responsible for enacting laws, overseeing government functions, and representing the electorate. In contrast, the shadow parliament, often composed of opposition members, mirrors the structures and committees of the actual parliament to scrutinize government policies and propose alternative solutions. Understanding the roles of both actual and shadow parliaments highlights the checks and balances essential for democratic governance within parliamentary systems.
Defining the Actual Parliament
The Actual Parliament is the officially recognized legislative body responsible for making, amending, and repealing laws within a sovereign state. It comprises elected representatives who hold the authority to debate policies, approve budgets, and oversee the executive branch through various committees. This institution functions as the core mechanism of democratic governance, ensuring transparency, accountability, and the enactment of legislation reflecting the electorate's will.
Understanding the Shadow Parliament
The shadow parliament is an organized group of opposition members who scrutinize government policies and propose alternative strategies, functioning as a government-in-waiting. Its key role includes holding the actual parliament accountable by questioning decisions, debating legislation, and representing diverse public interests. Understanding the shadow parliament reveals its importance in promoting democratic transparency and preparing leadership transitions within parliamentary systems.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
The Actual Parliament enacts legislation, oversees government functions, and represents the electorate through elected officials, ensuring accountability and governance. In contrast, the Shadow Parliament, primarily composed of opposition members, scrutinizes government policies, offers alternative proposals, and holds the ruling party accountable through constructive criticism and debate. Key responsibilities of the Actual Parliament include lawmaking and policy approval, while the Shadow Parliament focuses on monitoring, challenging, and providing a government-in-waiting framework.
Composition and Structure Differences
The actual parliament consists of elected representatives from various political parties, organized into formal legislative bodies such as the House of Commons and the House of Lords in the UK, or the House of Representatives and Senate in the US. The shadow parliament, typically formed by opposition parties, mirrors the actual parliament's structure but lacks official legislative power, functioning instead as a system of scrutiny and alternative policymaking. While the actual parliament includes government ministers and committee members with decision-making authority, the shadow parliament comprises shadow ministers tasked with critiquing government policies and proposing alternative solutions.
Legislative Functions: Comparison
The actual parliament holds the formal authority to draft, debate, and enact legislation, ensuring laws reflect the electorate's mandate and constitutional framework. The shadow parliament functions as a critical body, scrutinizing proposed bills, offering alternative policies, and holding the government accountable through opposition strategies. Both entities play complementary roles in enhancing legislative transparency, but only the actual parliament possesses the legal power to pass binding laws.
Influence on Policy and Governance
The actual parliament holds formal legislative authority, enacting laws and overseeing government operations, directly shaping national policy and governance structures. The shadow parliament, often consisting of opposition members, plays a critical role in scrutinizing government actions and proposing alternative policies, indirectly influencing decision-making processes. By holding the ruling party accountable and fostering public debate, the shadow parliament strengthens democratic governance and policy development.
Public Perception and Accountability
Actual parliaments hold legislative authority and are directly accountable to the electorate, fostering public trust through transparent decision-making processes and official oversight mechanisms. Shadow parliaments consist of opposition members who scrutinize government actions and propose alternative policies, enhancing accountability by offering public critique and maintaining political balance. Public perception often favors actual parliaments for their formal power but values shadow parliaments for promoting democratic accountability and political responsiveness.
Historical Evolution and Examples
The concept of a shadow parliament emerged from the British parliamentary system as a mechanism for the opposition to shadow government ministers, allowing for organized scrutiny and alternative policy propositions. Historically, the evolution of shadow parliaments reflects democratic practices in countries like the United Kingdom, Australia, and Canada, where shadow cabinets function as official opposition counterparts to the ruling government's cabinet. Examples include the UK's Shadow Cabinet, established in the 19th century, which plays a crucial role in maintaining parliamentary accountability and preparing opposition leaders for potential governance.
Impact on Democratic Processes
Actual parliaments hold legislative authority, shaping policies through elected representatives who directly reflect public mandates, while shadow parliaments serve to scrutinize government actions and provide alternative policy proposals without formal legislative power. The dynamic between these bodies strengthens democratic processes by fostering accountability, enhancing transparency, and encouraging robust debate, which prevents the concentration of power. Effective shadow parliaments contribute to a healthier democracy by ensuring diverse viewpoints influence governance and by holding ruling parties accountable between election cycles.
Actual parliament Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com