Rule by majority ensures that decisions reflect the preference of the greater number within a group, promoting fairness and democratic participation. This principle allows for efficient governance while balancing diverse opinions and interests. Dive into the rest of the article to understand how majority rule impacts your community and decision-making processes.
Table of Comparison
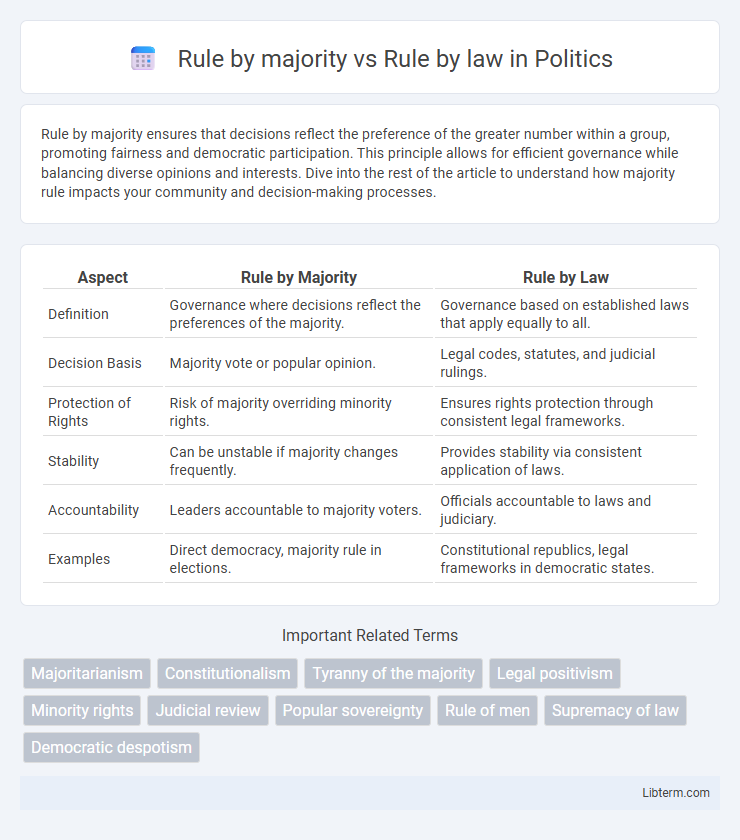
| Aspect | Rule by Majority | Rule by Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance where decisions reflect the preferences of the majority. | Governance based on established laws that apply equally to all. |
| Decision Basis | Majority vote or popular opinion. | Legal codes, statutes, and judicial rulings. |
| Protection of Rights | Risk of majority overriding minority rights. | Ensures rights protection through consistent legal frameworks. |
| Stability | Can be unstable if majority changes frequently. | Provides stability via consistent application of laws. |
| Accountability | Leaders accountable to majority voters. | Officials accountable to laws and judiciary. |
| Examples | Direct democracy, majority rule in elections. | Constitutional republics, legal frameworks in democratic states. |
Understanding Majority Rule: Principles and Practice
Majority rule is a foundational democratic principle where decisions reflect the preferences of more than half the participants, ensuring governance aligns with the collective will. It operates within constitutional frameworks that protect minority rights, preventing the tyranny of the majority while promoting fair representation. Effective implementation requires transparent voting processes, equal participation, and adherence to established legal standards to maintain legitimacy and social stability.
The Foundations of Rule by Law
Rule by law is founded on the principle that laws govern society, ensuring fairness, accountability, and protection of fundamental rights through established legal frameworks. It emphasizes the supremacy of codified laws applied equally to all, preventing arbitrary decisions and abuse of power. Unlike rule by majority, which can lead to the tyranny of the majority, rule by law upholds consistent legal standards that safeguard minority rights and maintain social order.
Historical Origins: Majority Rule vs Rule by Law
The historical origins of majority rule trace back to ancient Athens, where democratic governance was established through citizen assemblies making decisions by vote. Rule by law originates from Roman legal traditions emphasizing codified statutes applied uniformly to all individuals, ensuring legal order and preventing arbitrary power. These foundational systems shaped modern political frameworks, distinguishing participatory decision-making from structured legal authority.
Key Differences Between Majority Rule and Rule by Law
Majority rule prioritizes decision-making based on the preferences of the numerical majority, emphasizing democratic consensus in governance. Rule by law ensures that all actions and decisions conform to established legal frameworks, protecting individual rights and maintaining order regardless of majority opinion. The key difference lies in majority rule's dependence on popular support versus rule by law's reliance on impartial legal standards to maintain fairness and stability.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Majority Rule
Majority rule ensures decisions represent the preference of the larger portion of a population, promoting democratic legitimacy and responsiveness. However, it risks marginalizing minority groups and can lead to the "tyranny of the majority," where minority rights are disregarded. While majority rule facilitates efficient decision-making, it may lack safeguards against majoritarian abuses and inconsistent application of justice compared to rule by law.
The Importance of Rule by Law in Democratic Societies
The importance of rule by law in democratic societies lies in its ability to ensure fairness, accountability, and protection of individual rights beyond majority preferences. Rule by law establishes clear, consistent legal frameworks that prevent arbitrary decisions and safeguard minority groups against the tyranny of the majority. This legal foundation upholds democratic principles by promoting equality, justice, and predictable governance essential for social stability and public trust.
When Majority Rule Undermines Legal Protections
Majority rule can undermine legal protections when the interests of the majority infringe on the fundamental rights guaranteed by constitutional law, leading to the erosion of minority safeguards. In democratic systems, unchecked majority decisions risk marginalizing vulnerable populations by prioritizing popular opinion over established legal norms and human rights frameworks. Ensuring judicial oversight and constitutional checks prevents the tyranny of the majority from compromising legal equality and individual liberties.
Balancing Popular Will with Legal Frameworks
Balancing popular will with legal frameworks requires integrating majority rule mechanisms while upholding constitutional safeguards that protect minority rights and prevent arbitrary governance. Democratic systems employ checks and balances, judicial review, and codified legal principles to ensure that majority decisions align with fundamental rights and justice. This synergy promotes stable governance by harmonizing public opinion with the rule of law.
Case Studies: Majority Rule vs Rule by Law in Action
Case studies comparing majority rule and rule by law highlight contrasts in governance outcomes, such as South Africa's transition from apartheid demonstrating majority rule through democratic elections ensuring societal representation. Conversely, China exemplifies rule by law, where legal frameworks reinforce state authority despite limited political plurality. These examples reveal how majority rule prioritizes popular sovereignty, while rule by law emphasizes structured legal control and institutional stability.
Ensuring Justice: Lessons for Modern Governance
Rule by majority emphasizes popular sovereignty where decisions reflect the will of most citizens, ensuring democratic legitimacy and inclusivity. Rule by law focuses on a stable and predictable legal framework that applies equally to all, preventing arbitrary power and safeguarding rights. Modern governance benefits from blending majority rule with robust legal institutions to ensure justice, accountability, and protection of minority interests.
Rule by majority Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com