Government plays a crucial role in shaping policies that impact economic growth, public welfare, and national security. Efficient governance ensures transparency, accountability, and effective delivery of public services to meet the needs of citizens. Explore this article to understand how government structures influence your daily life and societal development.
Table of Comparison
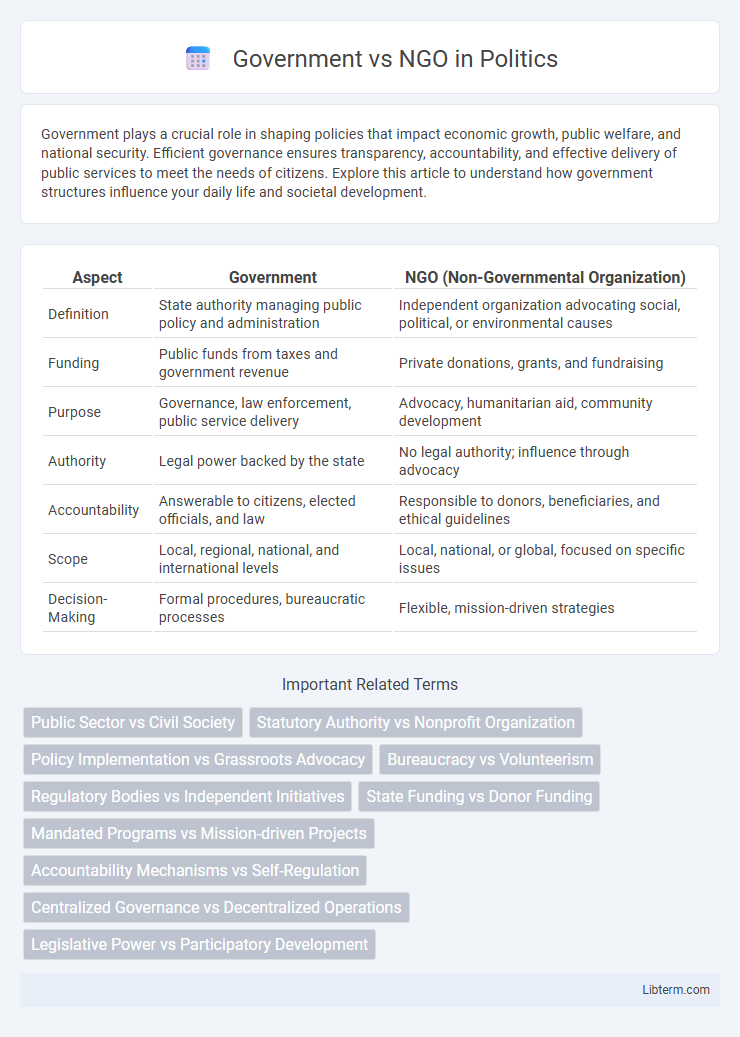
| Aspect | Government | NGO (Non-Governmental Organization) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State authority managing public policy and administration | Independent organization advocating social, political, or environmental causes |
| Funding | Public funds from taxes and government revenue | Private donations, grants, and fundraising |
| Purpose | Governance, law enforcement, public service delivery | Advocacy, humanitarian aid, community development |
| Authority | Legal power backed by the state | No legal authority; influence through advocacy |
| Accountability | Answerable to citizens, elected officials, and law | Responsible to donors, beneficiaries, and ethical guidelines |
| Scope | Local, regional, national, and international levels | Local, national, or global, focused on specific issues |
| Decision-Making | Formal procedures, bureaucratic processes | Flexible, mission-driven strategies |
Understanding Government and NGOs: Key Differences
Governments are formal institutions with legal authority to enact and enforce laws, collect taxes, and provide public services, while NGOs (Non-Governmental Organizations) are voluntary, nonprofit entities that operate independently from the government to address social, environmental, or humanitarian issues. Governments have sovereign power and are accountable to the state and citizens through elections and public policies, whereas NGOs rely on private funding, donations, and grants and are often driven by specific missions or advocacy goals. Understanding these key differences highlights the distinct roles each plays in society, with governments focusing on regulation and public welfare, and NGOs emphasizing community support, awareness, and specialized interventions.
Roles and Responsibilities in Society
Governments create and enforce laws, provide public services, and ensure national security, playing a central role in maintaining order and promoting economic development. NGOs focus on addressing social issues, advocating for human rights, and delivering humanitarian aid, often filling gaps left by government programs. Both entities collaborate to enhance community well-being, but governments hold regulatory authority while NGOs operate through voluntary funding and grassroots involvement.
Funding Sources and Financial Structures
Government funding primarily derives from tax revenues, enabling large-scale budgets with allocated annual appropriations that support public services and infrastructure. NGOs rely on diverse financial structures, including private donations, grants from foundations, international aid, and fundraising campaigns, which often result in variable and project-specific funding streams. The stability of government budgets contrasts with the fluctuating nature of NGO finances, influencing organizational strategies and long-term program planning.
Policy-Making vs. Grassroots Advocacy
Governments primarily engage in policy-making by creating and implementing laws and regulations that address broad societal issues through formal legislative processes. NGOs focus on grassroots advocacy by mobilizing local communities, raising public awareness, and influencing policy through direct action and community organizing. While governments have the authority to enforce policies, NGOs drive change from the ground up by amplifying citizen voices and fostering participatory democracy.
Levels of Accountability and Transparency
Governments operate under strict legal frameworks requiring high levels of accountability and transparency through public audits, legislative oversight, and freedom of information laws. NGOs, while committed to transparency, often follow voluntary disclosure practices and rely on donor requirements to maintain accountability. The differing structures influence how each addresses public scrutiny and stakeholder responsibility in effecting social change.
Impact on Social Development
Government agencies implement large-scale social development programs funded by public resources, often focusing on infrastructure, education, and healthcare access. NGOs complement these efforts by addressing specific community needs through grassroots initiatives, advocacy, and capacity-building, often reaching marginalized populations more effectively. Both entities play crucial roles in enhancing social equity and promoting sustainable development outcomes.
Collaboration Between Government and NGOs
Collaboration between government and NGOs enhances public service delivery by combining governmental authority with NGO grassroots expertise and community trust. Joint initiatives in healthcare, education, and disaster relief leverage NGO innovation and government resources to meet social needs more efficiently. This partnership strengthens policy implementation, promotes transparency, and improves accountability in addressing complex societal challenges.
Challenges Faced by Governments and NGOs
Governments face bureaucratic red tape, limited budget allocations, and political constraints that hinder swift decision-making and implementation of policies. NGOs often struggle with funding instability, operational scalability, and navigating regulatory requirements imposed by governments. Both entities must collaborate effectively to overcome communication gaps and ensure efficient resource utilization for social impact.
Influences on Public Opinion and Behavior
Governments shape public opinion and behavior through policy-making, legislation, and official communication channels, wielding authority to enforce laws and allocate resources. NGOs influence public attitudes by mobilizing grassroots support, conducting awareness campaigns, and providing expert advocacy on social and environmental issues. While government actions reflect institutional power, NGOs leverage community engagement and credibility to sway public perspectives and behavioral norms.
Future Prospects for Government-NGO Partnerships
Government-NGO partnerships are poised for growth as collaborative frameworks evolve to address global challenges such as climate change, public health, and social inequality. Advancements in digital technology and data sharing enhance transparency and efficiency, enabling more impactful community-driven initiatives. Strengthened policy alignment and increased funding support create opportunities for sustainable development and inclusive governance.
Government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com