Electronic ballots streamline the voting process by enabling secure, accurate, and efficient casting and counting of votes through digital systems. These ballots reduce errors commonly associated with paper voting and enhance accessibility for voters with disabilities. Explore the rest of the article to understand how electronic ballots can transform your voting experience and bolster election integrity.
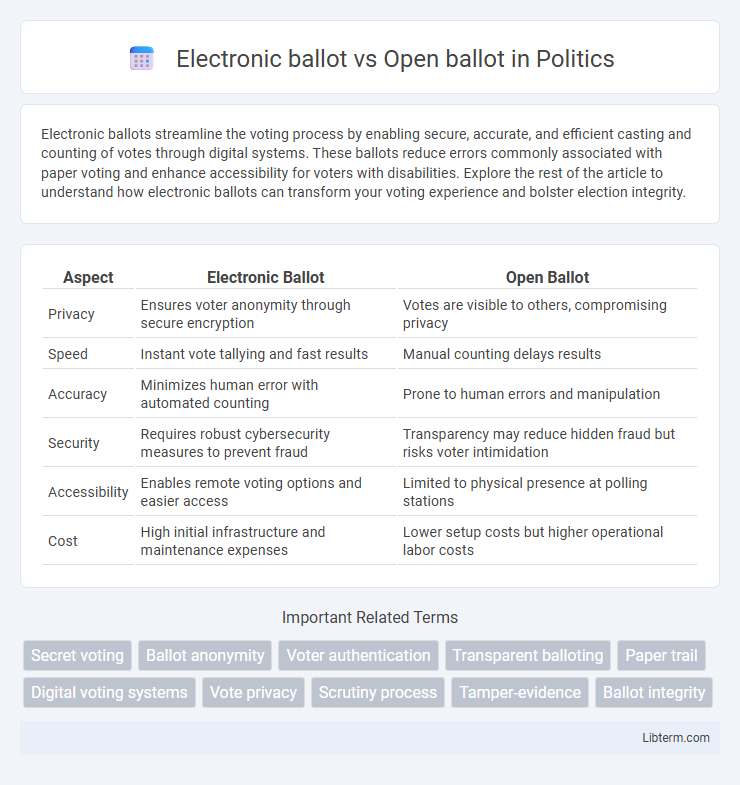
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Electronic Ballot | Open Ballot |
|---|---|---|
| Privacy | Ensures voter anonymity through secure encryption | Votes are visible to others, compromising privacy |
| Speed | Instant vote tallying and fast results | Manual counting delays results |
| Accuracy | Minimizes human error with automated counting | Prone to human errors and manipulation |
| Security | Requires robust cybersecurity measures to prevent fraud | Transparency may reduce hidden fraud but risks voter intimidation |
| Accessibility | Enables remote voting options and easier access | Limited to physical presence at polling stations |
| Cost | High initial infrastructure and maintenance expenses | Lower setup costs but higher operational labor costs |
Introduction to Voting Systems
Electronic ballot systems utilize digital technology to record and count votes efficiently, enhancing accuracy and speed in elections, while open ballot systems require voters to publicly declare their choices, potentially compromising privacy and increasing social pressure. Electronic voting machines offer secure encryption and audit trails to maintain election integrity, contrasting with open ballots that lack confidentiality and may be prone to coercion. The transition from open ballots to electronic systems represents a significant advancement in modern voting methodologies, promoting transparency, security, and voter anonymity.
What is Electronic Ballot?
Electronic ballot refers to a digital voting system where voters cast their ballots using electronic devices such as touchscreens, computers, or specialized voting machines. This method enhances accuracy and speed in vote counting, reduces human errors, and improves accessibility for voters with disabilities. Unlike the open ballot system where votes are publicly declared, the electronic ballot ensures voter privacy and confidentiality through encrypted data transmission and secure authentication protocols.
What is Open Ballot?
Open ballot is a voting method where voters publicly disclose their choices, allowing votes to be observed by others, often used to promote transparency or social pressure. Unlike electronic ballots, open ballots lack privacy, making them susceptible to influence or intimidation. This voting style is common in settings without advanced technology or in community-based decision-making processes.
Historical Context and Evolution
The electronic ballot system originated in the late 20th century as advancements in computer technology allowed for faster vote counting and improved election security compared to the traditional open ballot method widely used throughout history. Open ballot systems, prevalent in many 19th-century democratic processes, involved voters publicly declaring their choices, which often led to voter intimidation and lack of privacy. The evolution toward electronic ballots reflects a global shift aiming to enhance electoral integrity, reduce fraud, and protect voter anonymity in increasingly complex democratic frameworks.
Security and Integrity Comparison
Electronic ballots offer enhanced security features such as encryption, biometric verification, and tamper-evident logs that significantly reduce the risks of vote manipulation and fraud. Open ballots, while transparent and simple, expose votes to potential coercion, bribery, and privacy breaches, undermining voter anonymity and election integrity. The integrity of electronic ballots is reinforced through cryptographic protocols and audit trails, whereas open ballots rely heavily on manual oversight and physical safeguards vulnerable to human error.
Transparency and Voter Privacy
Electronic ballots enhance transparency by enabling real-time vote tallying and audit trails, ensuring accurate and verifiable election results. In contrast, open ballots provide visible voter choices, which compromise voter privacy and can lead to potential coercion or vote manipulation. Balancing transparency with voter privacy, electronic ballots are increasingly favored for maintaining election integrity while protecting voter anonymity.
Implementation Challenges
Electronic ballot systems face implementation challenges such as cybersecurity threats, high infrastructure costs, and ensuring voter privacy, which require robust encryption and auditing technologies. Open ballots, while simpler to implement, struggle with risks of voter intimidation and lack of confidentiality, complicating efforts to maintain election integrity. Both methods must address logistical issues and public trust to achieve effective and transparent electoral processes.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Electronic ballots enhance accessibility by allowing voters with disabilities to use adaptive technologies and remote devices, increasing voting opportunities for marginalized groups. Open ballots, often requiring physical presence and literacy, can exclude individuals who face mobility challenges or fear social repercussions. By contrast, electronic voting platforms offer customizable interfaces and privacy, fostering greater inclusivity across diverse populations.
Impact on Election Outcomes
Electronic ballots enhance election accuracy by minimizing human error and accelerating vote tallying, leading to faster and more reliable results. Open ballots can influence voter behavior through social pressure or intimidation, potentially skewing election outcomes by reducing voter anonymity. The confidentiality offered by electronic ballots promotes voter freedom, increasing the likelihood of genuine preference expression and fairer election results.
Future Trends in Voting Methods
Electronic ballots are increasingly favored for their speed and accuracy in vote tallying, with advancements in blockchain technology enhancing security and transparency. Open ballots, while promoting voter accountability and public observation, face challenges related to privacy and coercion, limiting their scalability in modern elections. Future trends suggest hybrid voting systems integrating electronic ballots with robust encryption protocols to balance voter privacy and election integrity, enabling more accessible and reliable democratic processes.
Electronic ballot Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com