Mail-in ballots offer a convenient way for voters to participate in elections without visiting polling places, ensuring your voice is counted from the comfort of your home. This voting method increases accessibility while maintaining security through verified signatures and tracking systems. Discover how mail-in ballots work and why they're a crucial part of modern elections by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
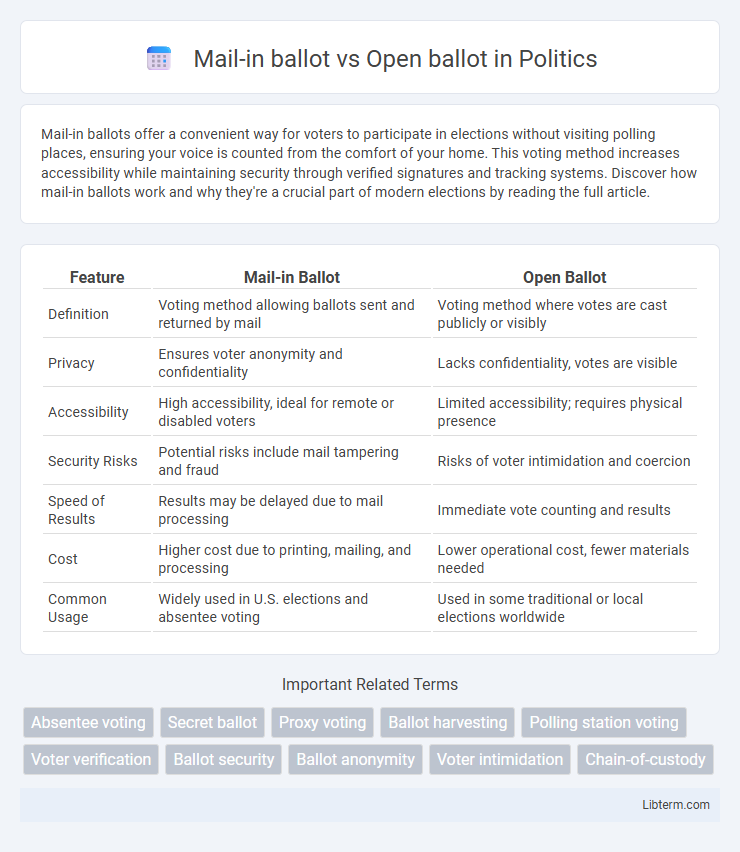
| Feature | Mail-in Ballot | Open Ballot |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voting method allowing ballots sent and returned by mail | Voting method where votes are cast publicly or visibly |
| Privacy | Ensures voter anonymity and confidentiality | Lacks confidentiality, votes are visible |
| Accessibility | High accessibility, ideal for remote or disabled voters | Limited accessibility; requires physical presence |
| Security Risks | Potential risks include mail tampering and fraud | Risks of voter intimidation and coercion |
| Speed of Results | Results may be delayed due to mail processing | Immediate vote counting and results |
| Cost | Higher cost due to printing, mailing, and processing | Lower operational cost, fewer materials needed |
| Common Usage | Widely used in U.S. elections and absentee voting | Used in some traditional or local elections worldwide |
Introduction to Mail-in and Open Ballots
Mail-in ballots allow voters to cast their votes remotely by receiving and returning ballots through postal mail, enhancing accessibility and convenience in elections. Open ballots, often used in public or traditional voting settings, involve voters visibly casting their choices, which can increase transparency but may affect voter privacy. Understanding the distinctions between mail-in and open ballots is crucial for evaluating election security, voter participation, and overall electoral integrity.
Defining Mail-in Ballots
Mail-in ballots are voting materials sent to registered voters who cast their votes remotely, typically by post, ensuring convenience and accessibility while maintaining election integrity through secure verification processes. Unlike open ballots, which require voters to publicly disclose their choices during in-person or electronic voting, mail-in ballots prioritize voter privacy by allowing individuals to mark and return their votes confidentially from their homes. The increased adoption of mail-in ballots aims to enhance voter turnout and reduce in-person crowding at polling stations.
Understanding Open Ballots
Open ballots allow voters to cast their votes publicly, revealing their choices to others, which contrasts with mail-in ballots where voting is done privately by sending ballots through the postal service. This transparency in open ballots can influence voter behavior due to social pressure or intimidation, impacting election outcomes. Understanding open ballots requires analyzing their role in promoting accountability versus the risk of compromising voter privacy and election fairness.
Key Differences Between Mail-in and Open Ballots
Mail-in ballots require voters to receive, mark, and return their ballots via postal mail, ensuring privacy and convenience, while open ballots are cast publicly, often by a show of hands or voice vote, lacking this confidentiality. Mail-in voting enhances accessibility and reduces in-person polling site congestion, whereas open ballots may increase transparency but risk voter intimidation or social pressure. The key difference lies in the balance between voter anonymity with mail-in ballots and public visibility with open ballots.
Security Concerns and Safeguards
Mail-in ballots face security concerns such as potential vote tampering, ballot loss, and signature forgery, prompting safeguards like signature verification, barcode tracking, and secure drop boxes. Open ballots, often used in in-person voting, mitigate these risks by allowing immediate ballot verification and counting under observation, but raise privacy concerns due to lack of anonymity. Robust protocols, including surveillance, chain-of-custody documentation, and voter identification, are critical to maintaining election integrity across both methods.
Accessibility and Voter Participation
Mail-in ballots significantly enhance accessibility by allowing voters to cast their votes remotely, benefiting individuals with disabilities, limited transportation, or restrictive schedules. Open ballots, often requiring in-person attendance at polling stations, may pose barriers for those facing mobility challenges or time constraints, potentially reducing voter participation. Studies indicate that mail-in voting correlates with higher turnout rates, especially among elderly and rural populations, by providing a more flexible and inclusive voting process.
Impact on Election Transparency
Mail-in ballots increase voter accessibility but raise concerns about verifying voter identity and ballot security, potentially affecting election transparency. Open ballots, where votes are cast publicly, offer higher transparency by allowing immediate verification and reducing the risk of fraud but may compromise voter privacy. Balancing transparency with confidentiality is crucial to maintaining trust in the electoral process.
Common Misconceptions
Mail-in ballots are often misunderstood as less secure than open ballots, but they use multiple verification methods like signature matching and barcodes to ensure authenticity. Open ballots, where votes are cast publicly, are mistakenly believed to be more transparent, yet they compromise voter privacy and can lead to undue influence or intimidation. Both systems include robust safeguards tailored to maintain election integrity, debunking myths around vulnerability or transparency.
Global Practices and Trends
Mail-in ballots have gained popularity globally for increasing voter accessibility and reducing in-person crowding, with countries like the United States, Germany, and Australia adopting comprehensive postal voting systems. Open ballots, where votes are publicly cast and counted, are less common but remain in use in regions emphasizing transparency through public vote verification, such as parts of India and some local elections in Africa. Trends indicate a shift toward hybrid voting models combining mail-in and secure electronic verification to balance privacy, accessibility, and election integrity.
Conclusion: Weighing the Pros and Cons
Mail-in ballots offer increased accessibility and convenience, reducing in-person crowding and allowing voters to participate remotely. Open ballots provide transparency and immediate vote verification but may compromise voter privacy and increase social pressure. Balancing confidential voting rights with ease of access is crucial in determining the optimal electoral method.
Mail-in ballot Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com