Lobbying influences policy decisions by engaging directly with lawmakers and stakeholders to advocate for specific interests or causes. It involves strategic communication, relationship-building, and presenting compelling evidence to shape legislation or regulations effectively. Discover how understanding lobbying can empower your role in shaping public policy in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
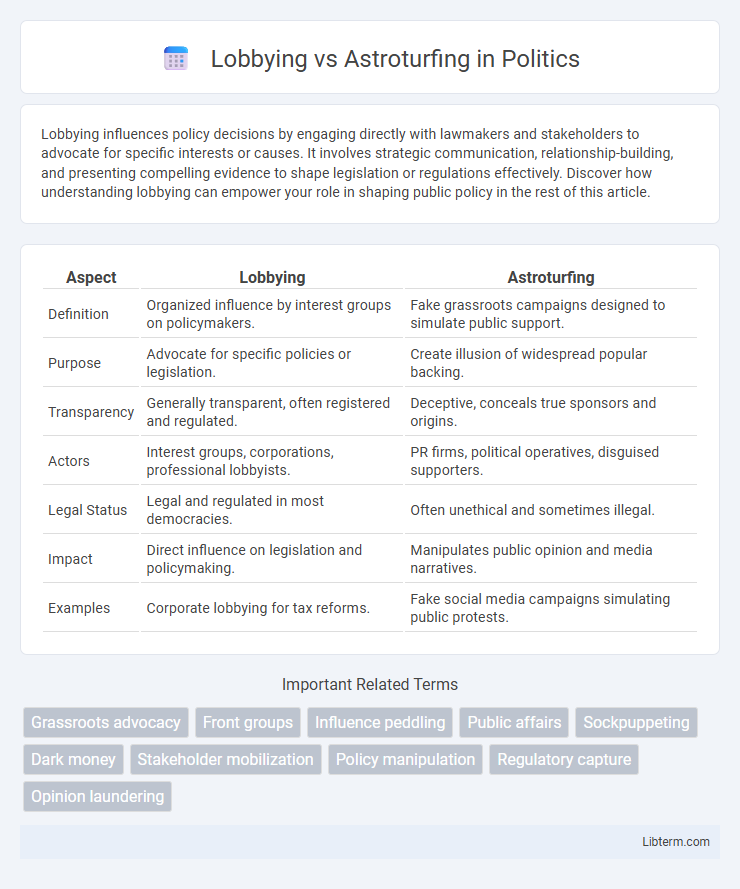
| Aspect | Lobbying | Astroturfing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organized influence by interest groups on policymakers. | Fake grassroots campaigns designed to simulate public support. |
| Purpose | Advocate for specific policies or legislation. | Create illusion of widespread popular backing. |
| Transparency | Generally transparent, often registered and regulated. | Deceptive, conceals true sponsors and origins. |
| Actors | Interest groups, corporations, professional lobbyists. | PR firms, political operatives, disguised supporters. |
| Legal Status | Legal and regulated in most democracies. | Often unethical and sometimes illegal. |
| Impact | Direct influence on legislation and policymaking. | Manipulates public opinion and media narratives. |
| Examples | Corporate lobbying for tax reforms. | Fake social media campaigns simulating public protests. |
Understanding Lobbying: Definition and Purpose
Lobbying involves direct interaction with policymakers to influence legislation and public policy in favor of specific interests or causes, typically conducted by registered advocates or professional lobbyists. Its primary purpose is to provide lawmakers with information, expertise, and perspectives to shape decisions that align with the interests of clients, organizations, or industries. Unlike astroturfing, which creates a false impression of grassroots support, lobbying operates transparently within legal frameworks to facilitate informed policymaking.
What is Astroturfing? Core Concepts Explained
Astroturfing is a deceptive practice where orchestrated campaigns create the illusion of genuine grassroots support, often using fake social media accounts, paid influencers, or fabricated testimonials. Unlike lobbying, which involves transparent advocacy efforts aimed at influencing policy through official channels, astroturfing manipulates public perception by masking corporate or political interests as spontaneous public opinion. Core concepts of astroturfing include anonymity, false representation, and strategic dissemination to sway public debate and policy without accountability.
Key Differences Between Lobbying and Astroturfing
Lobbying involves organized efforts by interest groups or individuals to influence policymakers through transparent and legal means, often backed by genuine constituent support or stakeholder interests. Astroturfing refers to deceptive campaigns designed to create the illusion of grassroots support by artificially generating public opinion, frequently using fake testimonials, paid actors, or misleading tactics. The key difference lies in transparency and authenticity: lobbying openly advocates for specific agendas, while astroturfing manipulates public perception to mask the true source and intent of the message.
Legal Framework: Regulations and Ethics
Lobbying operates within a legal framework defined by transparency and disclosure laws, requiring registered lobbyists to report activities and expenditures to ensure accountability. Astroturfing, often involving deceptive practices to mimic grassroots support, is typically illegal or heavily regulated due to its potential to mislead the public and policymakers. Ethical standards in lobbying emphasize honesty and public interest, while astroturfing violates these norms by undermining genuine democratic processes through manipulation and false representation.
Methods and Strategies Used in Lobbying
Lobbying employs direct methods such as meetings with policymakers, providing expert testimony, and grassroots mobilization to influence legislation and regulatory decisions. Strategies often involve building long-term relationships, leveraging political contributions, and crafting persuasive communication tailored to lawmakers' interests and priorities. Unlike astroturfing, which uses deceptive fake grassroots campaigns, lobbying relies on transparent advocacy supported by factual data and organized stakeholder engagement.
Tactics and Techniques of Astroturfing
Astroturfing employs deceptive tactics such as creating fake grassroots campaigns through fabricated social media accounts, paid influencers, and orchestrated online reviews to simulate genuine public support. Techniques include the coordinated dissemination of fabricated narratives, strategic use of bots to amplify messages, and recruitment of unwitting individuals to spread disinformation organically. Unlike lobbying, which involves transparent petitioning and direct engagement with policymakers, astroturfing relies on stealth and manipulation to influence public opinion and policy decisions covertly.
Impact on Public Opinion and Policy Decisions
Lobbying represents organized efforts by interest groups to influence policy decisions through transparent communication and advocacy, often shaping legislation and regulatory frameworks. Astroturfing, by contrast, involves deceptive tactics that simulate grassroots movements to manipulate public opinion and obscure the true source of influence, undermining democratic processes. The impact on public opinion differs significantly: lobbying fosters informed debate, while astroturfing distorts perceptions, leading to potentially skewed policy outcomes based on fabricated consensus.
Identifying Genuine Advocacy vs. Deceptive Practices
Genuine advocacy involves transparent communication by interest groups openly representing their constituents to influence public policy, while astroturfing disguises orchestrated campaigns as grassroots movements to manipulate public opinion. Identifying these deceptive practices requires analyzing funding sources, the authenticity of participant engagement, and the consistency of messaging with declared values. Effective scrutiny of lobbying disclosures and verifying independent support can distinguish legitimate efforts from covert manipulation.
Case Studies: Notable Examples of Lobbying and Astroturfing
The 2020 Volkswagen emissions scandal demonstrated how aggressive lobbying delayed regulatory oversight, protecting corporate interests despite environmental concerns. In contrast, the 2010 Citizens United case exemplified astroturfing, where large financial groups disguised political spending as grassroots support to influence elections covertly. These case studies highlight how lobbying legitimizes direct policy influence while astroturfing manipulates public opinion under the guise of genuine activism.
Safeguarding Democracy: Transparency and Accountability
Lobbying involves transparent advocacy efforts by interest groups to influence policymakers through open communication and registered activities, ensuring accountability in democratic processes. Astroturfing, by contrast, disguises coordinated campaigns as grassroots movements, undermining public trust and obscuring true interests behind policy debates. Safeguarding democracy requires stringent transparency measures and rigorous enforcement of disclosure laws to differentiate genuine lobbying from deceptive astroturfing tactics.
Lobbying Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com