Coalition building involves uniting diverse groups around a common goal to amplify influence and resources effectively. Successful coalitions require clear communication, shared objectives, and mutual trust to create lasting partnerships. Discover how strategic coalition building can empower your initiatives by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
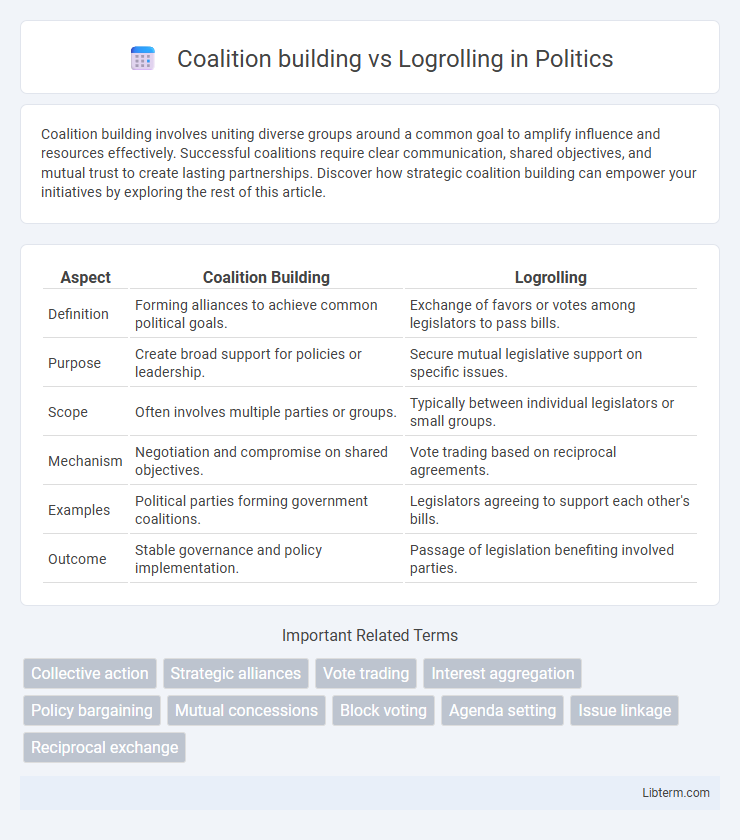
| Aspect | Coalition Building | Logrolling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Forming alliances to achieve common political goals. | Exchange of favors or votes among legislators to pass bills. |
| Purpose | Create broad support for policies or leadership. | Secure mutual legislative support on specific issues. |
| Scope | Often involves multiple parties or groups. | Typically between individual legislators or small groups. |
| Mechanism | Negotiation and compromise on shared objectives. | Vote trading based on reciprocal agreements. |
| Examples | Political parties forming government coalitions. | Legislators agreeing to support each other's bills. |
| Outcome | Stable governance and policy implementation. | Passage of legislation benefiting involved parties. |
Understanding Coalition Building
Coalition building involves the strategic alliance of diverse stakeholders to achieve a common policy goal by merging interests and resources in a collaborative framework. This process emphasizes negotiation, trust-building, and identifying shared objectives among parties to create a durable and effective partnership. Unlike logrolling, which focuses on reciprocal voting agreements, coalition building seeks to develop broad consensus and sustainable support through inclusive dialogue and compromise.
Defining Logrolling in Politics
Logrolling in politics refers to the practice where legislators exchange support for each other's proposed bills or amendments to secure mutual benefits and pass legislation. This strategic vote trading contrasts with coalition building, which involves forming alliances based on shared interests or policy goals rather than reciprocal agreements. Logrolling often enhances legislative efficiency but can lead to compromises that prioritize political exchange over policy merit.
Core Principles of Coalition Building
Coalition building centers on uniting diverse stakeholders around shared goals through trust-building, communication, and negotiation, emphasizing collaboration and mutual benefit to achieve collective impact. Core principles include establishing common interests, fostering inclusivity, and leveraging complementary strengths to create a durable alliance. In contrast, logrolling primarily involves reciprocal vote trading among legislators to secure individual gains rather than focusing on a broad, cohesive partnership.
Key Mechanisms of Logrolling
Logrolling hinges on the strategic exchange of support between legislators to achieve mutual policy goals, where each party agrees to vote for the other's preferred legislation. This mechanism relies on reciprocal favoritism, leveraging interdependence to build stable voting coalitions that might not form based solely on policy alignment. Effective logrolling requires precise negotiation of trade-offs, ensuring that each participant gains sufficient benefit to secure their commitment to the coalition.
Strategic Advantages of Coalition Building
Coalition building offers strategic advantages by fostering long-term partnerships through shared goals and trust, enhancing collective bargaining power across diverse stakeholders. This approach enables the pooling of resources and expertise, creating a unified front that increases influence in policy-making and decision processes. Unlike logrolling, which is often transactional and short-term, coalition building cultivates sustainable alliances that adapt to evolving political landscapes.
Potential Pitfalls of Logrolling
Logrolling often leads to inefficient policy outcomes as legislators trade votes on unrelated issues, resulting in the passage of measures that may lack broad public support or economic justification. This practice can foster the growth of pork-barrel spending and create accountability problems, making it difficult to assess the true merit of individual policies. In contrast, coalition building emphasizes aligning shared interests to create more sustainable and transparent legislative partnerships.
Coalition Building vs. Logrolling: Main Differences
Coalition building involves forming alliances among groups or parties to pursue shared policy goals, emphasizing mutual interests and compromise. Logrolling, a legislative strategy, centers on exchanging favors where lawmakers agree to support each other's proposals, often prioritizing individual or localized benefits. The main difference lies in coalition building's focus on collective agenda-setting versus logrolling's quid pro quo vote trading.
Impact on Policy Outcomes
Coalition building fosters broad alliances by aligning diverse interests around shared policy goals, increasing the likelihood of comprehensive and sustainable policy outcomes. Logrolling, based on reciprocal vote trading, often results in narrowly focused agreements that prioritize individual gains over collective benefits, which can lead to fragmented or less effective policies. The impact of coalition building on policy outcomes tends to be more robust and enduring, while logrolling may produce short-term victories with limited long-term policy coherence.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Coalition building involves forming alliances among diverse interest groups to achieve common policy goals, as seen in the 1930s New Deal alliances that united labor unions, farmers, and urban voters to support social reforms. Logrolling, a tactic where legislators exchange support for each other's bills, was famously employed during the passage of the Interstate Highway Act of 1956, where members of Congress agreed to fund highways in their districts in exchange for backing the overall legislation. Both strategies reveal how political actors leverage collaboration and negotiation to navigate complex legislative processes and secure desired outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach in Legislative Negotiations
Coalition building fosters long-term alliances by aligning shared interests among lawmakers to achieve common legislative goals, making it ideal for comprehensive policy initiatives. Logrolling involves exchanging specific legislative favors or votes, best suited for securing support on individual bills or narrow issues where mutual benefit is clear. Selecting the right approach depends on the complexity of the legislation, the necessity of durable partnerships, and the strategic importance of vote trading to maximize legislative success.
Coalition building Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com