Voter suppression tactics, such as strict ID laws, limited polling places, and purging voter rolls, undermine the democratic process by disproportionately affecting marginalized communities. These barriers reduce voter turnout and weaken the representation of diverse voices in elections. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these practices impact your voting rights and what can be done to address them.
Table of Comparison
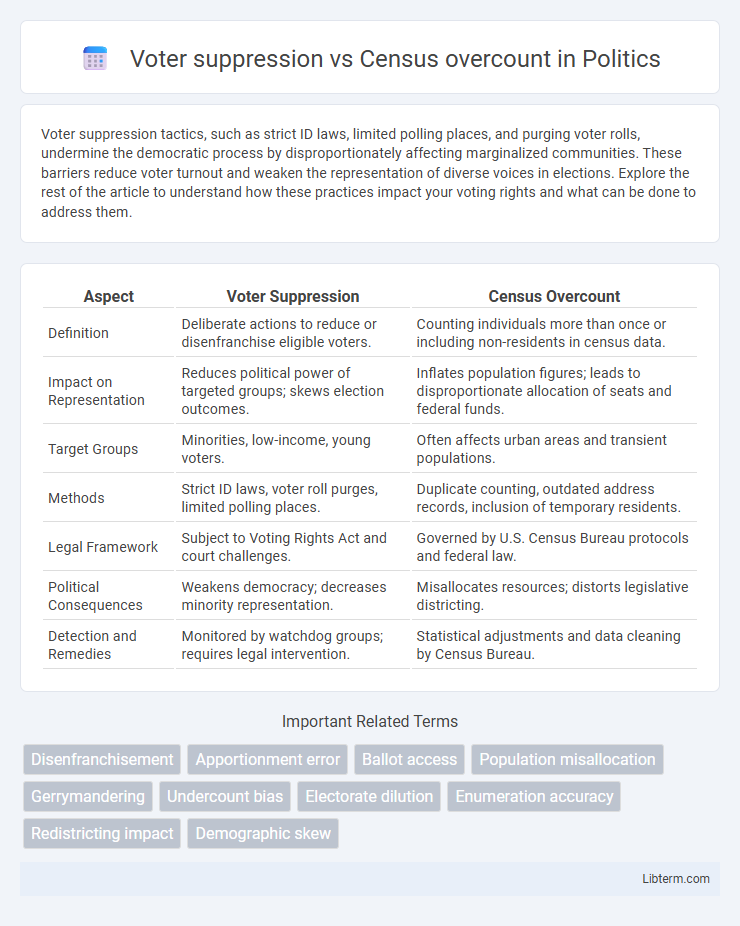
| Aspect | Voter Suppression | Census Overcount |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate actions to reduce or disenfranchise eligible voters. | Counting individuals more than once or including non-residents in census data. |
| Impact on Representation | Reduces political power of targeted groups; skews election outcomes. | Inflates population figures; leads to disproportionate allocation of seats and federal funds. |
| Target Groups | Minorities, low-income, young voters. | Often affects urban areas and transient populations. |
| Methods | Strict ID laws, voter roll purges, limited polling places. | Duplicate counting, outdated address records, inclusion of temporary residents. |
| Legal Framework | Subject to Voting Rights Act and court challenges. | Governed by U.S. Census Bureau protocols and federal law. |
| Political Consequences | Weakens democracy; decreases minority representation. | Misallocates resources; distorts legislative districting. |
| Detection and Remedies | Monitored by watchdog groups; requires legal intervention. | Statistical adjustments and data cleaning by Census Bureau. |
Introduction to Voter Suppression and Census Overcount
Voter suppression systematically restricts eligible citizens from exercising their right to vote through tactics like strict ID laws, purging voter rolls, and limiting polling locations. Census overcount occurs when individuals are mistakenly counted more than once or non-residents are included, leading to inaccurate population data. Both voter suppression and census overcount impact political representation and resource allocation, influencing electoral outcomes and government funding.
Defining Voter Suppression: Key Tactics and Impacts
Voter suppression encompasses tactics such as strict voter ID laws, purging of voter rolls, limited polling locations, and misinformation campaigns designed to disenfranchise specific demographic groups. These methods disproportionately affect minority, low-income, and young voters, undermining equitable political representation. Contrary to concerns about census overcount, which can amplify political influence for certain areas, voter suppression directly restricts eligible citizens' access to the ballot, skewing democratic participation and election outcomes.
Understanding Census Overcount: Causes and Consequences
Census overcount occurs when individuals are counted more than once or when people are recorded as living in places they do not reside, influenced by factors such as transient populations, reporting errors, and duplication of records. This inflates population figures, leading to misallocation of federal resources and skewed political representation in congressional districts. Understanding the causes of census overcount is crucial for addressing its consequences on electoral fairness and equitable distribution of public funding.
Historical Context: Voter Suppression in the United States
Voter suppression in the United States has deep historical roots dating back to the post-Reconstruction era, where mechanisms like literacy tests, poll taxes, and grandfather clauses were systematically employed to disenfranchise African American voters. These tactics significantly skewed political representation by reducing voter turnout and impacting electoral outcomes in favor of certain groups. In contrast, concerns about census overcount, while important for resource allocation and congressional apportionment, have historically posed less direct impact on voter access compared to the overt barriers established through voter suppression efforts.
The Mechanics of Census Overcount and Undercount
Census overcount occurs when certain populations are counted more than once or inaccurately, often due to duplicate records, address errors, or data processing issues, leading to inflated demographic figures. Undercount primarily affects marginalized groups, including minorities and low-income households, who are often missed due to lack of participation, distrust, or logistical barriers during data collection. These discrepancies impact political representation and resource allocation, with overcount skewing population data and undercount exacerbating voter suppression by diminishing the visibility of underrepresented communities.
Effects on Representation: Comparing Voter Suppression and Census Errors
Voter suppression reduces electoral participation, disproportionately affecting minority and marginalized communities, which undermines fair representation in legislative bodies. Census overcounts inflate population data for certain areas, leading to misallocated federal funding and distorted congressional apportionment that shifts political power inaccurately. Both issues create imbalances in political influence, but voter suppression directly skews voter turnout while census errors impact long-term resource distribution and districting.
Demographic Groups Most Affected
Voter suppression disproportionately impacts minority groups such as African Americans, Latinos, and Native Americans by limiting access through restrictive ID laws and reduced polling locations. Census overcount issues primarily affect non-Hispanic White populations and higher-income households, leading to inflated representation and resource allocation. These disparities skew political power and federal funding, intensifying inequalities across demographic lines.
Legal and Policy Responses to Voter Suppression and Census Overcount
Legal and policy responses to voter suppression emphasize strengthening the Voting Rights Act, enforcing strict penalties for discriminatory practices, and expanding access to voter registration and polling locations. Measures addressing census overcount focus on improving data accuracy through enhanced outreach to underrepresented populations, refining address canvassing methods, and implementing rigorous post-enumeration surveys to detect and correct duplications. Both issues require coordinated federal and state efforts to ensure fair representation and uphold democratic principles.
The Interplay between Census Data and Voting Rights
Census data plays a critical role in enforcing voting rights by determining the allocation of congressional seats and electoral districts, which directly affects voter representation. Voter suppression tactics often exploit inaccuracies in census counts to disenfranchise marginalized communities, while census overcounts can lead to misallocation of political power, diluting minority votes. Ensuring accurate census enumeration is essential to maintaining equitable voting rights and preventing both underrepresentation and the manipulation of electoral boundaries.
Solutions and Future Directions for Fair Representation
Implementing independent redistricting commissions and expanding voter access through mail-in ballots and automatic registration can reduce voter suppression and promote fair representation. Enhancing Census accuracy by improving outreach in hard-to-count communities and using advanced data analytics ensures equitable resource allocation and political representation. Future strategies should integrate technology and community engagement to address both undercounting and suppression for a more inclusive democracy.
Voter suppression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com