Electoral stability ensures consistent governance by maintaining trust in the democratic process and reducing political volatility. It fosters a predictable political environment essential for economic growth and social development. Explore the rest of the article to understand how electoral stability impacts your country's future.
Table of Comparison
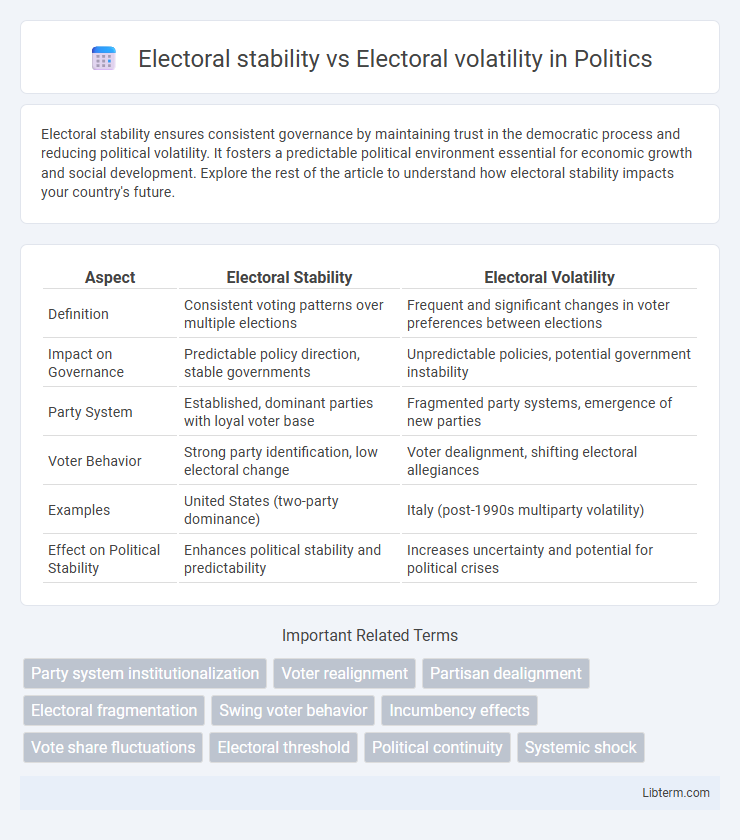
| Aspect | Electoral Stability | Electoral Volatility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistent voting patterns over multiple elections | Frequent and significant changes in voter preferences between elections |
| Impact on Governance | Predictable policy direction, stable governments | Unpredictable policies, potential government instability |
| Party System | Established, dominant parties with loyal voter base | Fragmented party systems, emergence of new parties |
| Voter Behavior | Strong party identification, low electoral change | Voter dealignment, shifting electoral allegiances |
| Examples | United States (two-party dominance) | Italy (post-1990s multiparty volatility) |
| Effect on Political Stability | Enhances political stability and predictability | Increases uncertainty and potential for political crises |
Understanding Electoral Stability and Volatility
Electoral stability refers to consistent voting patterns and party dominance over multiple election cycles, indicating predictable political behavior and sustained voter loyalty. Electoral volatility measures the degree of change in electoral preferences between elections, often caused by shifting socio-economic conditions, emerging political issues, or voter realignment. Understanding these concepts is crucial for analyzing party system institutionalization, election forecasting, and democratic resilience in various political contexts.
Historical Context of Electoral Patterns
Electoral stability refers to consistent voting behavior and party dominance over multiple election cycles, often rooted in long-standing social, economic, or cultural factors within a given country. Electoral volatility indicates significant shifts in voter preferences and party support, frequently triggered by political realignments, social upheaval, or emerging issues disrupting traditional patterns. Historical analysis reveals that established democracies tend to exhibit higher electoral stability, while transitional or developing political systems commonly experience greater volatility due to evolving party systems and voter alignments.
Key Drivers of Electoral Stability
Electoral stability is primarily driven by strong party identification, consistent voter loyalty, and institutional factors such as proportional representation systems that encourage voter alignment with specific parties. Effective governance and satisfied electorate reducing political dissatisfaction also contribute significantly to maintaining stability in voting patterns. Socioeconomic factors like higher education levels and political socialization further reinforce stable electoral preferences across election cycles.
Factors Leading to Electoral Volatility
Electoral volatility often results from factors such as changing voter preferences, party system fragmentation, and socio-economic shifts impacting electoral behavior. New parties entering the political arena, scandals involving established parties, and fluctuating political alliances contribute significantly to unstable voting patterns. High electoral volatility reflects unpredictability in election outcomes, contrasting with electoral stability marked by consistent voter loyalty and established party dominance.
Measuring and Analyzing Electoral Fluctuations
Electoral stability refers to consistent voting patterns and party dominance over multiple election cycles, while electoral volatility captures the degree of change in voter preferences between elections. Measuring electoral fluctuations involves quantitative metrics such as the Pedersen Index, which calculates net changes in party vote shares to assess shifts in political support. Analytical approaches combine statistical analysis of vote share data with qualitative factors like voter behavior and party realignments to interpret the causes and implications of electoral volatility.
Impact of Stable vs Volatile Elections on Governance
Electoral stability fosters consistent policy implementation and strengthens institutional trust, facilitating effective governance and long-term planning. In contrast, electoral volatility often leads to fragmented legislatures, frequent government changes, and policy uncertainty, which can hinder development and weaken democratic processes. Stable elections support the continuity of government initiatives, whereas volatile elections can disrupt decision-making and reduce political accountability.
Electoral Systems and Their Role in Stability
Electoral systems significantly influence electoral stability by shaping party systems and voter behavior, with proportional representation often promoting multiparty stability and majoritarian systems favoring two-party dominance. High electoral volatility typically emerges in fragmented or transitional systems where voter loyalty is weaker and party alignment shifts frequently. Stability in electoral outcomes is enhanced when systems create clear incentives for party consolidation and consistent voter identification.
Case Studies: Stable vs Volatile Democracies
Electoral stability characterizes democracies like Germany and Sweden, where consistent party systems and voter alignment ensure predictable election outcomes, fostering policy continuity and institutional trust. In contrast, volatile democracies such as Brazil and Italy display frequent party realignments and fluctuating voter preferences, leading to unpredictability in governance and challenges in policy implementation. Case studies reveal that stable democracies benefit from institutionalized party systems and high civic engagement, while volatile democracies often struggle with weak political institutions and fragmented electorates.
Implications for Political Parties and Candidates
Electoral stability fosters predictable voting patterns, allowing political parties and candidates to develop long-term strategies and build strong voter bases. In contrast, electoral volatility presents challenges for political actors in forecasting election outcomes, necessitating adaptive campaign approaches and policy platforms to appeal to shifting voter preferences. High volatility often results in fragmented party systems and increased competition, demanding constant innovation and responsiveness from candidates to maintain electoral relevance.
Navigating the Future: Strategies for Managing Electoral Change
Electoral stability ensures consistent party dominance and voter loyalty, fostering predictable governance and policy continuity. Electoral volatility reflects shifting voter preferences and emerging political movements, challenging existing power structures and prompting adaptive strategies. Navigating the future requires integrating data analytics, voter engagement, and responsive policymaking to effectively manage electoral change and sustain democratic resilience.
Electoral stability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com