A coalition government forms when multiple political parties agree to cooperate, combining their seats to create a majority in the legislature. This arrangement often requires compromise to blend different party policies into a unified agenda. Discover how coalition governments impact political stability and decision-making by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
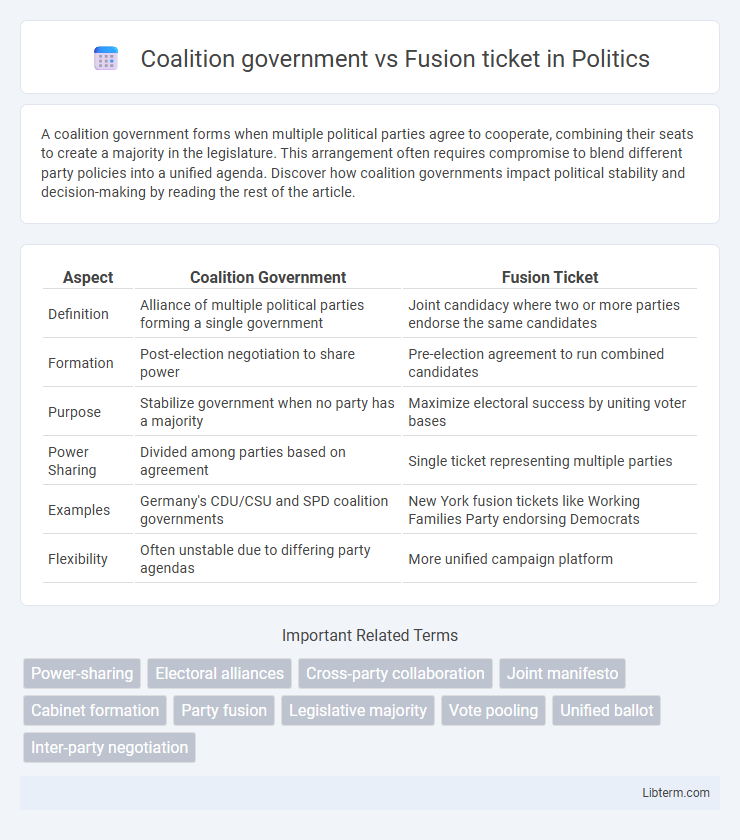
| Aspect | Coalition Government | Fusion Ticket |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alliance of multiple political parties forming a single government | Joint candidacy where two or more parties endorse the same candidates |
| Formation | Post-election negotiation to share power | Pre-election agreement to run combined candidates |
| Purpose | Stabilize government when no party has a majority | Maximize electoral success by uniting voter bases |
| Power Sharing | Divided among parties based on agreement | Single ticket representing multiple parties |
| Examples | Germany's CDU/CSU and SPD coalition governments | New York fusion tickets like Working Families Party endorsing Democrats |
| Flexibility | Often unstable due to differing party agendas | More unified campaign platform |
Introduction to Coalition Governments and Fusion Tickets
Coalition governments form when multiple political parties collaborate to create a unified administration, often necessary in parliamentary systems lacking a clear majority. Fusion tickets involve different parties nominating the same candidate to pool votes and increase election chances, typically seen in U.S. political history. Both mechanisms aim to consolidate political power but operate differently: coalition governments share governance roles post-election, while fusion tickets align pre-election strategies.
Historical Background of Coalition Governments
Coalition governments have historically emerged in parliamentary systems during periods of political fragmentation or crisis, exemplified by the UK's wartime coalitions in 1915 and 1940. These alliances involve multiple political parties uniting to secure a parliamentary majority, often prioritizing stability and consensus over singular party agendas. In contrast, fusion tickets, primarily seen in U.S. elections during the late 19th century, represent a strategic collaboration of candidates from separate parties running jointly rather than forming a sustained governing alliance.
Origins and Evolution of Fusion Tickets
Fusion tickets originated in the late 19th-century United States as a strategic alliance between multiple political parties to consolidate votes against dominant parties. Unlike coalition governments, which involve formal power-sharing agreements post-election, fusion tickets combined candidacies before elections to present a unified ballot line. This practice evolved primarily in states with multi-party competition, influencing electoral dynamics by fostering cooperation among diverse political groups.
Key Characteristics of Coalition Governments
Coalition governments are formed when multiple political parties collaborate to achieve a majority, sharing power and responsibilities within the executive branch. Key characteristics include negotiated policy agendas, power-sharing arrangements, and collective decision-making that reflect diverse party interests. Unlike fusion tickets, coalition governments involve formal agreements between parties post-election to ensure stability and representation across a broader political spectrum.
Defining Features of Fusion Tickets
Fusion tickets are electoral strategies where multiple political parties endorse the same candidate to consolidate votes and increase the candidate's chances of winning, differing from coalition governments that involve formal power-sharing agreements post-election. A defining feature of fusion tickets is the use of a single candidate appearing on the ballot as the nominee of two or more parties, enabling votes from different party lines to be combined. This approach leverages cross-party support without merging party platforms or creating joint governance structures, emphasizing vote maximization rather than institutional alliance.
Advantages of Coalition Governments
Coalition governments offer increased political stability by uniting multiple parties and fostering collaboration, which helps in representing a broader spectrum of voter interests. These governments encourage compromise and consensus-building, promoting more balanced and inclusive policy-making that can reduce political polarization. By pooling resources and expertise from different parties, coalition governments enhance governance efficiency and improve legislative effectiveness.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Fusion Tickets
Fusion tickets allow multiple political parties to combine their support behind a single candidate, enhancing vote totals and broadening appeal across diverse voter bases. This strategy can prevent vote splitting in closely contested elections, increasing the chance of victory for allied parties but may also cause ideological dilution and internal conflicts between coalition members. Voters might face confusion due to overlapping party affiliations, potentially undermining clear policy distinctions and accountability.
Impact on Political Stability and Governance
Coalition governments often improve political stability by bringing multiple parties together, fostering compromise, and preventing dominance by a single party, which can lead to inclusive governance and balanced policy-making. Fusion tickets, combining candidates from different parties into a single list, may streamline elections but risk diluting party ideologies, potentially complicating voter choices and causing instability when post-election collaboration is weak. Both approaches influence governance dynamics differently, with coalitions promoting negotiation and fusion tickets emphasizing electoral unity, each affecting the predictability and effectiveness of political institutions.
Global Examples: Coalition Governments vs. Fusion Tickets
Coalition governments, commonly found in parliamentary systems of countries like Germany, India, and Israel, involve multiple political parties collaborating to form a majority, often leading to diverse policy compromises. Fusion tickets, prevalent in U.S. local elections and historically in New York State, combine candidates from different parties on a single ballot line to consolidate voter support without merging party identities. While coalition governments emphasize shared governance and legislative cooperation across parties, fusion tickets aim primarily to maximize electoral success by uniting party endorsements behind a single candidate.
Conclusion: Comparing Coalition Governments and Fusion Tickets
Coalition governments and fusion tickets both aim to unify diverse political groups but differ in structure and function; coalition governments involve formal alliances to share power post-election, while fusion tickets combine candidates before elections to consolidate support. Coalition governments often provide more stable governance through negotiated policy compromises, whereas fusion tickets primarily enhance electoral viability without guaranteeing post-election cooperation. Understanding these distinctions clarifies strategic choices parties make to maximize political influence and legislative effectiveness.
Coalition government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com