Subsidies play a crucial role in supporting industries, reducing costs, and promoting economic growth by providing financial assistance from the government. These financial aids help stabilize markets and encourage innovation by lowering barriers to entry for businesses. Explore this article to understand how subsidies impact your industry and economy at large.
Table of Comparison
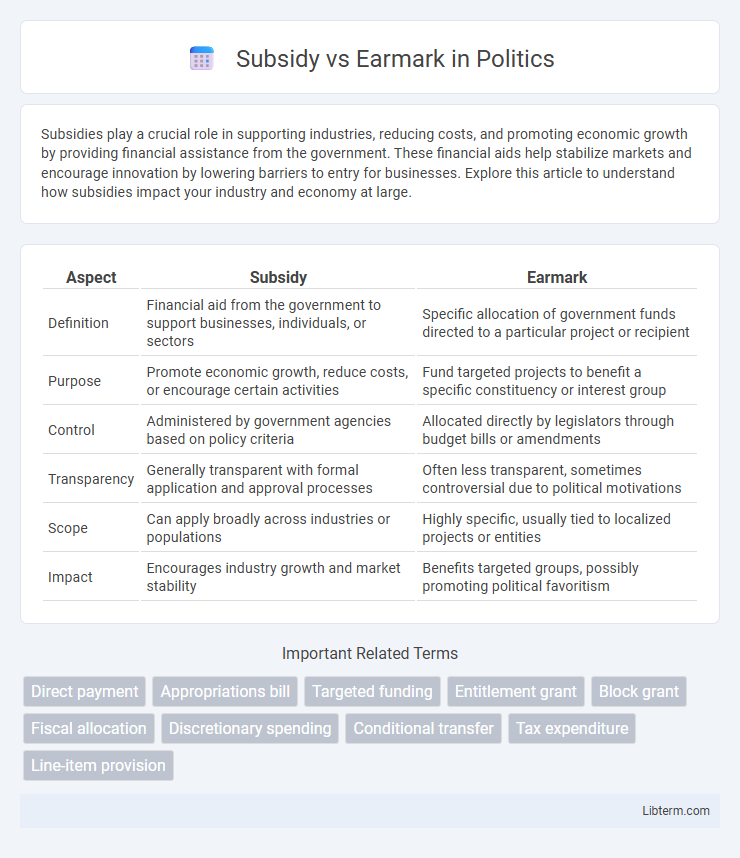
| Aspect | Subsidy | Earmark |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial aid from the government to support businesses, individuals, or sectors | Specific allocation of government funds directed to a particular project or recipient |
| Purpose | Promote economic growth, reduce costs, or encourage certain activities | Fund targeted projects to benefit a specific constituency or interest group |
| Control | Administered by government agencies based on policy criteria | Allocated directly by legislators through budget bills or amendments |
| Transparency | Generally transparent with formal application and approval processes | Often less transparent, sometimes controversial due to political motivations |
| Scope | Can apply broadly across industries or populations | Highly specific, usually tied to localized projects or entities |
| Impact | Encourages industry growth and market stability | Benefits targeted groups, possibly promoting political favoritism |
Introduction to Subsidies and Earmarks
Subsidies are financial assistance programs provided by the government to support businesses, industries, or individuals to promote economic growth and stability. Earmarks refer to designated government funds allocated by legislators for specific projects or purposes within their districts, often bypassing the standard allocation process. Understanding the distinction between subsidies and earmarks is critical for analyzing fiscal policy and public expenditure transparency.
Defining Subsidies: Purpose and Types
Subsidies are financial aids provided by the government to support businesses, reduce production costs, encourage economic activities, and promote social welfare. They include direct subsidies such as grants and tax credits, as well as indirect subsidies like low-interest loans and price supports, each designed to stimulate specific sectors or address market failures. Understanding the purpose and types of subsidies highlights their role in fostering economic development and stabilizing markets.
What Are Earmarks? Key Concepts Explained
Earmarks are provisions in legislation that allocate specific funds to particular projects, organizations, or regions, often bypassing the regular competitive funding process. These directed funds ensure targeted spending, typically in infrastructure, education, or community development, reflecting legislators' priorities. Unlike general subsidies, earmarks are explicitly designated within government budgets to support localized or specialized initiatives.
Historical Background: Subsidies vs Earmarks
Subsidies have a long historical background rooted in government efforts to support industries, agriculture, and economic sectors, dating back to ancient economies where rulers granted financial aid to promote trade and production. Earmarks emerged more recently in the legislative process of the United States, gaining prominence in the mid-20th century as specific provisions within appropriations bills that direct funds to particular projects, often serving local or special interests. Both tools reflect different approaches to fiscal policy, with subsidies broadly aimed at economic stimulation and earmarks focused on targeted spending within government budgets.
Mechanisms: How Subsidies Operate
Subsidies operate through direct financial assistance or tax incentives provided by the government to lower production costs and encourage specific economic activities. These mechanisms reduce expenses for targeted industries or consumers, promoting growth and innovation without specifying exact expenditure areas. Unlike earmarks, which allocate funds for particular projects in legislative bills, subsidies function as broad economic tools influencing market behavior.
Process of Allocating Earmarks
The process of allocating earmarks involves legislators directing specific funds within appropriations bills to particular projects, often based on local or constituent interests. These allocations bypass the usual competitive grant procedures, allowing targeted funding for infrastructure, education, or community development initiatives. Earmark requests undergo review by committee leaders and are incorporated into broader budget legislation, ensuring direct support for designated programs without open application processes.
Economic Impacts: Subsidies Compared to Earmarks
Subsidies directly lower production costs or consumer prices, stimulating economic activity and encouraging innovation within targeted industries, often leading to increased employment and GDP growth. Earmarks allocate government funds to specific projects without necessarily influencing market behavior or efficiency, sometimes resulting in less optimal economic outcomes or misallocation of resources. The economic impact of subsidies tends to be more pronounced and sustained compared to earmarks, which can create localized benefits but lack broad market incentives.
Political Influence on Subsidy and Earmark Decisions
Political influence heavily shapes subsidy and earmark decisions, often reflecting the priorities of influential lawmakers and interest groups rather than purely economic criteria. Subsidies are frequently allocated to industries with strong lobbying power, while earmarks direct federal funds to specific projects favored by political representatives to secure local support and win votes. Consequently, both mechanisms can distort market efficiencies by channeling resources based on political considerations rather than objective need or performance.
Controversies and Criticisms of Both Approaches
Subsidies face criticism for distorting market competition and fostering dependency on government support, often leading to inefficient allocation of resources and budget deficits. Earmarks attract controversy due to their potential to encourage pork-barrel spending, lack of transparency, and favoritism toward specific projects or constituents. Both approaches raise concerns over accountability, with critics arguing that subsidies and earmarks can undermine fair economic practices and democratic decision-making.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Subsidies and Earmarks
Selecting between subsidies and earmarks depends on policy goals and fiscal impact, as subsidies provide broad economic stimulation through financial support to industries or consumers, while earmarks allocate specific budget funds for targeted projects. Subsidies tend to encourage innovation and market growth with less political negotiation, whereas earmarks often address localized needs but may face scrutiny for potential inefficiencies or favoritism. Effective decision-making requires evaluating transparency, economic efficiency, and long-term benefits aligned with government priorities.
Subsidy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com