Resolution defines the clarity and detail of an image, expressed in pixels, that impacts visual quality across devices. Higher resolution ensures sharper and more vivid visuals, essential for photography, display screens, and printing. Explore the full article to understand how resolution affects your digital experiences and how to choose the best settings for your needs.
Table of Comparison
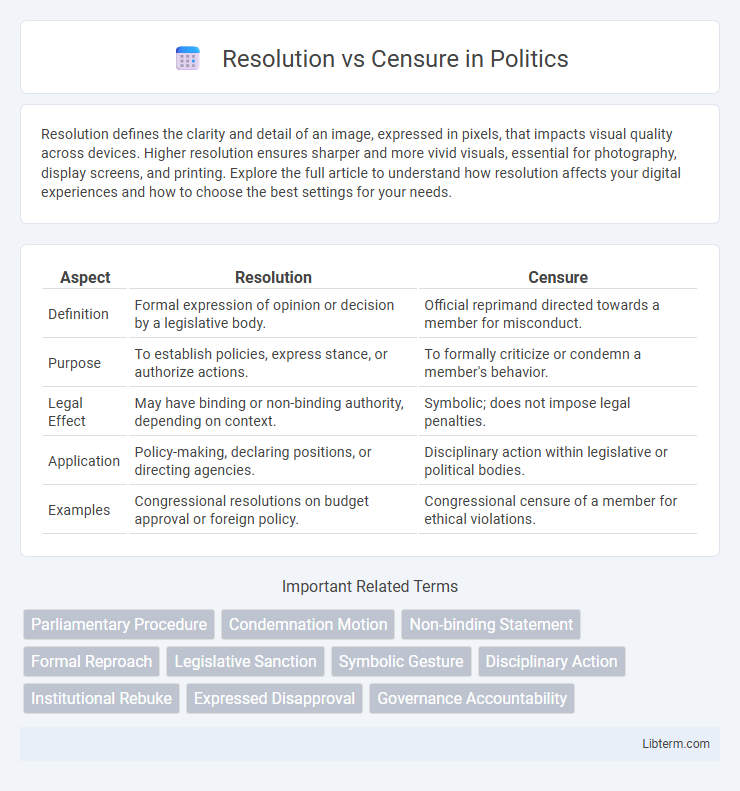
| Aspect | Resolution | Censure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal expression of opinion or decision by a legislative body. | Official reprimand directed towards a member for misconduct. |
| Purpose | To establish policies, express stance, or authorize actions. | To formally criticize or condemn a member's behavior. |
| Legal Effect | May have binding or non-binding authority, depending on context. | Symbolic; does not impose legal penalties. |
| Application | Policy-making, declaring positions, or directing agencies. | Disciplinary action within legislative or political bodies. |
| Examples | Congressional resolutions on budget approval or foreign policy. | Congressional censure of a member for ethical violations. |
Understanding the Concepts: Resolution and Censure
Resolution refers to a formal decision or expression adopted by a governing body or organization to address specific issues or actions, often serving as a declaration of intent or policy. Censure involves an official reprimand or condemnation directed at a member, typically indicating disapproval of behavior or decisions without removing the individual from office. Understanding the distinction between resolution as a proactive measure and censure as a punitive action is essential in comprehending governance and legislative processes.
Definition of Resolution in Governance
A resolution in governance refers to a formal expression of opinion, will, or intent voted on by an official body, such as a board or legislative assembly, to address specific issues or authorize actions. It functions as a binding decision that guides organizational policies, legal frameworks, or governmental procedures. Resolutions differ from censures by their constructive purpose, aiming to establish directives rather than reprimanding members for misconduct.
What Does Censure Mean in Political Contexts?
Censure in political contexts refers to a formal statement of disapproval issued by a legislative body or political organization against a member for misconduct or violation of rules. Unlike a resolution, which may express positions or make recommendations, censure carries a reprimanding tone intended to publicly condemn and warn the individual without removing them from office. It serves as a disciplinary action that can impact a politician's reputation and influence within the governing institution.
Key Differences Between Resolution and Censure
Resolution is a formal expression of opinion or intention adopted by a deliberative body to address specific issues or propose actions, while censure is a formal statement of disapproval directed toward an individual or entity for misconduct. Resolutions often serve policy-making or procedural purposes, whereas censure functions as a disciplinary measure reflecting ethical or behavioral violations. The key differences lie in their intent, scope, and consequences: resolutions aim to guide or influence decisions, censure aims to reprimand and signal accountability.
Historical Examples of Resolutions
Historical examples of resolutions include the United Nations General Assembly Resolution 194, which addressed the rights of Palestinian refugees in 1948, setting a precedent for international peace efforts. The U.S. Congress's Joint Resolution for War against Japan in 1941 exemplifies a formal legislative decision authorizing military action. These resolutions serve as formal expressions of intent or policy adopted by legislative or international bodies, distinct from censures that criticize or reprimand individuals or groups.
Notable Instances of Censure
Notable instances of censure include the 1832 censure of President Andrew Jackson by the U.S. Senate over his removal of federal deposits from the Bank of the United States, reflecting congressional disapproval without legal consequences. In 1983, Senator McCarthy faced censure for conduct deemed unbecoming of a senator, highlighting the Senate's use of censure to uphold ethical standards. More recently, in 2010, Senator David Vitter was censured by the Louisiana legislature for ethical violations, demonstrating state-level applications of censure as a formal reprimand.
Legal and Procedural Implications
Resolution and censure carry distinct legal and procedural implications within legislative bodies. A resolution is a formal expression of the opinion or decision of a legislative assembly, often non-binding and used to direct internal operations or state policy, whereas censure is a formal condemnation of a member's behavior, typically carrying reputational consequences without legal penalties. Resolutions require a procedural vote to pass and may influence policy, while censure demands a higher threshold of votes and serves as an official reprimand affecting the member's standing and privileges within the body.
Impact on Individuals and Institutions
Resolution acts as a formal expression of collective stance by institutions, often leading to policy changes or reinforcing organizational values, which can enhance institutional credibility but rarely imposes direct penalties on individuals. Censure directly targets individuals, publicly condemning behavior deemed inappropriate, potentially damaging personal reputations and careers while signaling institutional intolerance of misconduct. The impact on institutions varies; resolutions demonstrate proactive governance and commitment to issues, whereas censures can expose underlying conflicts or governance challenges.
Public Perception: Resolution vs Censure
A resolution typically signals official approval or agreement and fosters positive public perception by demonstrating unity and proactive governance. In contrast, censure acts as a formal reprimand that highlights misconduct or disapproval, often leading to negative public sentiment and reduced trust in the individual or entity censured. Public perception is shaped by the clarity and consequences of each action, where resolutions are viewed as constructive engagements and censures as accountability measures.
Choosing the Right Approach: Resolution or Censure?
Choosing the right approach between a resolution and censure depends on the severity and nature of the issue at hand. Resolutions are formal statements expressing collective decisions or intentions, suitable for policy decisions or endorsements without punitive intent. Censure serves as a formal reprimand targeting specific misconduct, making it appropriate when the goal is to publicly address and condemn unacceptable behavior within an organization or governing body.
Resolution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com