Federalism divides power between national and state governments, ensuring a balance that protects local autonomy while maintaining national unity. This system allows states to tailor policies to their unique needs while adhering to overarching federal laws. Explore the rest of the article to understand how federalism impacts your daily life and shapes governance in the United States.
Table of Comparison
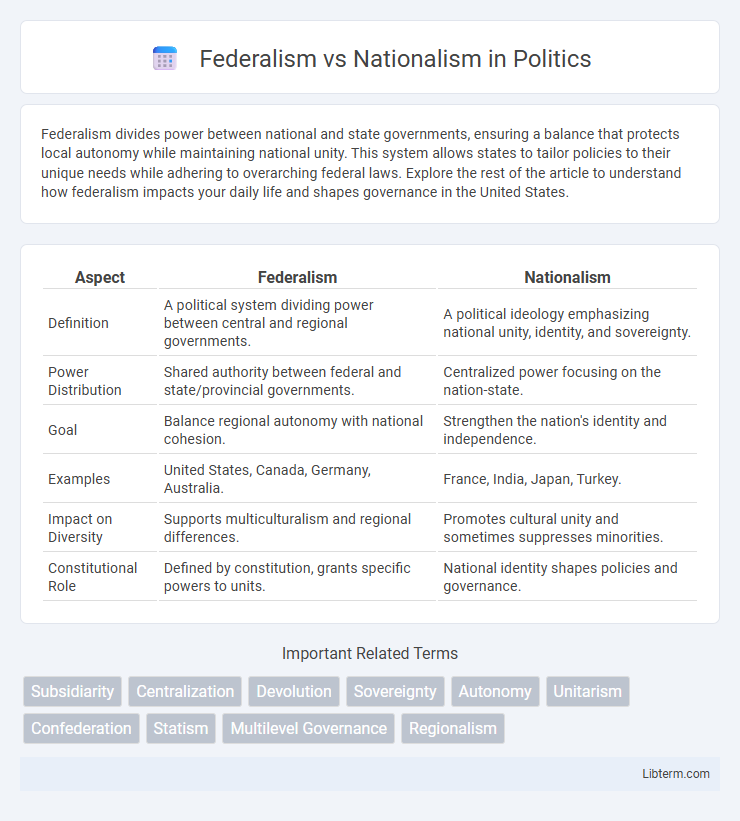
| Aspect | Federalism | Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A political system dividing power between central and regional governments. | A political ideology emphasizing national unity, identity, and sovereignty. |
| Power Distribution | Shared authority between federal and state/provincial governments. | Centralized power focusing on the nation-state. |
| Goal | Balance regional autonomy with national cohesion. | Strengthen the nation's identity and independence. |
| Examples | United States, Canada, Germany, Australia. | France, India, Japan, Turkey. |
| Impact on Diversity | Supports multiculturalism and regional differences. | Promotes cultural unity and sometimes suppresses minorities. |
| Constitutional Role | Defined by constitution, grants specific powers to units. | National identity shapes policies and governance. |
Understanding Federalism: Key Principles
Federalism is a political system that divides power between a central government and regional governments, allowing both to operate independently in certain policy areas. Key principles include the distribution of authority, the protection of regional diversity, and the creation of a system of checks and balances to prevent any single level of government from becoming too powerful. This structure promotes cooperation and conflict resolution between different levels of government while ensuring local autonomy within a unified nation-state.
Defining Nationalism: Core Concepts
Nationalism centers on the belief that a shared identity, culture, language, or history should unite a people under a sovereign state. It emphasizes national self-determination, prioritizing the interests and autonomy of the nation above regional or global considerations. This ideology often fosters collective pride and political unity, influencing state policies and international relations.
Historical Evolution of Federalism
Federalism evolved as a political system balancing power between central authorities and regional governments, with roots tracing back to the Articles of Confederation in the United States and the Federalist Papers advocating for a stronger union in the 18th century. The historical development of federalism also includes significant influences from Swiss and Canadian governance models, which illustrated diverse approaches to power-sharing and autonomy within a single nation-state. This evolution highlights federalism's role in managing the tensions between national integrity and regional diversity, shaping modern constitutional designs worldwide.
The Rise and Impact of Nationalist Movements
Nationalist movements surged during the 19th and 20th centuries, emphasizing the sovereignty and unity of a distinct nation, often challenging federal structures that divided power between central and regional governments. These movements fueled the creation of nation-states, such as Germany and Italy, by consolidating fragmented territories under a single national identity. The impact of nationalism led to the redefinition of borders, intensified conflicts over self-determination, and a shift from multi-ethnic empires to centralized nation-states focused on homogenous cultural and political cohesion.
Federalism vs Nationalism: Fundamental Differences
Federalism is a political system where power is constitutionally divided between a central authority and constituent political units, allowing regional governments to exercise autonomy in specific areas. Nationalism centers on the promotion of a unified national identity and the prioritization of the sovereignty and interests of a nation-state above regional or local entities. The fundamental difference lies in federalism's emphasis on shared governance and decentralized power, whereas nationalism emphasizes unity, centralized authority, and the primacy of national interests.
Advantages and Challenges of Federal Systems
Federal systems offer advantages such as enhanced regional autonomy, allowing diverse populations to self-govern and address local needs more effectively, which often leads to increased political stability and citizen participation. They enable the distribution of power across multiple levels of government, reducing the risk of authoritarian rule and fostering innovation through policy experimentation among states or provinces. Challenges include potential conflicts between central and regional authorities, administrative complexity, and uneven resource distribution that can exacerbate inequalities and hamper national unity.
Pros and Cons of Nationalist Policies
Nationalist policies often promote strong centralized governance, which can enhance national unity and effective decision-making on issues like defense and economic strategy. However, such policies may suppress regional diversity and minority rights, leading to social fragmentation and resistance within diverse populations. The emphasis on national sovereignty can also hinder international cooperation and globalization efforts, potentially limiting economic growth and diplomatic relations.
Federalism and Nationalism in Contemporary Politics
Federalism in contemporary politics emphasizes the distribution of power between central and regional governments, enabling diverse communities to maintain autonomy while fostering unity. Nationalism centers on promoting a collective national identity and sovereignty, often prioritizing centralized authority to protect cultural heritage and political independence. The balance between federalism and nationalism shapes governance structures and influences policy decisions in multi-ethnic and multi-regional states.
Case Studies: Countries Shaped by Federalism and Nationalism
Countries like the United States and Germany exemplify federalism through their decentralized governance structures that allocate significant power to subnational entities, fostering regional autonomy and diversity. In contrast, France and Japan demonstrate nationalism with centralized governance that emphasizes national unity, centralized policy-making, and cultural homogeneity. These case studies highlight how federalism supports regional identities and local governance, while nationalism prioritizes a cohesive national identity and centralized control.
The Future of Governance: Balancing Federalism and Nationalism
The future of governance hinges on balancing federalism's emphasis on regional autonomy with nationalism's focus on unified national identity, creating resilient political structures. Federalism fosters decentralized decision-making, allowing diverse communities to maintain cultural distinctiveness, while nationalism promotes collective goals and social cohesion across the entire state. Effective governance models will integrate both principles, ensuring local empowerment while sustaining national unity in increasingly complex global and domestic contexts.
Federalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com