Isolationism focuses on a nation's deliberate choice to minimize political, economic, and military involvement with other countries to protect its own interests and sovereignty. This approach often leads to reduced foreign conflicts and an emphasis on self-reliance. Explore the full article to understand how isolationism impacts global relations and your country's future.
Table of Comparison
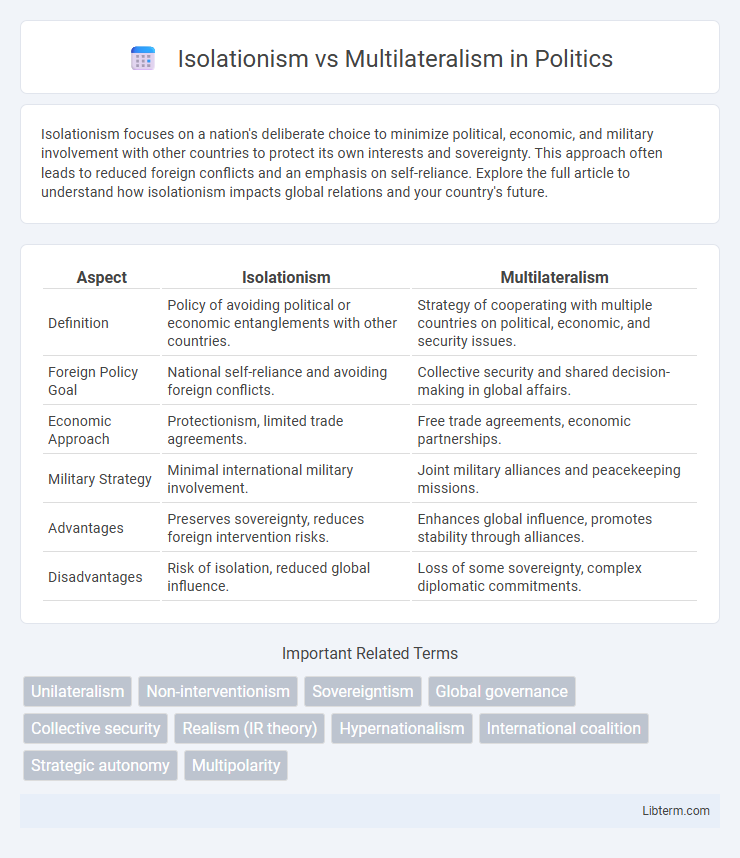
| Aspect | Isolationism | Multilateralism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Policy of avoiding political or economic entanglements with other countries. | Strategy of cooperating with multiple countries on political, economic, and security issues. |
| Foreign Policy Goal | National self-reliance and avoiding foreign conflicts. | Collective security and shared decision-making in global affairs. |
| Economic Approach | Protectionism, limited trade agreements. | Free trade agreements, economic partnerships. |
| Military Strategy | Minimal international military involvement. | Joint military alliances and peacekeeping missions. |
| Advantages | Preserves sovereignty, reduces foreign intervention risks. | Enhances global influence, promotes stability through alliances. |
| Disadvantages | Risk of isolation, reduced global influence. | Loss of some sovereignty, complex diplomatic commitments. |
Understanding Isolationism: Definition and Core Principles
Isolationism is a foreign policy strategy centered on minimizing a nation's involvement in international alliances, conflicts, and organizations to prioritize domestic interests and sovereignty. Core principles include non-interventionism, avoidance of entangling alliances, and reduced reliance on global commitments. This approach emphasizes self-sufficiency, national security, and economic independence by limiting external political or military engagements.
The Roots and History of Isolationism in Global Politics
Isolationism in global politics traces back to the early 19th century, notably manifested in the United States' Monroe Doctrine of 1823, which aimed to limit European intervention in the Western Hemisphere. This policy of non-involvement in foreign alliances and conflicts was reinforced through the interwar period following World War I, as nations sought to avoid entanglements that led to widespread devastation. Isolationism's historical roots are deeply connected to the desire for national sovereignty, economic self-sufficiency, and the prevention of external influences disrupting domestic stability.
Exploring Multilateralism: Key Features and Objectives
Multilateralism involves multiple countries working collaboratively on global issues through international institutions like the United Nations and the World Trade Organization to foster cooperation and peace. Key features include shared decision-making, collective security, and adherence to international law, aiming to address transnational challenges such as climate change, trade regulation, and conflict resolution. Its primary objectives are to promote stability, mutual benefit, and the prevention of unilateral actions that could destabilize global order.
The Evolution of Multilateralism in International Relations
The evolution of multilateralism in international relations reflects a strategic shift from isolationist policies toward cooperative engagement among multiple nations to address global challenges. Key developments include the establishment of institutions such as the United Nations, World Trade Organization, and regional alliances like the European Union, which facilitate collective decision-making, conflict resolution, and economic integration. This transition underscores the increasing recognition that complex global issues--ranging from security to climate change--require collaborative frameworks beyond unilateral or bilateral actions.
Key Differences: Isolationism vs Multilateralism
Isolationism centers on a nation's deliberate avoidance of political or economic entanglements with other countries to prioritize self-sufficiency and reduce foreign influence. Multilateralism involves multiple countries collaborating through international institutions and agreements to address global challenges and promote collective security. Key differences include their approaches to foreign policy engagement, with isolationism favoring unilateral decision-making and minimal external commitments, while multilateralism emphasizes cooperation, diplomacy, and shared responsibilities.
Economic Impacts: Trade, Globalization, and Policy Outcomes
Isolationism restricts international trade and limits access to global markets, often resulting in slower economic growth and reduced competitiveness. Multilateralism promotes trade liberalization and economic integration, enhancing globalization through collaborative policies that encourage market access and investment flows. Countries embracing multilateralism typically experience increased economic diversification and stronger policy outcomes driven by cooperative international frameworks.
Security and Defense: Alliances Versus Autonomy
Isolationism emphasizes national sovereignty and self-reliance in security and defense, avoiding entangling alliances to maintain strategic autonomy and reduce external commitments. Multilateralism promotes collective security through alliances like NATO and the UN, leveraging shared defense responsibilities to deter threats and enhance global stability. Balancing autonomy with alliance obligations impacts defense budgets, interoperability, and response effectiveness in addressing complex international security challenges.
Case Studies: Historical Examples of Isolationist and Multilateral Strategies
The United States' pre-World War II isolationism, characterized by the Neutrality Acts and reluctance to join international alliances, contrasts sharply with its post-World War II multilateral approach through institutions like the United Nations and NATO. Japan's Meiji Restoration era exemplified isolationism by limiting foreign influence to preserve sovereignty, whereas the European Union represents a comprehensive multilateral framework fostering economic integration and collective decision-making. These historical cases highlight how isolationist policies prioritized national sovereignty and non-intervention, while multilateral strategies enhanced cooperation, security, and global governance.
Contemporary Challenges: Isolationism and Multilateralism in the 21st Century
Isolationism in the 21st century often leads to diminished global influence and missed opportunities in addressing transnational issues such as climate change, pandemics, and cybersecurity threats. Multilateralism fosters collaboration through international organizations like the United Nations, World Health Organization, and Paris Agreement, enabling collective responses to complex global challenges. The tension between national sovereignty and global cooperation remains a central debate as countries balance domestic interests with the necessity of coordinated action in an interconnected world.
The Future Debate: Balancing National Interests and Global Cooperation
The future debate on isolationism versus multilateralism centers on balancing national sovereignty with the demands of global cooperation in addressing transnational issues such as climate change, security threats, and economic stability. Nations face increasing pressure to protect domestic interests while participating in international organizations like the United Nations, World Trade Organization, and multilateral treaties that promote collective action. Strategic diplomacy and adaptive policies will shape how countries navigate this tension, influencing global governance and the effectiveness of international cooperation in the coming decades.
Isolationism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com