Open seat dynamics significantly influence electoral outcomes by creating highly competitive races without an incumbent advantage, leading to increased voter engagement and campaign intensity. Candidates must focus on mobilizing their base, clearly communicating policy positions, and capitalizing on emerging voter concerns to secure a win. Explore the rest of this article to understand how open seat dynamics shape political strategies and election results.
Table of Comparison
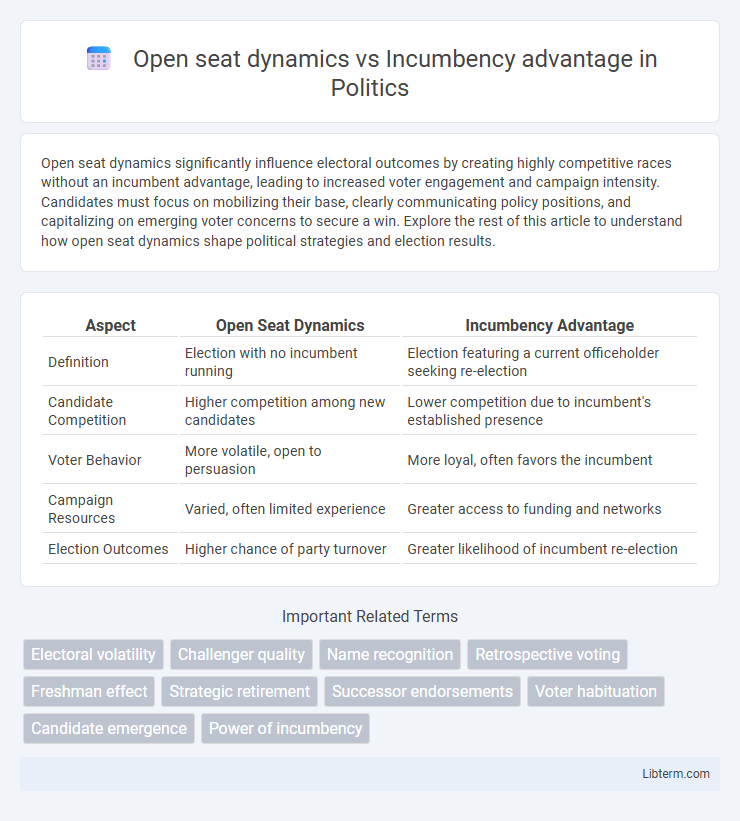
| Aspect | Open Seat Dynamics | Incumbency Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Election with no incumbent running | Election featuring a current officeholder seeking re-election |
| Candidate Competition | Higher competition among new candidates | Lower competition due to incumbent's established presence |
| Voter Behavior | More volatile, open to persuasion | More loyal, often favors the incumbent |
| Campaign Resources | Varied, often limited experience | Greater access to funding and networks |
| Election Outcomes | Higher chance of party turnover | Greater likelihood of incumbent re-election |
Understanding Open Seat Dynamics
Open seat dynamics significantly impact electoral competition by eliminating the incumbency advantage, which typically includes name recognition, established donor networks, and existing constituent relationships. Without an incumbent running, candidates face a more level playing field, often resulting in increased campaign spending and higher voter engagement due to the perceived opportunity for change. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for political strategists, as open seats often attract a larger and more diverse candidate pool, intensifying primary and general election contests.
Defining Incumbency Advantage
Incumbency advantage refers to the electoral edge enjoyed by current officeholders due to name recognition, established voter base, and easier access to campaign finance. In contrast, open seat dynamics involve contests where no incumbent is running, often leading to more competitive elections because candidates lack these built-in advantages. The incumbency advantage significantly raises re-election rates, with empirical data showing that incumbents win approximately 90% of their races in U.S. congressional elections.
Historical Trends: Open Seats vs. Incumbent Races
Historical trends reveal that open seat races tend to be more competitive and volatile compared to incumbent races, where the incumbency advantage often leads to higher reelection rates. Data from multiple election cycles show incumbents winning approximately 80-90% of the time, underscoring name recognition, established voter base, and access to resources. Open seats, lacking these advantages, frequently result in closer contests and greater opportunities for party turnover.
Candidate Recruitment and Party Strategies
Open seat dynamics increase competition as no incumbent holds the position, prompting parties to aggressively recruit high-quality candidates to capitalize on the opportunity. Incumbency advantage often discourages strong challengers, leading parties to allocate fewer resources towards recruitment and instead focus on supporting the sitting officeholder. Strategic decisions hinge on these dynamics, with parties prioritizing open seats for candidate development and investing in incumbent defense where advantages are significant.
Voter Perception and Election Outcomes
Open seat races often lead to heightened voter engagement due to the absence of an incumbent, which can result in more competitive elections and unpredictable outcomes. Incumbency advantage typically provides candidates with greater name recognition, established donor networks, and a track record that influences voter perception positively. Consequently, incumbents usually experience higher re-election rates, while open seats create opportunities for party turnover and shifts in voter allegiance.
Fundraising Patterns: Incumbents vs. Newcomers
Open seat elections typically generate a more level playing field in fundraising as newcomers attract extensive financial support seeking to capitalize on the lack of an incumbent. Incumbents benefit from established donor networks and name recognition, which often result in larger, more consistent campaign contributions compared to challengers. Fundraising patterns indicate incumbents maintain a significant advantage through early and sustained fundraising efforts, while newcomers rely heavily on momentum and initial fundraising surges during open seat contests.
Impact of Name Recognition
Open seat dynamics significantly reduce the impact of name recognition compared to incumbency advantage, where established politicians benefit from widespread voter familiarity. Incumbents leverage their existing public profiles, media exposure, and constituent services to maintain strong name recognition, which often translates into higher voter trust and electoral success. In open seat races, candidates must invest more in building name recognition from the ground up, making campaign strategies centered on visibility and outreach critical for gaining voter support.
Policy Continuity and Change Possibilities
Open seat dynamics create greater opportunities for policy change as new candidates can introduce fresh agendas without the constraints of an existing officeholder's record, enhancing the potential for shifts in legislative priorities. Incumbency advantage fosters policy continuity through established name recognition, donor networks, and constituent relationships that support the reelection of sitting officials likely to maintain existing policy frameworks. The presence of an incumbent typically reduces the likelihood of dramatic policy shifts, while open seats increase electoral competition and raise the prospects for innovative or divergent policy initiatives.
Media Coverage Differences
Open seat elections generate more balanced media coverage as no candidate benefits from incumbent recognition, leading to heightened voter focus on candidate policies and backgrounds. Incumbency advantage results in disproportionate media attention favoring the sitting official due to established name recognition and access to press resources. This disparity influences voter perceptions, reinforcing the incumbent's visibility while often marginalizing challengers in media narratives.
Predicting Future Electoral Success
Open seat dynamics significantly increase electoral competitiveness by removing the advantage of incumbency, making voter preferences and candidate quality critical predictors of success. Incumbency advantage offers higher name recognition, established fundraising networks, and proven voter support, often leading to predictable re-election outcomes. Predictive models for future electoral success weigh these factors, emphasizing candidate strength and district partisanship in open seats, while incumbent performance metrics dominate forecasts in contested races.
Open seat dynamics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com