Judicial intervention occurs when courts step in to resolve disputes or enforce laws in cases where other branches of government or entities have failed to act effectively. It ensures that legal rights are protected and that justice prevails in complex or controversial situations. Explore the rest of this article to understand how judicial intervention impacts your rights and the legal system.
Table of Comparison
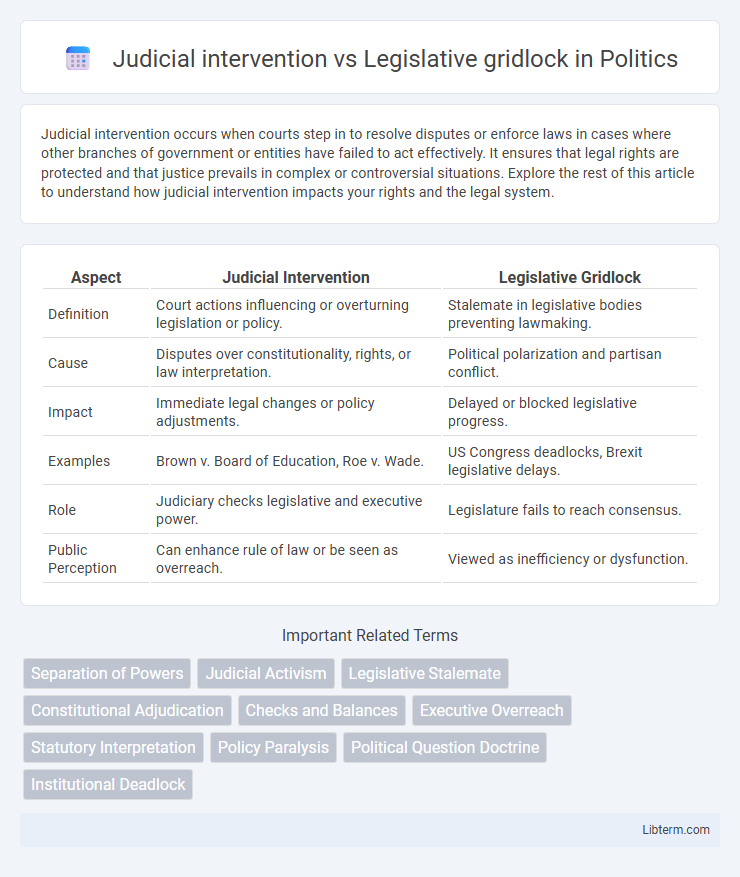
| Aspect | Judicial Intervention | Legislative Gridlock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Court actions influencing or overturning legislation or policy. | Stalemate in legislative bodies preventing lawmaking. |
| Cause | Disputes over constitutionality, rights, or law interpretation. | Political polarization and partisan conflict. |
| Impact | Immediate legal changes or policy adjustments. | Delayed or blocked legislative progress. |
| Examples | Brown v. Board of Education, Roe v. Wade. | US Congress deadlocks, Brexit legislative delays. |
| Role | Judiciary checks legislative and executive power. | Legislature fails to reach consensus. |
| Public Perception | Can enhance rule of law or be seen as overreach. | Viewed as inefficiency or dysfunction. |
Understanding Judicial Intervention
Judicial intervention occurs when courts step in to resolve disputes or enforce laws due to a failure or deadlock in the legislative process, often ensuring constitutional compliance and protection of individual rights. It acts as a critical check within the separation of powers, especially during legislative gridlock where legislative bodies cannot pass necessary laws or policies. Understanding judicial intervention highlights the courts' role in maintaining legal stability and upholding democratic principles in scenarios where legislative action stalls.
Defining Legislative Gridlock
Legislative gridlock occurs when political parties or branches of government are unable to reach consensus, resulting in a stalemate that prevents the passage of laws. This impasse often arises from polarization, conflicting interests, or institutional checks and balances, which slow down or halt legislative processes. Judicial intervention frequently addresses these deadlocks by interpreting laws or constitutional provisions to resolve disputes and ensure governance continuity.
Historical Context: Courts and Congress
Judicial intervention has historically risen during periods of legislative gridlock when Congress fails to address critical issues, prompting courts to interpret constitutional mandates to fill governance gaps. The U.S. Supreme Court's landmark rulings, such as Brown v. Board of Education and Citizens United v. FEC, exemplify judiciary responses to legislative stalemates on civil rights and campaign finance regulation. Congressional gridlock often results from partisan polarization, amplifying the courts' role in shaping national policy and maintaining institutional balance.
Causes of Legislative Inaction
Legislative inaction often stems from partisan polarization, where conflicting ideological positions prevent consensus on policy issues. The complexity of interests among diverse stakeholders contributes to stalemates, as legislators struggle to balance competing demands from their constituencies. Institutional factors, such as procedural rules and filibuster mechanisms, further exacerbate gridlock by allowing minority factions to block legislation.
Judicial Responses to Political Stalemate
Judicial intervention often emerges as a critical mechanism to resolve legislative gridlock when elected officials fail to enact necessary policies, particularly in constitutional or civil rights issues. Courts interpret laws and can mandate government action, providing a judicial check that ensures political stalemates do not paralyze governance or infringe on citizens' rights. This judicial responsiveness reinforces the balance of powers by upholding legal standards amid partisan deadlock.
Consequences of Judicial Overreach
Judicial overreach often results in the judiciary invalidating legislation beyond constitutional limits, leading to significant disruptions in the balance of power. This can undermine legislative authority, creating constitutional uncertainty and weakening democratic processes by circumventing elected lawmakers. Consequences include policy instability, erosion of public trust in institutions, and potential conflicts between branches of government.
Balancing Powers: Separation of Authority
Judicial intervention addresses legislative gridlock by ensuring laws align with constitutional principles, maintaining the balance of powers among branches. Courts interpret statutes and can invalidate legislative actions that overstep legal boundaries, preserving separation of authority. This dynamic prevents any one branch from overpowering others, safeguarding democratic governance.
Landmark Cases of Judicial Intervention
Landmark cases of judicial intervention, such as Brown v. Board of Education and Roe v. Wade, demonstrate the Supreme Court's role in resolving legislative gridlock by addressing critical social and constitutional issues. These decisions exemplify how judicial review can override legislative hesitation, ensuring protection of civil rights and liberties when Congress fails to act. Judicial intervention in landmark cases often serves as a catalyst for legal and social change, balancing the checks and balances within the U.S. government.
Public Perception: Courts vs. Legislature
Public perception often views judicial intervention as a necessary corrective measure when legislative gridlock prevents effective governance, fostering trust in courts to uphold constitutional principles. Conversely, prolonged legislative stalemates may erode confidence in elected officials, highlighting frustration with political partisanship and inefficacy. Surveys indicate that citizens tend to support judicial action in high-profile cases, especially when legislatures fail to address pressing social or economic issues.
Future Prospects: Reform and Collaboration
Judicial intervention in resolving legislative gridlock presents a critical mechanism for upholding constitutional principles amid political stalemates, but its future efficacy depends on clear guidelines limiting judicial overreach. Legislative reforms aimed at enhancing transparency, accountability, and bipartisan cooperation hold promise for reducing gridlock and mitigating the need for frequent judicial involvement. Collaborative frameworks integrating judicial insights and legislative innovation are essential to balance separation of powers while promoting effective governance.
Judicial intervention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com