Totalitarianism is a political system characterized by centralized control, where the government exerts complete authority over public and private life, suppressing dissent and individual freedoms. This regime often employs propaganda, surveillance, and state-controlled media to maintain power and manipulate the population. Discover how totalitarianism shapes societies and influences history by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
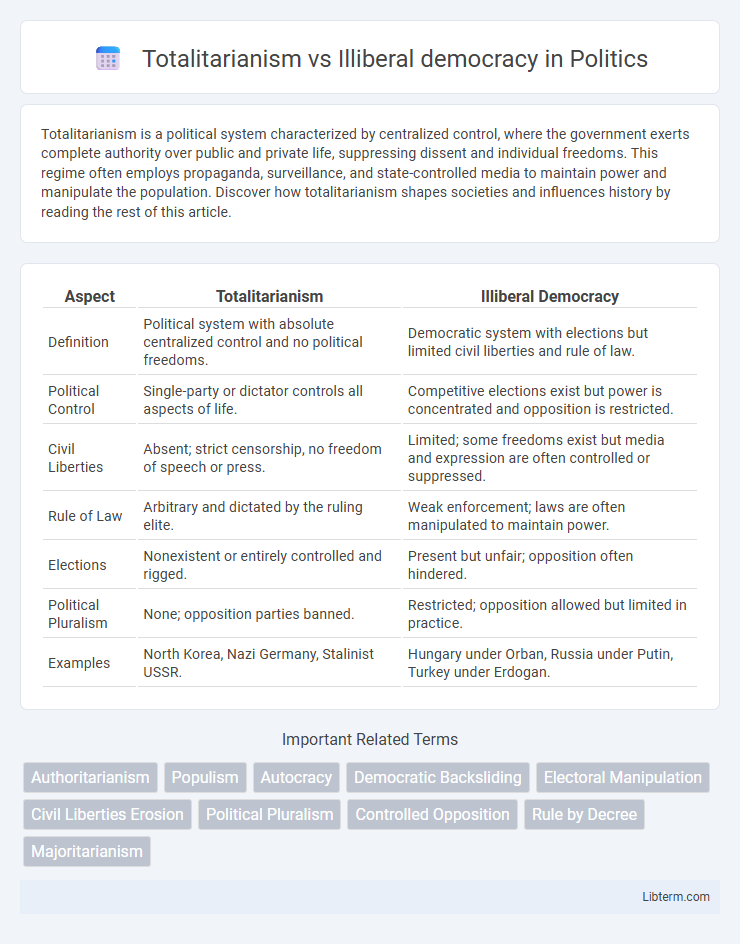
| Aspect | Totalitarianism | Illiberal Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political system with absolute centralized control and no political freedoms. | Democratic system with elections but limited civil liberties and rule of law. |
| Political Control | Single-party or dictator controls all aspects of life. | Competitive elections exist but power is concentrated and opposition is restricted. |
| Civil Liberties | Absent; strict censorship, no freedom of speech or press. | Limited; some freedoms exist but media and expression are often controlled or suppressed. |
| Rule of Law | Arbitrary and dictated by the ruling elite. | Weak enforcement; laws are often manipulated to maintain power. |
| Elections | Nonexistent or entirely controlled and rigged. | Present but unfair; opposition often hindered. |
| Political Pluralism | None; opposition parties banned. | Restricted; opposition allowed but limited in practice. |
| Examples | North Korea, Nazi Germany, Stalinist USSR. | Hungary under Orban, Russia under Putin, Turkey under Erdogan. |
Understanding Totalitarianism: Definition and Origins
Totalitarianism is a political system characterized by centralized control, absolute authority of the state, and suppression of individual freedoms, originating in the early 20th century with regimes like Nazi Germany and Stalinist Soviet Union. Its definition emphasizes an all-encompassing ideology that seeks to regulate both public and private life, distinguishing it from illiberal democracy, which retains formal elections but restricts political pluralism and civil liberties. Understanding totalitarianism requires analyzing historical contexts where authoritarian regimes employed propaganda, state terror, and mass mobilization to maintain power and eradicate opposition.
What Is Illiberal Democracy? Key Characteristics
Illiberal democracy is a governing system where elections occur, but citizens have limited civil liberties and the rule of law is weak. Key characteristics include restricted press freedom, diminished judicial independence, and curtailed political opposition, undermining true democratic accountability and transparency. This contrasts with totalitarianism, which exercises absolute state control over all aspects of life without meaningful electoral processes.
Historical Contexts: Rise of Totalitarian and Illiberal Regimes
Totalitarianism emerged prominently in the early 20th century with regimes like Nazi Germany and Stalinist Soviet Union, marked by absolute state control and suppression of dissent. Illiberal democracies gained traction in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, exemplified by countries such as Hungary and Turkey, where electoral processes exist but civil liberties and checks on power are undermined. Both systems reflect historical responses to political instability, economic crises, and societal fragmentation, shaping their distinctive forms of governance and control mechanisms.
Political Structures: Power Distribution and Control
Totalitarianism centralizes absolute power in a single party or leader, employing extensive state control over all political, social, and economic aspects to eliminate opposition and enforce uniform ideology. Illiberal democracies maintain electoral processes and some pluralism but concentrate power through weakened institutions, limited checks and balances, and constrained civil liberties, resulting in authoritarian tendencies within a nominally democratic framework. The key distinction lies in the degree of political repression and institutional autonomy, with totalitarian regimes exercising comprehensive domination and illiberal democracies allowing partial but controlled political competition.
Restrictions on Civil Liberties: A Comparative Analysis
Totalitarianism imposes extreme restrictions on civil liberties, including widespread censorship, surveillance, and the eradication of political opposition to maintain absolute state control. Illiberal democracy, while allowing some electoral processes, systematically undermines civil rights through limitations on press freedom, curtailment of judicial independence, and suppression of dissenting voices. Both regimes restrict freedoms, but totalitarianism exerts more pervasive and direct control over all aspects of public and private life, unlike illiberal democracies which disguise repression within a veneer of electoral legitimacy.
Role of Elections and Political Participation
Elections in totalitarian regimes function as controlled mechanisms to legitimize the ruling party without genuine political competition, severely limiting citizen participation and dissent. In illiberal democracies, elections occur regularly but often lack fairness, transparency, and equal competition, constraining the true expression of voter choice and undermining democratic accountability. Political participation in both systems is restricted, but illiberal democracies may allow limited opposition, whereas totalitarianism suppresses any form of political pluralism or organized resistance.
State Propaganda vs. Media Manipulation
State propaganda in totalitarian regimes is centralized, orchestrated by the government to control information flow, suppress dissent, and enforce ideological conformity. In contrast, media manipulation in illiberal democracies involves the strategic use of biased reporting, censorship, and disinformation to influence public opinion while maintaining a facade of pluralism. Both systems undermine independent journalism, but totalitarian propaganda exerts absolute control, whereas illiberal democracies distort media landscapes to consolidate power subtly.
Opposition: Repression and Tolerance
Totalitarianism enforces strict repression of opposition through surveillance, censorship, and elimination of dissent, ensuring absolute control over political and social life. Illiberal democracy allows limited opposition but often suppresses it through legal restrictions, media manipulation, and harassment, maintaining authoritarian tendencies under a nominally democratic framework. Both systems undermine genuine political competition, but illiberal democracy retains a facade of tolerance that can mask systemic repression.
Social and Economic Impacts of Governance Styles
Totalitarianism enforces strict government control over social behavior and economic activity, often resulting in suppressed individual freedoms, centralized economic planning, and limited market innovation. Illiberal democracies maintain electoral processes but restrict civil liberties and political pluralism, leading to social inequality and inconsistent economic policies that hinder sustainable growth. Both governance styles destabilize social trust and economic development but differ in the degree of authoritarian control and public participation in decision-making.
Global Trends: The Future of Totalitarianism and Illiberal Democracy
Global trends indicate a resurgence of totalitarian practices in authoritarian regimes, where centralized control suppresses political pluralism and civil liberties. Illiberal democracies continue to expand, characterized by elected leaders undermining democratic institutions, manipulating electoral processes, and restricting media freedoms. This evolving landscape challenges international norms, signaling a potential shift towards hybrid regimes blending authoritarian tactics with electoral legitimacy.
Totalitarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com