Appointed individuals play a crucial role in shaping organizational success by assuming key responsibilities and decision-making authority. Their expertise and dedication ensure that strategic goals are met efficiently, fostering growth and stability. Discover how appointed positions influence your industry and why understanding their impact is essential by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
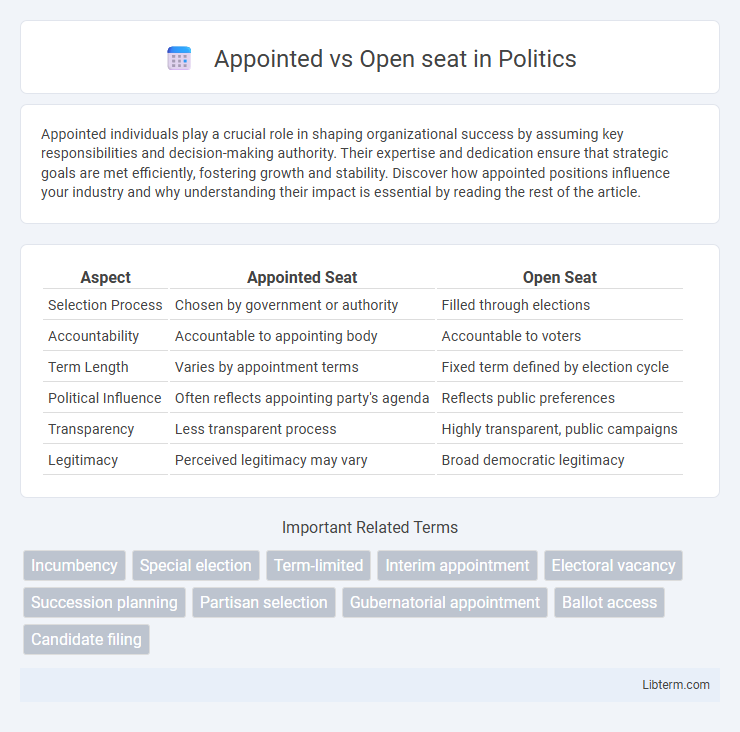
| Aspect | Appointed Seat | Open Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Selection Process | Chosen by government or authority | Filled through elections |
| Accountability | Accountable to appointing body | Accountable to voters |
| Term Length | Varies by appointment terms | Fixed term defined by election cycle |
| Political Influence | Often reflects appointing party's agenda | Reflects public preferences |
| Transparency | Less transparent process | Highly transparent, public campaigns |
| Legitimacy | Perceived legitimacy may vary | Broad democratic legitimacy |
Understanding Appointed and Open Seats
Appointed seats refer to positions filled by individuals selected through a formal nomination or appointment process, often by government officials or organizational leaders, rather than by public election. Open seats occur when no incumbent is running for reelection, creating competitive opportunities for new candidates in electoral races. Understanding the distinction helps clarify electoral dynamics and the strategic approaches candidates use in campaigns.
Key Differences Between Appointed and Open Seats
Appointed seats are filled by a designated authority without a public vote, often to quickly address vacancies or ensure expertise in a specific role. Open seats, conversely, are contested positions where candidates compete in elections, allowing voters direct influence on representation. The key difference lies in the selection method: appointment is an administrative decision, while open seats rely on democratic electoral processes.
Advantages of Appointed Seats
Appointed seats offer greater stability and continuity in organizational decision-making by reducing electoral unpredictability and ensuring consistent policy implementation. They allow for the selection of candidates based on expertise and alignment with strategic goals, enhancing governance effectiveness. This system minimizes political polarization by reducing the influence of populist pressures often seen in open-seat elections.
Benefits of Open Seats
Open seats in elections offer significant benefits by fostering competitive races that can increase voter engagement and turnout. Candidates running for open seats often benefit from a level playing field, as there is no incumbent advantage, leading to more diverse options for voters. Open seats also encourage new ideas and fresh leadership, potentially enhancing policy innovation and responsiveness to community needs.
Selection Process: Appointed vs Open Seats
The selection process for appointed seats involves a designated authority or committee choosing candidates based on predefined criteria, ensuring a controlled and strategic placement. In contrast, open seats allow candidates to compete freely through elections or open applications, promoting transparency and broader competition. Appointed seats often prioritize specific qualifications or affiliations, while open seats emphasize voter choice and democratic participation.
Impact on Representation and Diversity
Appointed seats may limit representation and reduce diversity by concentrating selection power within a small group, often reflecting existing biases or political agendas. Open seats encourage broader competition and voter participation, increasing the likelihood of diverse candidates who better represent community demographics. Studies show open-seat elections tend to produce more varied political and demographic representation than appointed positions.
Transparency and Accountability Issues
Appointed seats often raise transparency concerns due to their selection process lacking public input, which can reduce accountability to constituents. Open seats, filled through direct elections, promote greater transparency by allowing voters to evaluate candidates' platforms and hold them accountable through the electoral process. Consequently, open seats enhance democratic legitimacy by fostering a clear line of responsibility between officeholders and the electorate.
Case Studies: Appointed vs Open Seats in Practice
Case studies comparing appointed versus open seats reveal distinct impacts on governance and accountability. In jurisdictions with appointed seats, such as certain school boards, decision-making often reflects strategic expertise and alignment with governing bodies, enhancing policy consistency but sometimes reducing direct voter influence. Conversely, open seats, common in municipal councils, promote broader electoral competition and responsiveness to constituent preferences, demonstrated by increased voter engagement and diverse candidate pools in multiple documented elections.
Public Perception and Trust
Appointed seats often face public skepticism due to perceptions of reduced transparency and potential favoritism, which can erode trust in democratic processes. Open seats, by contrast, tend to generate higher public confidence as voters perceive these elections as more competitive and reflective of popular will. Studies show that communities with frequent open-seat elections report stronger civic engagement and trust in governance institutions.
Which System is Better for Effective Governance?
Appointed seats often ensure experienced individuals hold office, promoting stability and expertise in governance, while open seats encourage democratic participation and accountability by allowing voters to choose representatives directly. Effective governance benefits from a balance where appointed positions bring specialized skills and open seats reflect public will, enhancing transparency and responsiveness. Studies show mixed results, but integrating both systems tailored to specific institutional goals tends to yield optimal administrative performance and public trust.
Appointed Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com