Grants provide essential funding opportunities for businesses, nonprofits, and individuals seeking financial support without repayment obligations. Understanding the various types of grants, eligibility criteria, and application processes can significantly enhance your chances of securing the funds you need. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to successfully find and apply for the right grant opportunities.
Table of Comparison
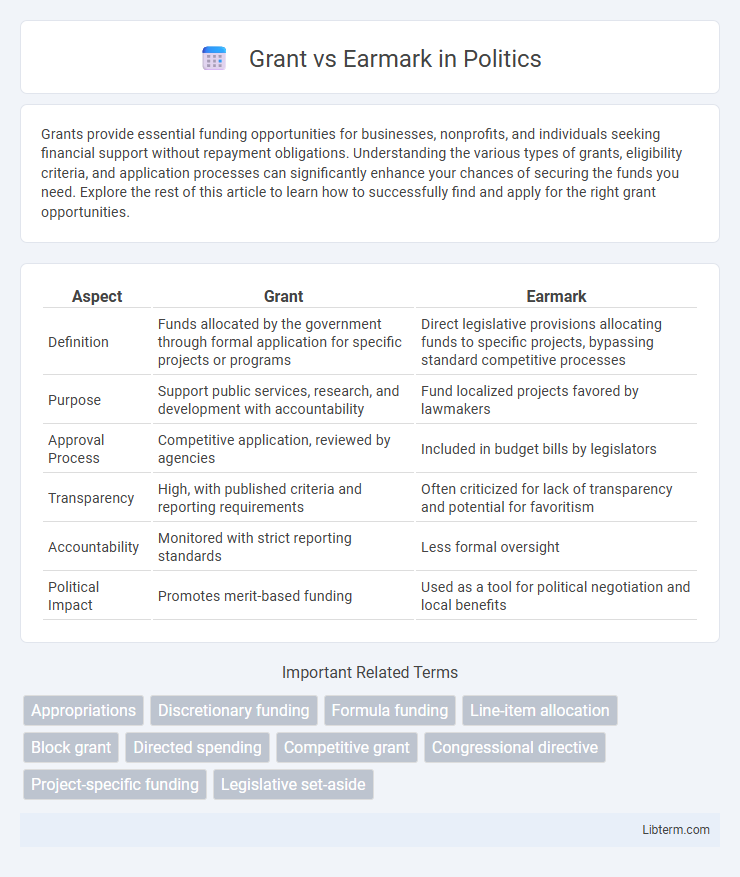
| Aspect | Grant | Earmark |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Funds allocated by the government through formal application for specific projects or programs | Direct legislative provisions allocating funds to specific projects, bypassing standard competitive processes |
| Purpose | Support public services, research, and development with accountability | Fund localized projects favored by lawmakers |
| Approval Process | Competitive application, reviewed by agencies | Included in budget bills by legislators |
| Transparency | High, with published criteria and reporting requirements | Often criticized for lack of transparency and potential for favoritism |
| Accountability | Monitored with strict reporting standards | Less formal oversight |
| Political Impact | Promotes merit-based funding | Used as a tool for political negotiation and local benefits |
Introduction to Grants and Earmarks
Grants are funds provided by federal, state, or local governments to support specific projects or services, awarded through a competitive or formula-based process that requires detailed applications and compliance with regulations. Earmarks refer to provisions inserted into legislation that direct government spending to specific projects or organizations, often negotiated by lawmakers to benefit their constituencies without a competitive application process. Understanding the distinctions between grants and earmarks is essential for navigating public funding, as grants emphasize merit-based allocation, while earmarks rely on legislative discretion.
Defining Grants: Structure and Purpose
Grants are funds provided by government agencies or organizations to support specific projects or initiatives, typically awarded through a competitive application process based on merit and eligibility criteria. They aim to promote public goods, research, education, or community development by offering financial assistance without expecting repayment. Structured as discrete allocations with defined objectives, grant funding ensures accountability through reporting requirements and performance evaluations.
What Are Earmarks? Key Characteristics
Earmarks are provisions included in legislation that direct funds to specific projects, organizations, or locations, bypassing the usual competitive grant process. They are characterized by their designation for particular purposes, often benefiting local constituencies or political supporters, and lack transparent review or standardized criteria. Earmarks contrast with competitive grants by enabling legislators to allocate resources directly, frequently leading to debates over transparency and fiscal responsibility.
Historical Context: Grants vs Earmarks
Grants have historically functioned as formal funding mechanisms provided by federal or state governments to support specific public projects, adhering to strict eligibility criteria and oversight. Earmarks gained prominence in the 20th century as congressional provisions directed funds to particular local projects, often bypassing competitive grant processes, leading to debates over transparency and government spending. The shift in political and public scrutiny during the early 2000s led to a decline in earmarks, while grants remained central to structured public funding initiatives.
Application Processes: Grants Compared to Earmarks
Grant application processes require formal submissions, including detailed proposals, budgets, and compliance with specific eligibility criteria, often reviewed through competitive evaluations by funding agencies. Earmarks bypass competitive applications as they are congressional directives allocating funds to specific projects, typically negotiated through legislators rather than through formal proposal submissions. The structured, transparent application requirements for grants contrast with the politically driven, discretionary nature of earmarks.
Funding Sources and Allocation Methods
Grants are typically awarded by federal agencies, foundations, or state governments through a competitive application process based on specific project criteria. Earmarks are funds expressly designated by legislators within appropriations bills to support particular projects or entities, bypassing the usual competitive selection process. While grants follow structured allocation methods driven by merit and regulatory compliance, earmarks reflect legislative priorities and direct funding to chosen recipients without open competition.
Oversight and Accountability Differences
Grants involve formal oversight mechanisms where federal agencies monitor compliance through reporting requirements, audits, and performance evaluations to ensure funds are used as intended. Earmarks bypass competitive grant processes and often lack the same level of transparency and accountability, leading to concerns about potential misuse and limited post-allocation monitoring. The structured accountability frameworks in grants contrast with the discretionary nature of earmarks, resulting in differing degrees of fiscal oversight.
Impact on Local Communities
Grants provide local communities with targeted funding to support specific projects, often fostering sustainable development and capacity building tailored to local needs. Earmarks direct federal funds to particular districts, enabling immediate infrastructure improvements but sometimes limiting flexibility in addressing broader community priorities. Both mechanisms influence local economic growth, yet grants typically encourage innovation while earmarks drive direct, short-term resource allocation.
Controversies and Criticisms
Grant programs face controversies regarding transparency and allocation efficiency, with critics arguing that funds may be disproportionately awarded due to political influence. Earmarks attract criticism for fostering legislative favoritism, often bypassing competitive review processes and contributing to government spending waste. Both mechanisms raise concerns about accountability, with watchdog groups highlighting potential misuse and the challenge of ensuring equitable distribution of public resources.
Choosing Between Grants and Earmarks
Choosing between grants and earmarks depends on the level of oversight and flexibility required for project funding. Grants typically involve a competitive application process emphasizing accountability and measurable outcomes, making them suitable for projects with well-defined goals and performance metrics. Earmarks, by contrast, provide direct legislative funding for specific projects often prioritized by lawmakers, offering more targeted support but less competitive scrutiny.
Grant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com