Caucuses are local gatherings where political party members discuss and select candidates for upcoming elections, influencing the political landscape directly. This process emphasizes active participation, allowing You to engage closely with grassroots politics and community decision-making. Discover how caucuses shape elections and what role they can play in your political involvement by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
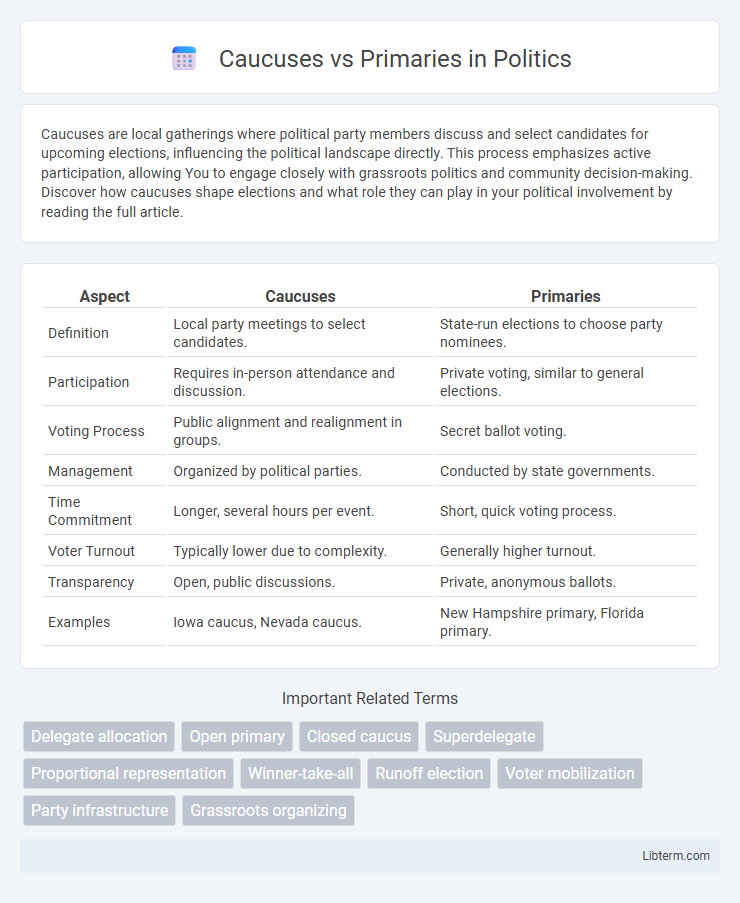
| Aspect | Caucuses | Primaries |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Local party meetings to select candidates. | State-run elections to choose party nominees. |
| Participation | Requires in-person attendance and discussion. | Private voting, similar to general elections. |
| Voting Process | Public alignment and realignment in groups. | Secret ballot voting. |
| Management | Organized by political parties. | Conducted by state governments. |
| Time Commitment | Longer, several hours per event. | Short, quick voting process. |
| Voter Turnout | Typically lower due to complexity. | Generally higher turnout. |
| Transparency | Open, public discussions. | Private, anonymous ballots. |
| Examples | Iowa caucus, Nevada caucus. | New Hampshire primary, Florida primary. |
Understanding Caucuses and Primaries
Caucuses and primaries are two key processes used by political parties in the United States to select their presidential nominees. Caucuses involve local meetings where party members openly discuss and vote for candidates, emphasizing active participation and community engagement. Primaries function as statewide elections where registered voters cast secret ballots, offering a more straightforward and accessible method to express candidate preference.
Historical Background of Caucuses and Primaries
Caucuses originated in the early 19th century as grassroots gatherings where party members openly discussed and chose candidates, reflecting a more direct form of democratic participation. Primaries emerged in the early 20th century, introduced to increase voter participation and reduce party elite control by allowing secret ballot voting in state-run elections. The shift toward primaries was influenced by Progressive Era reforms aimed at making candidate selection more transparent and accessible to the general electorate.
Key Differences Between Caucuses and Primaries
Caucuses involve local gatherings where party members discuss and vote openly to select candidates, emphasizing community engagement and real-time debate. Primaries operate as private, state-run elections where voters cast secret ballots, offering a straightforward, accessible method for selecting nominees. The key differences lie in format, participation style, and the level of voter involvement, with caucuses fostering interactive decision-making and primaries ensuring efficiency and privacy.
How Caucuses Work: Step-by-Step
Caucuses begin with voters gathering at local meeting places where participants openly discuss and debate the candidates before casting their votes. Attendees physically group themselves by candidate preference, allowing supporters to persuade undecided voters, and a viability threshold must be met for a candidate to earn delegates at the site. Final delegate allocation occurs based on these groupings, with results reported to state party officials to influence the nominee selection process.
How Primaries Work: Step-by-Step
Primaries operate through a structured voting process where registered party members cast secret ballots to select their preferred candidate. Voters receive a list of candidates and mark their choice privately at polling stations or via absentee ballots, ensuring a straightforward and accessible participation. Results from these ballots determine delegate allocations for party conventions, influencing the nomination of presidential candidates.
Advantages of the Caucus System
The caucus system fosters active political engagement by encouraging direct discussion and debate among participants, which can lead to more informed voting decisions. It allows for greater grassroots involvement, enabling local party members to influence candidate selection more effectively than in primary elections. This system can strengthen community bonds and increase commitment to the party's values by promoting face-to-face interaction and collective decision-making.
Benefits of Primary Elections
Primary elections offer a more inclusive and accessible method for selecting party candidates by allowing all registered voters to participate directly. This process increases voter turnout and provides a clearer reflection of public preferences across a broader demographic. Furthermore, primaries tend to reduce the influence of party insiders, promoting greater democratic engagement and transparency in the candidate selection process.
States Using Caucuses vs Primaries
States using caucuses, such as Iowa and Nevada, rely on local gatherings where voters openly discuss and select their preferred candidates, fostering a more community-driven and participatory approach. Primaries, employed by most states including California and New York, involve secret ballots similar to general elections, allowing for broader voter participation and streamlined vote counting. The choice between caucuses and primaries significantly influences electoral engagement, turnout rates, and campaign strategies across different states.
Impact on Voter Turnout and Participation
Caucuses typically result in lower voter turnout compared to primaries due to their time-consuming, in-person discussion format that limits accessibility for many voters. Primaries, especially those conducted via mail or at multiple polling locations, encourage higher participation by offering convenience and privacy. States using primaries often experience broader voter engagement, reflecting a more diverse electorate in candidate selection.
The Role of Caucuses and Primaries in Presidential Elections
Caucuses and primaries serve as essential mechanisms in the U.S. presidential election process by determining party nominees through voter participation. Caucuses involve local gatherings where registered party members discuss and vote publicly on their preferred candidates, emphasizing community engagement and grassroots influence. Primaries function as statewide elections with secret ballots, allowing a broader electorate to directly select delegates, which often leads to higher voter turnout and a more straightforward reflection of public preference.
Caucuses Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com