A resemblance model quantifies similarities between data points to improve pattern recognition and decision-making processes. It plays a crucial role in fields like image analysis, natural language processing, and recommendation systems by comparing features and attributes. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a resemblance model can enhance your data-driven applications.
Table of Comparison
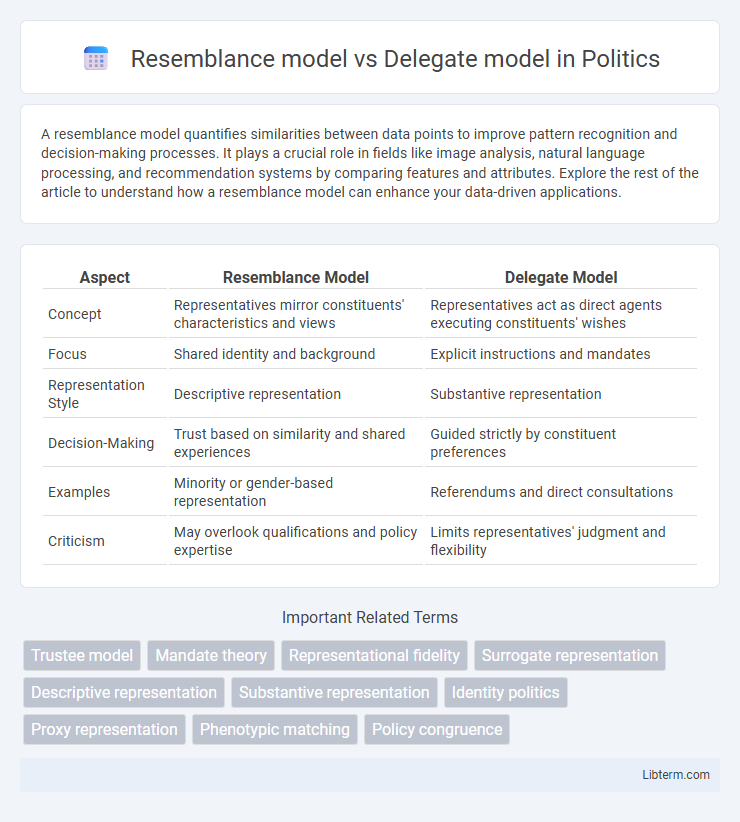
| Aspect | Resemblance Model | Delegate Model |
|---|---|---|
| Concept | Representatives mirror constituents' characteristics and views | Representatives act as direct agents executing constituents' wishes |
| Focus | Shared identity and background | Explicit instructions and mandates |
| Representation Style | Descriptive representation | Substantive representation |
| Decision-Making | Trust based on similarity and shared experiences | Guided strictly by constituent preferences |
| Examples | Minority or gender-based representation | Referendums and direct consultations |
| Criticism | May overlook qualifications and policy expertise | Limits representatives' judgment and flexibility |
Introduction to Representation Models
Representation models such as the Resemblance model focus on perceptual similarity by comparing visual or structural features to identify patterns, making them essential in cognitive science and AI for object recognition tasks. The Delegate model, in contrast, emphasizes functional similarity by assigning task-specific roles to components, enabling more dynamic and context-sensitive processing in machine learning frameworks. Both models provide foundational approaches to representation, with the Resemblance model prioritizing feature-based matching and the Delegate model leveraging role-based delegation for adaptability.
Defining the Resemblance Model
The Resemblance model defines itself by closely mirroring the structure and behavior of the target system it represents, emphasizing fidelity in replication. It models entities and relationships to reflect real-world counterparts with high accuracy, facilitating intuitive understanding and prediction. This approach contrasts with the Delegate model, which focuses on delegation of responsibilities rather than structural similarity.
Understanding the Delegate Model
The Delegate model leverages composition by having objects delegate responsibilities to helper classes, enhancing flexibility and reusability through clear separation of concerns. Understanding the Delegate model involves recognizing how it encapsulates behavior in delegate objects, allowing dynamic assignment of tasks without rigid inheritance hierarchies. This approach contrasts with the Resemblance model, which focuses more on structural similarity rather than behavioral delegation, emphasizing object relationships over shared functionality.
Historical Context and Evolution
The Resemblance model emerged in the early days of cognitive science, emphasizing prototype theory and family resemblance to categorize concepts based on shared features rather than strict definitions. The Delegate model evolved later within object-oriented programming, promoting delegation as a way to extend behavior by passing responsibilities to helper objects, addressing limitations of classical inheritance. This historical progression reflects a shift from conceptual classification in semantics to practical design patterns in software engineering, highlighting different responses to complexity in modeling systems.
Key Differences Between Models
The Resemblance model emphasizes simulating the behavior and attributes of the original object, creating a close imitation through inheritance or composition, whereas the Delegate model relies on delegation of responsibilities to helper objects, promoting flexibility and separation of concerns. Resemblance models often lead to tighter coupling due to direct inheritance or copying, while Delegate models facilitate code reuse and reduce dependencies by forwarding method calls to delegate classes or interfaces. Key differences include the approach to behavior sharing, with Resemblance models prioritizing similarity and Delegate models focusing on delegation and modular design.
Advantages of the Resemblance Model
The Resemblance Model offers advantages in clarity and simplicity by closely aligning the proxy object's interface with the subject it represents, making it more intuitive for developers to use. This model reduces cognitive load since clients interact with a familiar interface without needing to understand underlying complexities or differences. Its straightforward implementation improves maintainability and eases debugging compared to Delegate models, which often require managing separate interfaces and indirections.
Benefits of the Delegate Model
The Delegate Model offers enhanced flexibility by allowing objects to dynamically change behavior at runtime through delegation of responsibilities, improving code maintainability and scalability. It promotes clean separation of concerns by assigning specific tasks to distinct delegate objects, facilitating easier debugging and testing. This model reduces inheritance-related issues, enabling reusable and modular code structures suited for complex application development.
Challenges and Criticisms
The Resemblance model faces challenges related to defining clear criteria for identity over time, often criticized for its reliance on subjective similarity judgments that can vary across contexts. The Delegate model encounters criticisms regarding the transfer of responsibility, as it may obscure the continuity of personal identity by emphasizing function or roles rather than intrinsic qualities. Both models struggle with balancing objective metrics and philosophical coherence, leading to ongoing debates about their applicability in ethics and cognitive science.
Real-World Applications and Examples
The Resemblance model excels in image recognition applications such as facial verification systems used by security agencies, where it identifies entities based on visual similarity. In contrast, the Delegate model is prominent in software architectures like the Model-View-Controller (MVC) framework, delegating responsibilities to specialized components to enhance modularity and maintainability, as seen in large-scale web applications. Real-world usage of the Delegate model includes iOS app development, where delegation patterns manage user interactions and event handling efficiently.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Model
Choosing between the Resemblance model and the Delegate model depends on the specific use case and design goals of a software system. The Resemblance model offers simplicity and direct inheritance benefits, making it suitable for scenarios with clear hierarchical relationships. The Delegate model provides greater flexibility and decoupling by allowing objects to delegate responsibilities, ideal for dynamic behavior changes and composition over inheritance.
Resemblance model Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com