Economic integration promotes the removal of trade barriers and the harmonization of economic policies among countries, enhancing market efficiency and fostering regional growth. This process can lead to increased investment flows, greater competition, and improved consumer choices within integrated markets. Explore the full article to understand how economic integration could impact your country's economic landscape and opportunities.
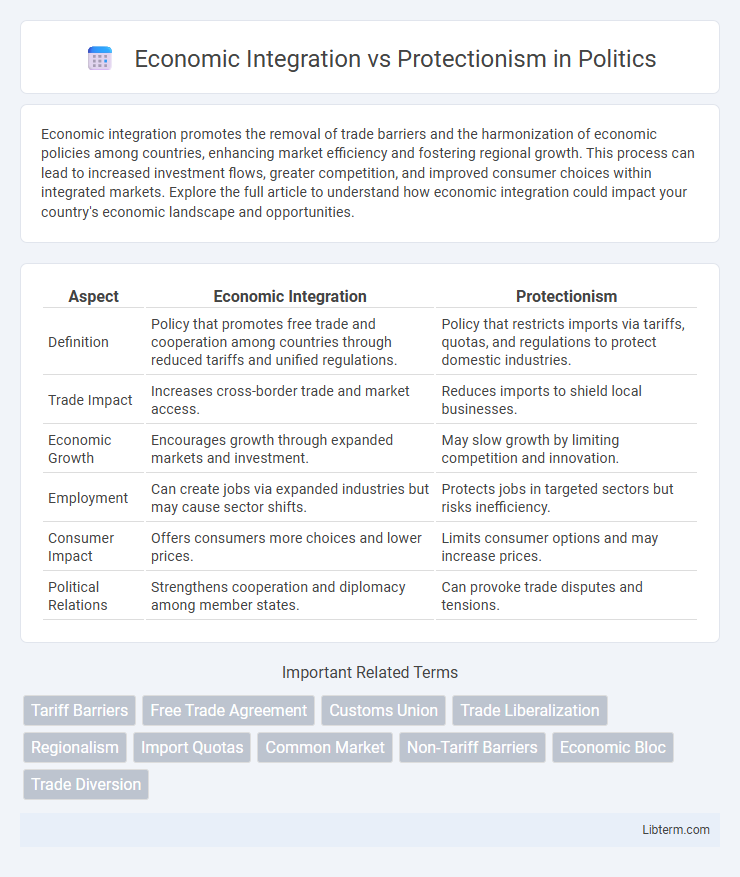
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Economic Integration | Protectionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Policy that promotes free trade and cooperation among countries through reduced tariffs and unified regulations. | Policy that restricts imports via tariffs, quotas, and regulations to protect domestic industries. |
| Trade Impact | Increases cross-border trade and market access. | Reduces imports to shield local businesses. |
| Economic Growth | Encourages growth through expanded markets and investment. | May slow growth by limiting competition and innovation. |
| Employment | Can create jobs via expanded industries but may cause sector shifts. | Protects jobs in targeted sectors but risks inefficiency. |
| Consumer Impact | Offers consumers more choices and lower prices. | Limits consumer options and may increase prices. |
| Political Relations | Strengthens cooperation and diplomacy among member states. | Can provoke trade disputes and tensions. |
Understanding Economic Integration
Economic integration involves the unification of economic policies and markets among countries to facilitate free trade, investment, and labor mobility, improving overall economic efficiency and growth. It ranges from free trade areas to full economic unions, including common tariffs, harmonized regulations, and shared monetary policies. Understanding economic integration highlights its role in reducing trade barriers, enhancing regional cooperation, and creating competitive advantages for participating nations.
Defining Protectionism
Protectionism refers to government policies that restrict international trade to protect domestic industries from foreign competition, often through tariffs, quotas, and subsidies. These measures aim to preserve local jobs, maintain economic independence, and reduce trade deficits but can lead to increased prices and reduced market efficiency. Economic integration contrasts by promoting free trade and cooperation among nations to enhance economic growth and resource allocation.
Historical Evolution of Trade Policies
The historical evolution of trade policies reveals a dynamic shift from protectionism, characterized by high tariffs and restrictive quotas in the 19th and early 20th centuries, to economic integration marked by the formation of regional trade agreements like the European Union and NAFTA in the late 20th century. This transition facilitated the reduction of trade barriers, promoting cross-border investment, economic interdependence, and the global expansion of supply chains. Key milestones include the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) established in 1947 and the subsequent World Trade Organization (WTO) in 1995, which institutionalized multilateral trade liberalization and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Key Differences Between Integration and Protectionism
Economic integration promotes the removal of trade barriers among member countries to facilitate the free flow of goods, services, and capital, enhancing economic cooperation and growth. Protectionism enforces tariffs, quotas, and import restrictions to shield domestic industries from foreign competition, aiming to preserve local jobs and industries. The key difference lies in integration driving open markets and mutual economic benefits, while protectionism emphasizes national economic sovereignty and limiting international trade exposure.
Economic Integration: Benefits and Challenges
Economic integration enhances trade efficiency by reducing tariffs and regulatory barriers, fostering increased market access and economic growth among member countries. It promotes resource allocation optimization and economies of scale, driving innovation and competitiveness within integrated regions. However, challenges include potential loss of national sovereignty, uneven economic benefits, and increased vulnerability to external economic shocks.
Protectionism: Advantages and Drawbacks
Protectionism safeguards domestic industries by imposing tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers, fostering job preservation and local economic growth. It can reduce foreign competition, allowing emerging industries to develop without external pressures. However, protectionism often leads to higher consumer prices, limits product choices, and may provoke trade wars, ultimately hampering global economic efficiency and innovation.
Impact on Global Trade and Markets
Economic integration promotes the removal of trade barriers, leading to increased market access, higher trade volumes, and enhanced economic efficiency across member countries. In contrast, protectionism imposes tariffs, quotas, and restrictions that hinder international trade, causing market distortions, reduced competition, and higher prices for consumers. The global trade environment thrives on integration through regional trade agreements like the EU and NAFTA, while protectionist policies from major economies can disrupt supply chains and reduce global market growth.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Economic integration fosters trade liberalization and market expansion, as seen in the European Union's success in creating a single market that boosts GDP and employment among member states. Conversely, protectionism, exemplified by the U.S.-China trade war, led to increased tariffs that disrupted global supply chains and slowed economic growth in both countries. Case studies reveal that while integration promotes long-term economic stability, protectionism often results in short-term gains but long-term inefficiencies and market distortions.
Future Trends in Global Trade Policies
Future trends in global trade policies indicate a gradual shift towards deeper economic integration through multilateral agreements and digital trade frameworks, enhancing cross-border supply chains and reducing tariffs. Protectionism may persist in strategic sectors due to geopolitical tensions and national security concerns, but overall global trade is expected to benefit from technology-driven efficiency and sustainability standards. Emerging markets will increasingly influence trade dynamics by leveraging regional trade blocs and innovation-focused partnerships.
Striking a Balance: The Path Forward
Striking a balance between economic integration and protectionism requires policy frameworks that promote trade liberalization while safeguarding domestic industries from unfair competition. Strategic tariffs and targeted subsidies can coexist with multilateral trade agreements to foster innovation and economic resilience. Achieving this equilibrium supports sustainable growth by harmonizing global connectivity with national economic priorities.
Economic Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com