Global markets impact your financial decisions through fluctuating currency values and international trade dynamics. Understanding these trends enables better investment strategies and risk management. Explore the rest of the article to learn how global factors shape economic opportunities worldwide.
Table of Comparison
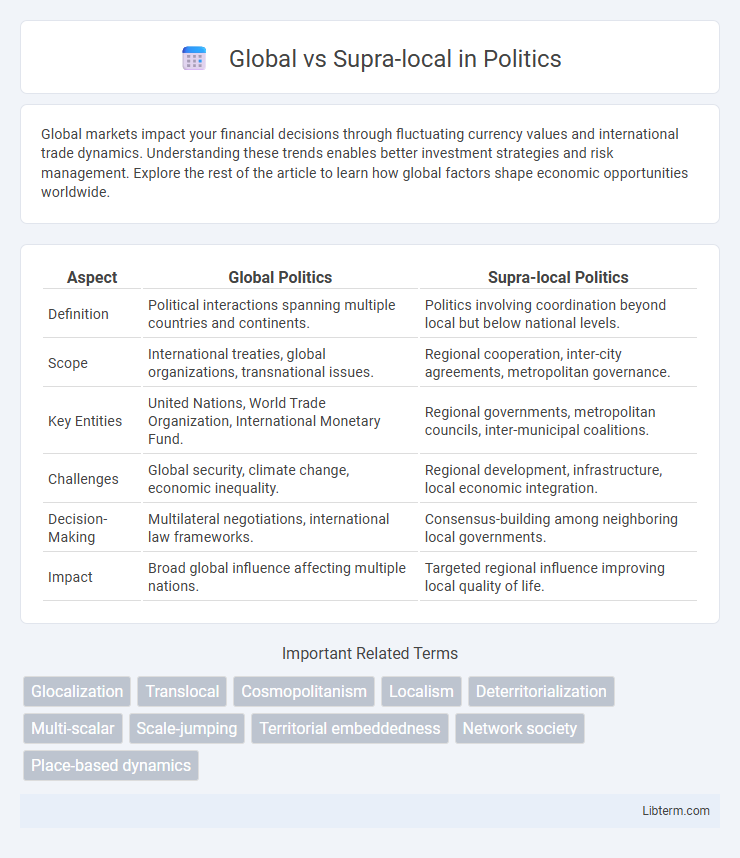
| Aspect | Global Politics | Supra-local Politics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political interactions spanning multiple countries and continents. | Politics involving coordination beyond local but below national levels. |
| Scope | International treaties, global organizations, transnational issues. | Regional cooperation, inter-city agreements, metropolitan governance. |
| Key Entities | United Nations, World Trade Organization, International Monetary Fund. | Regional governments, metropolitan councils, inter-municipal coalitions. |
| Challenges | Global security, climate change, economic inequality. | Regional development, infrastructure, local economic integration. |
| Decision-Making | Multilateral negotiations, international law frameworks. | Consensus-building among neighboring local governments. |
| Impact | Broad global influence affecting multiple nations. | Targeted regional influence improving local quality of life. |
Introduction to Global vs Supra-local
Global refers to phenomena or processes that encompass the entire world or multiple countries, emphasizing large-scale interconnectedness and broad impact. Supra-local denotes interactions or systems that operate above the local level but do not extend globally, often involving regional or multi-national frameworks within specific areas. Understanding the distinction between global and supra-local scales is crucial for analyzing economic, environmental, and political dynamics in a spatial context.
Defining “Global” in Contemporary Contexts
Defining "Global" in contemporary contexts involves recognizing interconnected systems that transcend national boundaries, integrating economic, cultural, and technological dimensions worldwide. Globalization reflects the complex networks of trade, communication, and migration facilitating real-time interaction and exchange across continents. This dynamic framework challenges traditional notions of sovereignty and necessitates adaptive policies addressing transnational issues such as climate change, digital governance, and global health.
Understanding Supra-local: Bridging Local and Global
Supra-local networks facilitate connections between local communities and the broader global framework, enhancing resource sharing and cultural exchange. These intermediaries optimize regional collaboration by integrating local knowledge with global trends, fostering innovation and sustainable development. Understanding supra-local dynamics is crucial for strategic planning and policy-making aimed at balanced regional growth and global competitiveness.
Historical Evolution of Global and Supra-local Concepts
The historical evolution of global and supra-local concepts reflects the gradual expansion of human societies from localized communities to interconnected regions and ultimately a worldwide network. Early civilizations developed supra-local structures through trade routes and political alliances, which later transformed into global systems facilitated by technological advancements like navigation and communication. This evolution illustrates the shift from regional influence to comprehensive global integration, shaping economic, cultural, and political dynamics across the world.
Key Differences: Global vs Supra-local Scope
Global scope encompasses multiple countries or continents, addressing international markets, regulations, and cultural diversity to create uniform strategies. Supra-local scope operates above local but below national levels, often targeting specific regions or clusters within a country to accommodate regional characteristics and demands. Key differences include scale, geographic reach, and the complexity of coordination, with global strategies requiring broader management of diverse environments compared to the more localized focus of supra-local initiatives.
Impacts on Culture and Identity
Global influences often lead to cultural homogenization, diluting unique local identities by promoting widespread norms, languages, and consumer habits. Supra-local dynamics, which operate between local and global scales, foster hybrid cultural expressions that blend traditional practices with external elements, preserving distinct community identities while embracing change. The interplay between global and supra-local forces shapes evolving cultural landscapes, affecting social norms, heritage preservation, and collective identity formation.
Economic Implications: Globalization vs Supra-local Networks
Globalization fosters economic integration by enabling multinational corporations to optimize supply chains and access international markets, driving increased trade volumes and investment flows. Supra-local networks emphasize localized economic collaboration among neighboring regions, promoting resilience through diversified local supply chains and targeted resource sharing. The economic implications highlight a trade-off between global efficiency and supra-local adaptability in addressing market fluctuations and supply chain disruptions.
Governance and Policy Challenges
Global governance faces challenges in harmonizing diverse national policies, addressing cross-border issues like climate change and trade, and ensuring compliance amid varying legal frameworks. Supra-local governance, operating above local but below national levels, struggles with limited authority and resources to implement policies uniformly across regions while balancing local interests. Both levels require innovative coordination mechanisms to overcome jurisdictional fragmentation and enhance policy coherence across multiple scales.
Case Studies: Examples of Global and Supra-local Dynamics
Case studies of global and supra-local dynamics reveal distinct patterns of influence and interaction, such as the global supply chain networks of multinational corporations exemplified by Apple Inc., which coordinates production, design, and sales across continents. Supra-local dynamics are evident in regional initiatives like the European Union's cross-border infrastructure projects that integrate multiple neighboring countries for economic and environmental benefits. These examples highlight the scale and complexity differences, with global dynamics encompassing worldwide reach and supra-local dynamics focusing on interconnected regions beyond local but below global levels.
Future Trends: Balancing Global and Supra-local Perspectives
Future trends emphasize integrating global and supra-local perspectives to create adaptive, resilient strategies that address both widespread challenges and highly localized needs. Advances in data analytics and AI enable precise identification of supra-local patterns within global frameworks, optimizing decision-making for sustainable development and urban planning. Organizations increasingly invest in multi-scale governance models to balance scalability with contextual specificity, enhancing responsiveness in an interconnected world.
Global Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com