Retrospective voting enables voters to evaluate political candidates or parties based on their past performance, especially regarding economic management, policy implementation, and governance outcomes. This approach helps You make informed decisions by reflecting on previous successes or failures rather than relying solely on future promises. Discover how retrospective voting shapes democratic processes and influences electoral outcomes by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
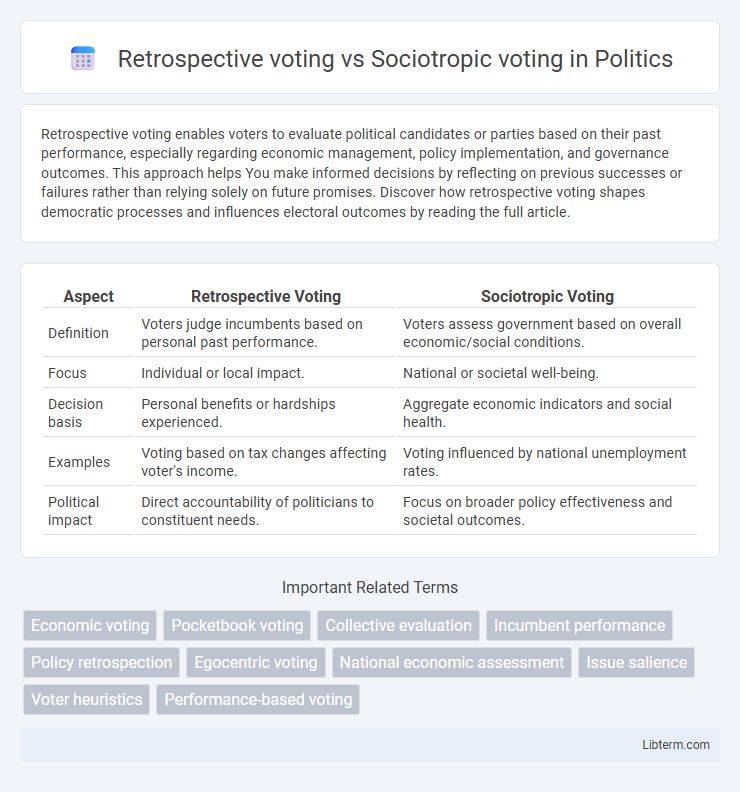
| Aspect | Retrospective Voting | Sociotropic Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voters judge incumbents based on personal past performance. | Voters assess government based on overall economic/social conditions. |
| Focus | Individual or local impact. | National or societal well-being. |
| Decision basis | Personal benefits or hardships experienced. | Aggregate economic indicators and social health. |
| Examples | Voting based on tax changes affecting voter's income. | Voting influenced by national unemployment rates. |
| Political impact | Direct accountability of politicians to constituent needs. | Focus on broader policy effectiveness and societal outcomes. |
Introduction to Voting Behavior Theories
Retrospective voting theory emphasizes voters' evaluation of an incumbent's past performance, especially economic conditions and policy outcomes, to decide electoral choices. Sociotropic voting involves voters considering the overall national economic and social environment rather than their personal circumstances when assessing government performance. Both theories contribute to understanding voting behavior by highlighting different cognitive processes voters use to make informed decisions based on collective versus individual experiences.
Defining Retrospective Voting
Retrospective voting refers to the electoral behavior where voters evaluate incumbents based on past performance and policy outcomes, emphasizing tangible results such as economic growth, employment rates, and public service effectiveness. This voting model contrasts with sociotropic voting, which considers voters' perceptions of societal-level conditions rather than personal circumstances. Retrospective voting plays a crucial role in democratic accountability by linking political support directly to government achievements or failures.
Understanding Sociotropic Voting
Sociotropic voting refers to the practice where voters base their electoral decisions on the overall economic and social conditions of their country rather than their personal circumstances. This behavior emphasizes collective welfare indicators, such as national unemployment rates, GDP growth, and inflation levels, influencing voter preferences for incumbents or challengers. Understanding sociotropic voting reveals how macroeconomic perceptions shape political accountability and election outcomes more powerfully than individual economic experiences.
Key Differences Between Retrospective and Sociotropic Voting
Retrospective voting centers on individual voters assessing their personal economic circumstances and experiences when deciding their electoral choices. Sociotropic voting involves evaluating the overall economic or social conditions of the country, prioritizing collective welfare over individual benefit. Key differences lie in the scope of evaluation--personal versus national--and the emphasis on individual outcomes in retrospective voting compared to broader societal impacts in sociotropic voting.
Psychological Foundations of Voter Decision-Making
Retrospective voting involves evaluating an incumbent's past performance on economic and social issues, relying heavily on memory and emotional responses to shape voter behavior. Sociotropic voting centers on a voter's perception of the overall national economic health rather than personal circumstances, influenced by social identity and collective well-being concerns. Psychological foundations in both mechanisms highlight cognitive biases, heuristics, and social identity theory as critical factors driving how voters assess political candidates and policies.
Influences on Voter Preferences and Choices
Retrospective voting emphasizes voters' evaluation of past government performance, particularly economic conditions and policy outcomes, which directly impacts their preferences and choices in elections. Sociotropic voting highlights voters' concerns about the overall national or community welfare rather than personal circumstances, leading them to base decisions on broader social indicators like unemployment rates or inflation. Both voting types significantly influence electoral behavior by shaping how voters interpret political accountability and policy effectiveness.
Retrospective Voting in Recent Elections
Retrospective voting plays a critical role in recent elections as voters evaluate incumbents based on past performance, including economic management, policy outcomes, and crisis responses. Studies show that economic indicators such as unemployment rates and inflation significantly influence voter decisions under retrospective judgments. This voting behavior contrasts with sociotropic voting, where voters consider broader social and economic conditions rather than individual or local experiences.
Sociotropic Voting Patterns Across Demographics
Sociotropic voting patterns reveal that voters evaluate the economy and social issues based on nationwide conditions rather than personal circumstances, influencing their electoral choices. Research indicates that demographic factors such as education, race, and income significantly shape sociotropic perceptions, with higher-educated and higher-income individuals more likely to engage in sociotropic voting. These demographic variations highlight the importance of collective economic assessments in understanding voter behavior and election outcomes.
Implications for Political Campaign Strategies
Retrospective voting, where voters evaluate incumbents based on past performance, encourages political campaigns to highlight successful policy outcomes and economic achievements to reinforce voter satisfaction. Sociotropic voting, emphasizing voters' perceptions of overall economic and social conditions, drives campaigns to address broad national issues and frame messaging around collective well-being rather than personal interests. Tailoring strategies to these voting behaviors can improve electoral effectiveness by aligning campaign narratives with voters' decision-making criteria.
Conclusion: Impact on Democratic Outcomes
Retrospective voting, based on evaluating past government performance, enhances accountability by encouraging voters to reward or punish incumbents, thereby promoting responsive governance. Sociotropic voting, which centers on collective economic conditions rather than personal experiences, often leads to assessments that drive broader policy changes reflecting societal welfare. Both voting behaviors significantly influence democratic outcomes by shaping electoral choices rooted in either individual performance evaluation or collective economic perceptions, ultimately affecting government stability and policy direction.
Retrospective voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com