Political polarization intensifies societal divisions by amplifying ideological differences and reducing opportunities for constructive dialogue. It often leads to gridlock in policymaking and decreases public trust in government institutions. Explore the complexities of political polarization and how it shapes today's political landscape in the rest of this article.
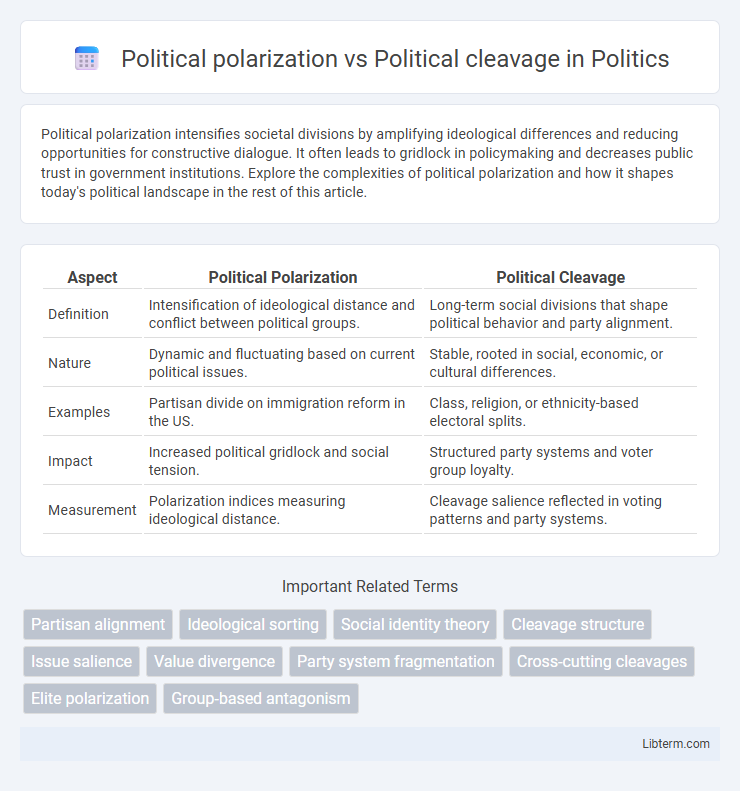
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Political Polarization | Political Cleavage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intensification of ideological distance and conflict between political groups. | Long-term social divisions that shape political behavior and party alignment. |
| Nature | Dynamic and fluctuating based on current political issues. | Stable, rooted in social, economic, or cultural differences. |
| Examples | Partisan divide on immigration reform in the US. | Class, religion, or ethnicity-based electoral splits. |
| Impact | Increased political gridlock and social tension. | Structured party systems and voter group loyalty. |
| Measurement | Polarization indices measuring ideological distance. | Cleavage salience reflected in voting patterns and party systems. |
Understanding Political Polarization: Definitions and Impacts
Political polarization refers to the increasing ideological distance and lack of overlap between opposing political parties or groups, often resulting in heightened conflict and reduced cooperation. Political cleavage, on the other hand, denotes the deep-seated divisions within society based on social, economic, ethnic, or religious lines that influence political alignment and voter behavior. Understanding political polarization involves analyzing its roots in these cleavages and assessing its impacts on democratic processes, governance, and social cohesion.
What is Political Cleavage? Origins and Characteristics
Political cleavage refers to the deep and enduring divisions in society that separate groups based on fundamental issues such as class, religion, ethnicity, or ideology, shaping political behavior and party systems. These cleavages originate from historical conflicts and social structures that create distinct social identities, often reinforcing group loyalty and persistent voting patterns. Characterized by their persistence and influence, political cleavages structure political competition by aligning social groups with specific political interests and values across generations.
Key Differences Between Political Polarization and Political Cleavage
Political polarization refers to the increasing ideological distance and oppositional attitudes between political parties or groups, often resulting in heightened conflict and reduced compromise. Political cleavage denotes the deep-seated social or cultural divisions, such as class, religion, or ethnicity, that shape political alignments and party systems over time. Key differences include polarization's emphasis on ideological extremes and conflict dynamics, whereas cleavage highlights structural societal divisions that underpin political identities.
Historical Contexts: Polarization vs Cleavage Across Time
Political polarization intensifies ideological divisions often driven by contemporary issues and media influence, while political cleavage refers to long-standing social and economic divisions embedded in a society's historical fabric. Historical contexts show that cleavages such as class, religion, or ethnicity have structured political alignments over centuries, shaping party systems and voter behavior. In contrast, polarization can fluctuate rapidly, reflecting short-term shifts in public opinion and political rhetoric, highlighting different temporal dynamics between the two phenomena.
Sociological Drivers of Political Polarization
Political polarization often intensifies through sociological drivers such as social identity theory, where individuals align their political beliefs with group affiliations like race, religion, or socioeconomic status, deepening in-group/out-group divisions. Political cleavages, defined as enduring societal divisions based on structural factors like class and ethnicity, become more pronounced as these identities influence voting behavior and partisan loyalty. Factors like media consumption, geographic segregation, and social networks amplify polarization by reinforcing existing biases and limiting cross-cutting interactions.
Social and Economic Roots of Political Cleavages
Political polarization intensifies as social and economic divisions deepen, rooted in disparities such as class, identity, and resource distribution that form enduring political cleavages. Social cleavages often stem from differences in ethnicity, religion, or cultural values, while economic cleavages arise from unequal income, wealth, and access to opportunities. These cleavages structure political behavior and party alignment, reinforcing enduring divides that drive polarized electoral outcomes and policy debates.
The Role of Media in Shaping Polarization and Cleavages
Media plays a crucial role in shaping political polarization and cleavages by selectively framing issues and amplifying partisan narratives that reinforce existing biases. Social media algorithms and cable news outlets contribute to echo chambers, fostering ideological homogeneity and deepening divisions between political groups. The increasing consumption of polarized content intensifies attitudinal divides, undermining cross-cutting cleavages that traditionally mitigate political fragmentation.
Political Consequences: Governance and Social Cohesion
Political polarization intensifies ideological divides, often resulting in legislative gridlock and weakened governance by reducing bipartisan cooperation. Political cleavage, based on enduring social or cultural differences such as class, religion, or ethnicity, shapes the stability of political parties and can either foster representation or exacerbate social fragmentation. Both phenomena impact social cohesion, where polarization erodes trust and collective identity, while cleavages risk entrenching group conflicts or enabling pluralistic democracy depending on institutional responses.
Case Studies: Polarization and Cleavage in Different Countries
Political polarization refers to the growing ideological distance and division between political parties or groups, while political cleavage involves the structural and long-lasting societal divisions such as class, religion, or ethnicity influencing political alignments. Case studies in countries like the United States illustrate intense polarization along partisan lines, driven by media and electoral dynamics, whereas India exemplifies political cleavages rooted in caste and religious identity shaping voter behavior. In contrast, Scandinavian countries demonstrate low polarization despite existing cleavages due to consensus-driven political cultures and inclusive policy frameworks.
Bridging Divides: Strategies for Reducing Political Fractures
Political polarization intensifies ideological divides causing increased social fragmentation, while political cleavage refers to deep-rooted, structural divisions like class, religion, or ethnicity. Bridging divides requires fostering inclusive dialogue, promoting bipartisan policymaking, and implementing education that emphasizes critical thinking and empathy. Effective strategies leverage conflict resolution techniques and community engagement to transform polarization into constructive political participation.
Political polarization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com