Power-sharing agreements foster cooperation by distributing authority among different groups, ensuring balanced representation and reducing conflict. Effective implementation of these agreements promotes political stability and social harmony within diverse societies. Discover how power-sharing agreements can impact governance and your community by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
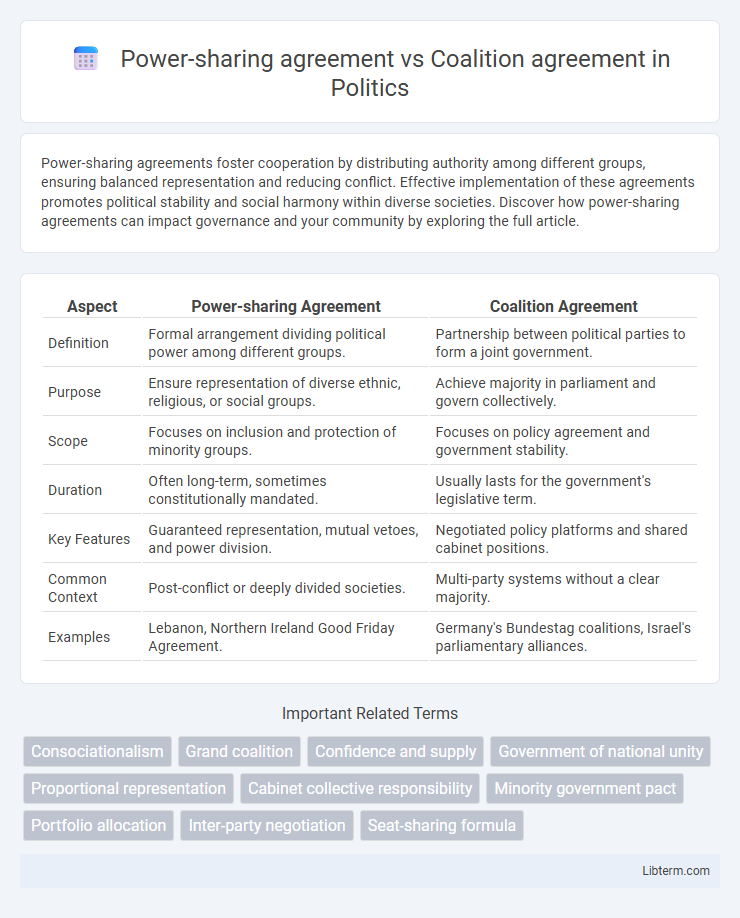
| Aspect | Power-sharing Agreement | Coalition Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal arrangement dividing political power among different groups. | Partnership between political parties to form a joint government. |
| Purpose | Ensure representation of diverse ethnic, religious, or social groups. | Achieve majority in parliament and govern collectively. |
| Scope | Focuses on inclusion and protection of minority groups. | Focuses on policy agreement and government stability. |
| Duration | Often long-term, sometimes constitutionally mandated. | Usually lasts for the government's legislative term. |
| Key Features | Guaranteed representation, mutual vetoes, and power division. | Negotiated policy platforms and shared cabinet positions. |
| Common Context | Post-conflict or deeply divided societies. | Multi-party systems without a clear majority. |
| Examples | Lebanon, Northern Ireland Good Friday Agreement. | Germany's Bundestag coalitions, Israel's parliamentary alliances. |
Introduction to Power-Sharing and Coalition Agreements
Power-sharing agreements involve distributing political power among different parties or groups to ensure inclusive governance and prevent dominance by a single entity. Coalition agreements are formal pacts between political parties that outline collaborative governance strategies and policy priorities to form a stable government. Both frameworks aim to enhance political stability but differ in their scope, with power-sharing focusing on equitable representation and coalition agreements emphasizing policy coordination.
Defining Power-Sharing Agreements
Power-sharing agreements are political arrangements designed to distribute governmental authority among diverse groups to promote inclusivity and stability, often involving formal provisions for representation of various ethnic, religious, or political factions. These agreements aim to prevent dominance by any single group by institutionalizing shared decision-making processes and mutual veto powers. Unlike coalition agreements, which primarily focus on temporary cooperation between parties to form a government, power-sharing agreements typically establish long-term frameworks for governance and conflict resolution.
Understanding Coalition Agreements
Coalition agreements outline the formal arrangement between multiple political parties to govern collectively, specifying policy priorities, ministerial roles, and conflict resolution mechanisms. These agreements ensure stable governance by clearly defining shared objectives and operational guidelines for coalition partners. Unlike broader power-sharing agreements, coalition agreements focus specifically on cooperation within the political executive to maintain a functioning government.
Core Features of Power-Sharing Models
Power-sharing agreements emphasize inclusive governance by distributing executive power among major political groups to maintain stability and represent diverse interests, often featuring mechanisms like proportional representation and mutual veto rights. Coalition agreements primarily focus on policy collaboration between political parties to form a government, defining shared legislative agendas and role allocations without necessitating equal power distribution. Core features of power-sharing models include consociational elements such as collective decision-making, autonomy for distinct groups, and safeguards against domination by any single party.
Key Elements in Coalition Agreements
Coalition agreements typically include key elements such as clear policy priorities, distribution of ministerial portfolios, conflict resolution mechanisms, and decision-making processes that ensure collective governance. These agreements emphasize collaboration and compromise among participating parties to form a stable government, unlike power-sharing agreements which often focus on equitable representation of distinct groups. Effective coalition agreements also outline timelines, accountability measures, and procedures for revisiting terms to maintain political cohesion.
Objectives and Motivations Behind Each Agreement
Power-sharing agreements aim to ensure inclusive governance by distributing political power among diverse groups to maintain stability and prevent conflict, often in divided societies or post-conflict settings. Coalition agreements focus on forming a temporary alliance between political parties to achieve a majority in the legislature and implement shared policy goals during a government term. While power-sharing prioritizes representation and peace-building, coalition agreements emphasize effective governance and policy coordination.
Comparative Analysis: Structure and Function
Power-sharing agreements evenly distribute decision-making authority among distinct parties, ensuring representation based on equal negotiation outcomes often seen in consociational democracies. Coalition agreements outline a collaborative framework where multiple political parties jointly govern, defining policy priorities and ministerial allocations to maintain majority support in parliamentary systems. Structurally, power-sharing emphasizes institutional balance and veto powers, while coalition agreements focus on policy compromise and legislative coordination.
Benefits and Challenges of Power-Sharing
Power-sharing agreements promote inclusivity and political stability by ensuring representation of diverse groups, reducing conflict risks and fostering consensus-driven governance. Challenges include potential gridlock due to differing party agendas, slower decision-making processes, and risks of unequal power distribution causing dissatisfaction among stakeholders. Effective power-sharing requires clear mechanisms for conflict resolution and a commitment to cooperation to balance interests and maintain long-term stability.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Coalition Agreements
Coalition agreements enable multiple political parties to form a unified government, enhancing stability and broad representation by integrating diverse viewpoints and policy priorities. However, coalition agreements often face drawbacks such as prolonged negotiation periods, potential policy compromises that dilute original party platforms, and increased risk of internal conflicts leading to government instability. These agreements require continuous cooperation and trust-building to maintain effective governance and prevent fragmentation.
Choosing the Right Agreement: Key Considerations
Choosing the right agreement between power-sharing and coalition involves assessing the political context, party goals, and stability requirements. Power-sharing agreements emphasize equal participation and mutual vetoes, suited for deeply divided societies seeking inclusive governance. Coalition agreements focus on policy compromises and joint decision-making, ideal for parties aiming to form a majority government and implement shared agendas.
Power-sharing agreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com