Political alignment shapes how individuals perceive policies, influence voting behavior, and engage in public discourse. Understanding your political stance can clarify the motivations behind electoral choices and party support. Explore the rest of this article to gain deeper insights into the complexities of political alignment.
Table of Comparison
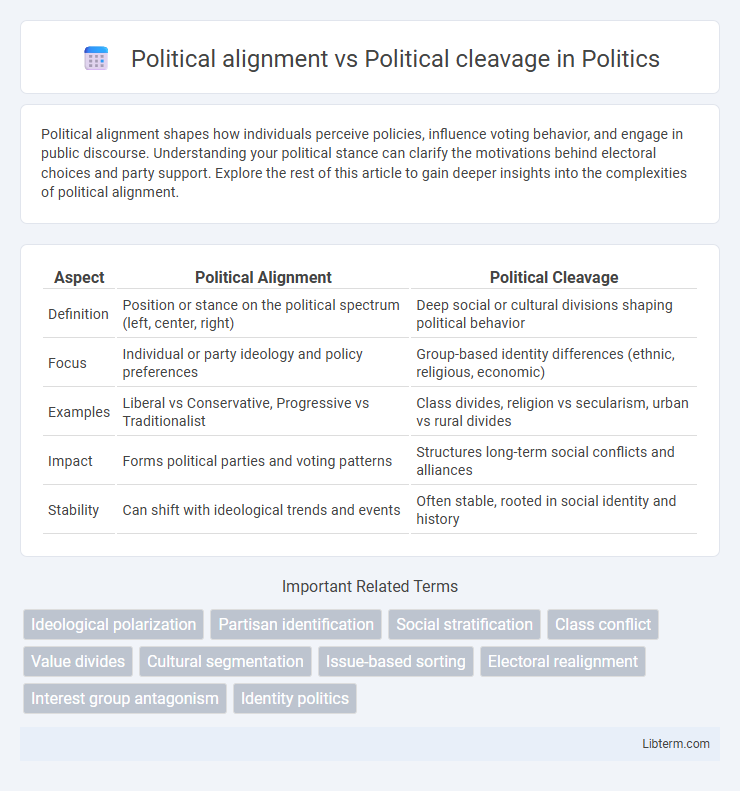
| Aspect | Political Alignment | Political Cleavage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Position or stance on the political spectrum (left, center, right) | Deep social or cultural divisions shaping political behavior |
| Focus | Individual or party ideology and policy preferences | Group-based identity differences (ethnic, religious, economic) |
| Examples | Liberal vs Conservative, Progressive vs Traditionalist | Class divides, religion vs secularism, urban vs rural divides |
| Impact | Forms political parties and voting patterns | Structures long-term social conflicts and alliances |
| Stability | Can shift with ideological trends and events | Often stable, rooted in social identity and history |
Defining Political Alignment
Political alignment refers to the consistent political attitudes, values, and beliefs that guide an individual's or group's stance on policies, ideologies, and party affiliations. It reflects a stable orientation within the political spectrum such as left-wing, right-wing, or centrist positions, influencing voting behavior and political participation. In contrast, political cleavage involves societal divisions based on factors like class, religion, ethnicity, or region, which create persistent conflicts and shape party systems.
Understanding Political Cleavage
Political cleavage refers to the deep and lasting social divisions that shape political conflict, often based on factors such as class, ethnicity, religion, or ideology. Understanding political cleavage involves analyzing how these divisions influence voting behavior, party formation, and policy debates within a society. Political alignment, by contrast, describes the patterns of support individuals or groups give to particular parties, often reflecting underlying cleavages but more focused on current political loyalty and behavior.
Historical Origins of Cleavages
Historical origins of political cleavages lie in deep-rooted social, economic, and cultural divisions that structured societies long before modern political parties emerged. Key cleavages often stem from conflicts such as class struggles, religious differences, and ethnic divisions, which shape collective group identities and political loyalties over time. These foundational splits influence political alignment by channeling voters' preferences and party formation according to entrenched social divisions.
Factors Influencing Political Alignment
Factors influencing political alignment include social class, religion, ethnicity, and economic interests, which shape individuals' attachment to specific political parties or ideologies. Geographic location and historical context also play critical roles by affecting exposure to political messages and group identities. Media consumption and peer networks further reinforce political alignment by shaping perceptions and attitudes toward political issues and candidates.
Types of Political Cleavages
Political cleavages refer to the deep and lasting divisions in society based on social, economic, ethnic, or cultural differences, shaping group identities and political behavior. Types of political cleavages commonly include class cleavage, which divides voters by socioeconomic status; religious cleavage, reflecting divergent faiths and their political interests; ethnic cleavage, often centered on language, race, or cultural heritage; and urban-rural cleavage, highlighting different priorities and lifestyles between city dwellers and rural populations. These cleavages influence party systems, voting patterns, and policy preferences, distinguishing them from political alignment, which describes individual or collective adherence to a particular political ideology or party over time.
Political Alignment in Contemporary Politics
Political alignment in contemporary politics refers to the consistent ideological positioning of individuals or groups along the political spectrum, often reflected in party loyalty and policy preferences. It shapes voting behavior and influences coalition-building within legislative bodies, impacting governance and policy outcomes. Unlike political cleavage, which denotes deep societal divisions such as class, race, or religion, political alignment captures stable affiliations that guide political participation and identity formation.
The Role of Social Identity in Cleavages
Political cleavages stem from deep-rooted social identities such as ethnicity, religion, and class, shaping group loyalties and influencing voting behavior within societies. Social identity theory explains how individuals align politically by reinforcing in-group cohesion and out-group differentiation, intensifying cleavage structures. This alignment often solidifies party systems and affects policy preferences by embedding political disputes in social categories.
Impact on Party Systems
Political alignment refers to a stable, long-term identification of individuals or groups with a particular political party or ideology, shaping consistent voting behavior. Political cleavage represents deep societal divisions such as class, religion, or ethnicity that create distinct voter groups and influence the structure of party competition. These cleavages significantly impact party systems by determining the number of parties, their ideological positions, and the stability or volatility within the political landscape.
Political Realignment and Cleavage Shifts
Political realignment involves a fundamental and lasting shift in the political landscape, often triggered by major social or economic changes that alter voter coalitions and party systems. Cleavage shifts refer to changes in the social divisions, such as class, religion, or ethnicity, that structure political preferences and voter alignments over time. Understanding political realignment requires analyzing how cleavage shifts disrupt traditional voting patterns, leading to new alliances and party dominance.
Implications for Democracy and Governance
Political alignment reflects individuals' consistent support for particular parties or ideologies, whereas political cleavage denotes deep societal divisions based on ethnicity, class, religion, or region. The persistence of strong political cleavages can lead to polarized electorates, complicating consensus-building and affecting democratic stability. Effective governance relies on managing these cleavages to prevent factionalism while political alignment helps anchor citizens' political identities and policy expectations.
Political alignment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com