Sunrise law requires organizations to identify and address privacy and data protection issues early in the development of new products or services, ensuring compliance with regulations and safeguarding user information. By integrating privacy considerations from the start, this proactive approach minimizes risks and enhances trust with your customers. Discover how implementing sunrise law principles can benefit your business in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
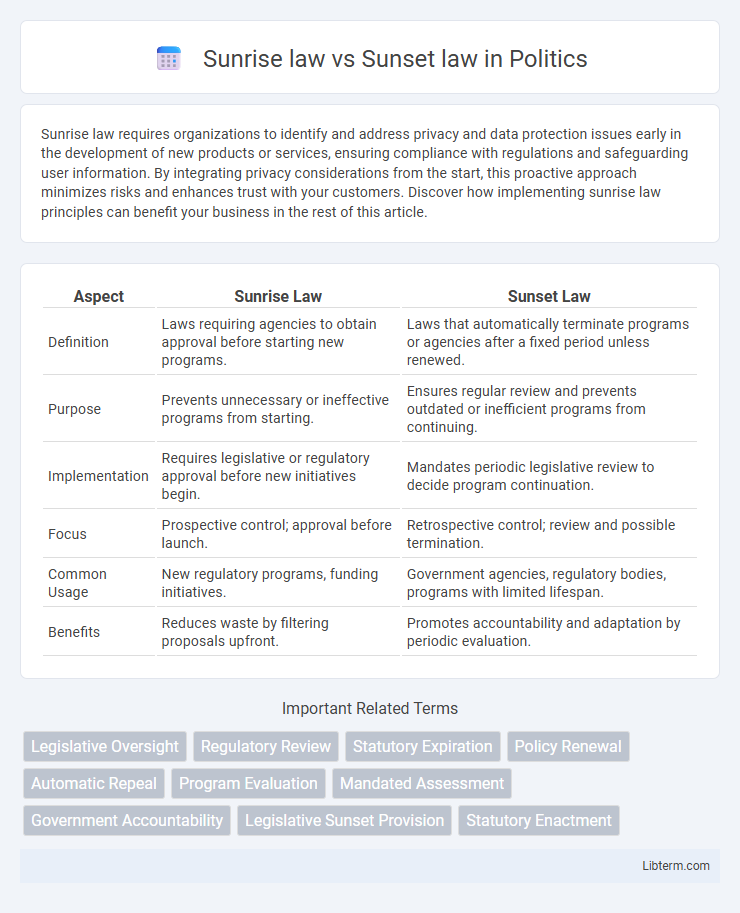
| Aspect | Sunrise Law | Sunset Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Laws requiring agencies to obtain approval before starting new programs. | Laws that automatically terminate programs or agencies after a fixed period unless renewed. |
| Purpose | Prevents unnecessary or ineffective programs from starting. | Ensures regular review and prevents outdated or inefficient programs from continuing. |
| Implementation | Requires legislative or regulatory approval before new initiatives begin. | Mandates periodic legislative review to decide program continuation. |
| Focus | Prospective control; approval before launch. | Retrospective control; review and possible termination. |
| Common Usage | New regulatory programs, funding initiatives. | Government agencies, regulatory bodies, programs with limited lifespan. |
| Benefits | Reduces waste by filtering proposals upfront. | Promotes accountability and adaptation by periodic evaluation. |
Understanding Sunrise Laws: Definition and Purpose
Sunrise laws require new regulatory agencies or programs to undergo a thorough review and approval process before they can be established, ensuring that they address a clear public need and operate efficiently. These laws aim to prevent unnecessary government expansion by evaluating the necessity, feasibility, and potential impact of proposed regulations. By mandating detailed justifications and legislative oversight, sunrise laws promote transparency and accountability in the creation of regulatory bodies.
What Are Sunset Laws? An Overview
Sunset laws are legal statutes designed to automatically terminate a government program, agency, or law after a predetermined period unless renewed through legislative action. These laws promote accountability by requiring periodic review and reassessment of the effectiveness and necessity of public policies or institutions. Many states in the U.S. employ sunset laws to prevent outdated or redundant regulations from remaining in effect indefinitely.
Key Differences Between Sunrise and Sunset Laws
Sunrise laws require new programs or regulations to receive formal approval before implementation, ensuring legislative oversight and preventing unnecessary policies. Sunset laws mandate the automatic expiration of existing laws or agencies after a set period unless actively renewed, promoting periodic review and accountability. These mechanisms balance innovation with regulation, with sunrise laws emphasizing preemptive evaluation and sunset laws focusing on ongoing assessment.
Historical Background of Sunrise and Sunset Legislation
Sunrise and sunset laws originated in the mid-20th century to promote governmental accountability and efficiency by systematically reviewing regulatory agencies and programs. Sunset laws mandate the automatic expiration of laws or agencies after a set period unless expressly renewed, reflecting efforts first institutionalized in Texas in 1977. Sunrise laws, conversely, require prior evaluation before new regulations or agencies are created, aiming to prevent unnecessary government expansion through careful cost-benefit analysis.
Criteria and Process for Enacting Sunrise Laws
Sunrise laws require comprehensive criteria including impact analysis, cost-benefit evaluation, and stakeholder consultation before enacting new regulations, ensuring accountability and necessity. The process involves rigorous review by legislative bodies or advisory commissions to assess potential legal, economic, and social effects. These laws mandate that proposed regulations demonstrate clear justification and effectiveness prior to implementation.
Implementation and Effects of Sunset Laws
Sunset laws require periodic review and automatic expiration of government programs or agencies unless expressly renewed, promoting accountability and efficiency by ensuring outdated or ineffective policies are terminated. Implementation involves scheduled legislative evaluations, often every few years, triggering data-driven assessments of a program's performance, cost-effectiveness, and public benefit. The effects of sunset laws include reduced government waste, increased transparency, and incentivized continuous improvement, though they may also cause uncertainty and disruptions if critical programs face abrupt termination without adequate transition planning.
Advantages of Sunrise Laws in Public Policy
Sunrise laws facilitate proactive evaluation of emerging technologies and businesses before market entry, reducing regulatory uncertainty and avoiding potential risks. These laws encourage innovation by providing clear guidelines and ensuring only viable, beneficial products or services receive approval. Public policy benefits from increased transparency and better allocation of regulatory resources, promoting economic growth and consumer protection simultaneously.
Limitations and Criticisms of Sunset Laws
Sunset laws impose automatic expiration dates on government programs and agencies, limiting long-term accountability and potentially disrupting valuable services when renewals face political challenges. Critics argue these laws create uncertainty, complicate budget planning, and may lead to the premature termination of effective initiatives due to procedural constraints rather than performance metrics. Unlike sunrise laws, which mandate evaluation before program creation, sunset laws focus on arbitrary deadlines, sometimes overlooking the nuanced impact and operational needs of ongoing programs.
Case Studies: Sunrise vs. Sunset Laws in Practice
Sunrise laws require new regulations to be evaluated before enactment, ensuring policies address real-world issues effectively, as demonstrated by Washington State's comprehensive cost-benefit analyses preventing unnecessary legislation. Sunset laws mandate periodic review and expiration of existing laws unless actively renewed, exemplified by Texas's automatic termination of state agencies every 12 years, which enhances governmental accountability and reduces outdated regulations. Case studies reveal that Sunrise laws emphasize proactive scrutiny while Sunset laws focus on ongoing legislative oversight, both contributing to dynamic legal frameworks.
Future Trends in Regulatory Oversight: Sunrise vs. Sunset
Future trends in regulatory oversight reveal increasing adoption of Sunrise laws that require legislative review before new regulations are enacted, promoting proactive evaluation and stakeholder engagement to ensure necessity and efficacy. Sunset laws continue to play a critical role by mandating periodic reviews and automatic expiration of existing regulations, reducing regulatory burdens and enhancing accountability. The interplay between Sunrise and Sunset laws fosters a dynamic regulatory environment focused on transparency, adaptability, and evidence-based policy making.
Sunrise law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com