Regime consolidation refers to the process by which a government strengthens its control and legitimacy over a state, ensuring stability and continuity in political power. This involves institutionalizing authority, managing opposition, and securing the loyalty of key political actors. Explore this article to understand the mechanisms behind regime consolidation and its impact on political systems.
Table of Comparison
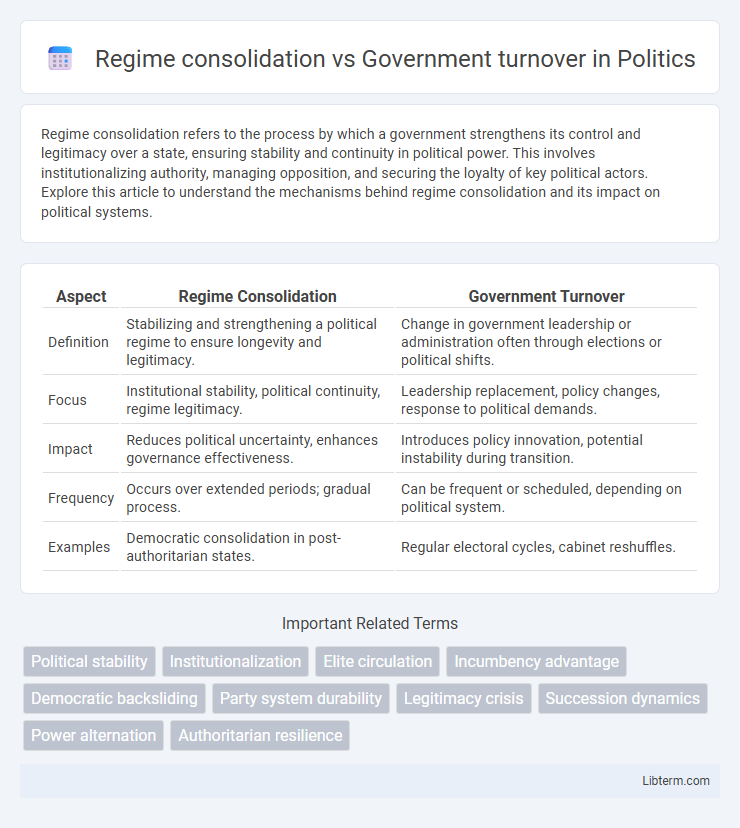
| Aspect | Regime Consolidation | Government Turnover |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stabilizing and strengthening a political regime to ensure longevity and legitimacy. | Change in government leadership or administration often through elections or political shifts. |
| Focus | Institutional stability, political continuity, regime legitimacy. | Leadership replacement, policy changes, response to political demands. |
| Impact | Reduces political uncertainty, enhances governance effectiveness. | Introduces policy innovation, potential instability during transition. |
| Frequency | Occurs over extended periods; gradual process. | Can be frequent or scheduled, depending on political system. |
| Examples | Democratic consolidation in post-authoritarian states. | Regular electoral cycles, cabinet reshuffles. |
Defining Regime Consolidation and Government Turnover
Regime consolidation refers to the process by which a political regime secures its stability and legitimacy, ensuring the continuation of its governing structures without significant opposition or disruption. Government turnover involves the replacement of one ruling administration or leadership with another, often through elections, coups, or other political mechanisms, indicating a shift in power dynamics. Understanding the distinction between regime consolidation and government turnover is crucial for analyzing political stability, as the former emphasizes regime durability while the latter highlights changes in executive authority.
Historical Contexts of Regime Stability
Regime consolidation refers to the process whereby a governing system achieves long-term stability and legitimacy, often marked by institutionalization and public acceptance, while government turnover indicates frequent changes in leadership or administration without necessarily altering the underlying regime. Historical contexts of regime stability highlight patterns where consolidated regimes, such as constitutional democracies or authoritarian states with strong institutions, resist government turnover disruptions, contrasting sharply with fragile regimes characterized by coups, revolutions, or political instability. Key examples include the prolonged stability of post-World War II Western democracies versus the frequent government turnovers during the interwar period in Europe and Latin America, underscoring the role of institutional structures, political culture, and economic development in fostering regime consolidation.
Factors Driving Regime Consolidation
Factors driving regime consolidation include strong institutional frameworks, effective control over security forces, and a cohesive ruling elite that suppresses dissent and manages elite competition. Economic stability and the ability to deliver public goods also enhance regime legitimacy and reduce incentives for government turnover. Control over media and information channels further stabilizes regimes by shaping public perception and limiting opposition mobilization.
Causes and Impacts of Government Turnover
Government turnover typically results from political instability, economic crises, or public dissatisfaction with policy outcomes, triggering shifts in leadership and administrative structures. Such changes can disrupt policy continuity and institutional memory, often leading to short-term economic uncertainty and weakened governance capacity. However, turnover may also catalyze political reform and democratic consolidation if new administrations introduce effective policies and restore public trust.
Institutional Mechanisms for Regime Durability
Institutional mechanisms for regime durability underpin regime consolidation by embedding power structures within legal frameworks and bureaucratic institutions, securing long-term control and limiting government turnover. Formalized rules, such as constitutions or electoral systems, create predictable governance patterns that reduce uncertainty and enhance regime legitimacy. Conversely, regimes with weak institutionalization experience frequent government turnovers due to fragile power bases and lack of systematic political continuity.
Political Consequences of Frequent Turnover
Frequent government turnover undermines regime consolidation by fostering political instability and eroding public trust in institutions. Political consequences include weakened policy continuity, compromised governance effectiveness, and increased susceptibility to authoritarian backsliding. Persistent leadership changes disrupt long-term development strategies and often trigger social unrest or factional conflicts.
Regime Consolidation and Democratic Resilience
Regime consolidation strengthens democratic resilience by embedding institutions that secure the rule of law, protect civil liberties, and encourage political participation, thereby reducing vulnerabilities to authoritarian backsliding. Effective regime consolidation involves establishing electoral integrity and independent judiciaries, which together sustain public trust and political stability. In contrast to frequent government turnover, robust consolidation ensures that democratic norms and practices persist despite leadership changes, promoting long-term stability and governance quality.
Case Studies: Consolidated Regimes vs High Turnover Governments
Consolidated regimes such as Singapore exhibit political stability with prolonged leadership and institutional resilience, fostering sustained policy implementation and investment confidence. In contrast, high government turnover countries like Italy experience frequent leadership changes that disrupt policy continuity and undermine governance effectiveness. Case studies reveal that regime consolidation correlates strongly with economic growth and social stability, whereas rapid government turnover often exacerbates political fragmentation and economic volatility.
Societal Responses to Regime Stability and Change
Societal responses to regime consolidation often involve increased political trust, civic engagement, and social cohesion, which reinforce regime stability by minimizing public dissent and resistance. In contrast, government turnover typically triggers varied societal reactions, including political mobilization, protests, and demands for reform, reflecting public dissatisfaction or desires for change. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for analyzing how social behavior influences the durability or transformation of political regimes.
Balancing Political Adaptability and System Stability
Regime consolidation enhances long-term system stability by institutionalizing political norms and reducing volatility, whereas government turnover reflects political adaptability through responsive leadership changes. Balancing these dynamics requires a framework that supports periodic leadership renewal without jeopardizing the foundational institutions that ensure regime continuity. Effective governance systems integrate mechanisms such as constitutional safeguards and flexible political processes to harmonize adaptability with stability.
Regime consolidation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com