Global governance encompasses the cooperation among international organizations, governments, and institutions to address worldwide challenges such as climate change, security, and economic stability. Effective global governance requires collective decision-making, enforcement mechanisms, and inclusive policies to ensure equitable development and peace. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these mechanisms impact Your role in shaping a sustainable future.
Table of Comparison
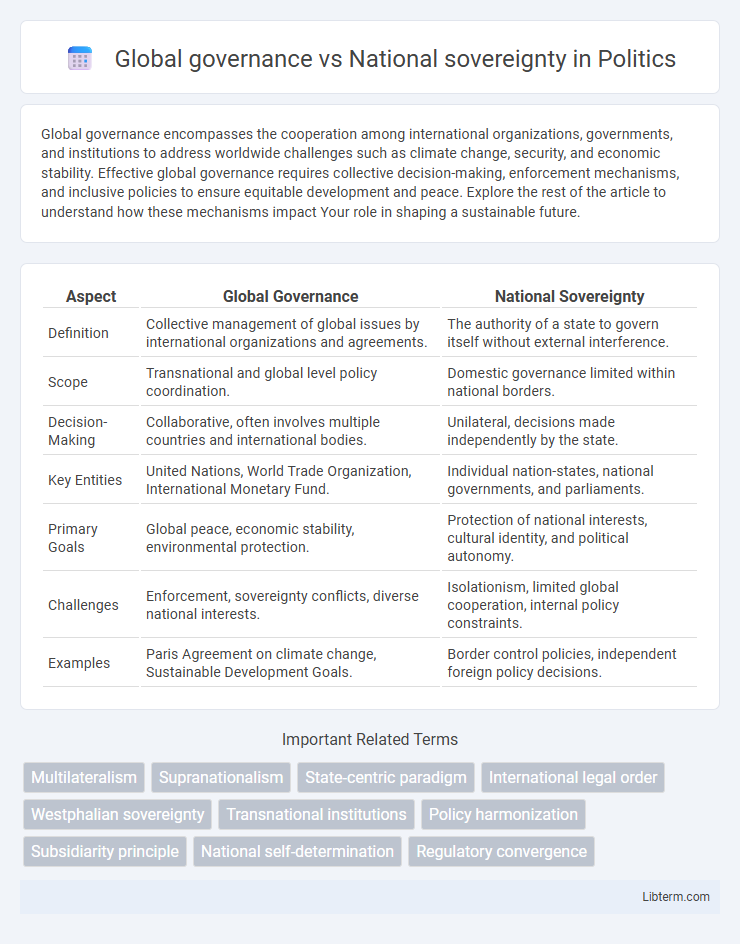
| Aspect | Global Governance | National Sovereignty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collective management of global issues by international organizations and agreements. | The authority of a state to govern itself without external interference. |
| Scope | Transnational and global level policy coordination. | Domestic governance limited within national borders. |
| Decision-Making | Collaborative, often involves multiple countries and international bodies. | Unilateral, decisions made independently by the state. |
| Key Entities | United Nations, World Trade Organization, International Monetary Fund. | Individual nation-states, national governments, and parliaments. |
| Primary Goals | Global peace, economic stability, environmental protection. | Protection of national interests, cultural identity, and political autonomy. |
| Challenges | Enforcement, sovereignty conflicts, diverse national interests. | Isolationism, limited global cooperation, internal policy constraints. |
| Examples | Paris Agreement on climate change, Sustainable Development Goals. | Border control policies, independent foreign policy decisions. |
Introduction to Global Governance and National Sovereignty
Global governance refers to the collective management of international issues through institutions like the United Nations and the World Trade Organization, aiming to address global challenges such as climate change and security. National sovereignty emphasizes a nation's authority to govern itself without external interference, safeguarding political independence and cultural identity. The tension between global governance and national sovereignty centers on balancing effective international cooperation with respecting individual state autonomy.
Defining Global Governance: Scope and Objectives
Global governance encompasses the frameworks, institutions, and processes that facilitate cooperation and regulation beyond national borders to address transnational challenges such as climate change, security, and economic stability. Its scope includes international organizations like the United Nations, World Trade Organization, and regional bodies, aimed at harmonizing policies, promoting peace, and ensuring sustainable development. The primary objectives of global governance are to manage collective action problems, uphold international law, and foster equitable resource distribution while respecting the diverse interests of sovereign states.
National Sovereignty: Principles and Importance
National sovereignty embodies the principle of supreme authority within a country's territorial boundaries, granting governments exclusive rights to govern without external interference. It ensures the protection of a nation's laws, culture, and political autonomy, serving as the foundation for democratic decision-making and national identity. Upholding national sovereignty is crucial for maintaining legal order, economic stability, and the ability to respond independently to global challenges.
Historical Evolution of Governance Models
The historical evolution of governance models reveals a shift from fragmented national sovereignty to increased global governance frameworks, driven by the complexities of international trade, security, and environmental challenges. Early nation-states maintained absolute sovereignty, but post-World War II institutions like the United Nations and World Trade Organization signaled a move toward cooperative governance, balancing national interests with collective global responsibilities. This transition highlights the tension between preserving state autonomy and embracing supranational structures necessary for addressing transnational issues.
Key Institutions in Global Governance
Key institutions in global governance such as the United Nations, World Trade Organization, and International Monetary Fund play crucial roles in fostering international cooperation and addressing transnational challenges. These institutions often navigate complex tensions between promoting collective action and respecting national sovereignty, as member states retain the authority to make decisions within their borders. Effective global governance depends on balancing institutional influence with the preservation of state autonomy to ensure legitimacy and compliance.
Tensions Between Global Governance and State Sovereignty
Tensions between global governance and state sovereignty arise from competing interests where international rules and institutions often challenge the absolute authority of nation-states over their own territory. Issues such as trade regulations, human rights enforcement, and environmental policies highlight conflicts as states resist external control to preserve autonomy. This dynamic creates ongoing debates about balancing effective global cooperation with respect for national independence and legal jurisdiction.
Case Studies: Sovereignty Challenges in Practice
The case studies of the European Union and the United Nations illustrate key sovereignty challenges where member states cede partial control to supranational institutions for collective benefits. In the EU, debates over policies like migration and fiscal regulations reveal tensions between shared governance and national interests. Similarly, UN peacekeeping missions often face resistance from host nations safeguarding sovereignty while balancing international mandates.
Benefits and Challenges of Global Governance
Global governance promotes coordinated efforts among countries to address transnational issues like climate change, pandemics, and economic stability, enhancing global security and resource management efficiency. It facilitates the establishment of international norms and regulations that can reduce conflicts and improve cooperation but often faces resistance from nations prioritizing national sovereignty and self-determination. Challenges include balancing diverse political interests and ensuring equitable representation while avoiding the dilution of national laws and cultural identities.
Balancing National Interests with International Obligations
Balancing national interests with international obligations requires navigating the tension between global governance frameworks and the sovereignty of individual states. States seek to protect their economic, political, and cultural priorities while adhering to international agreements on trade, security, and human rights. Effective cooperation hinges on mechanisms that respect sovereign decisions yet promote collective action for global challenges like climate change, pandemics, and transnational security threats.
Future Perspectives on Sovereignty in a Globalized World
The future of national sovereignty in a globalized world hinges on adapting governance frameworks to balance state autonomy with international cooperation on issues like climate change, cybersecurity, and trade. Emerging models of global governance emphasize multi-level collaboration, blending supranational institutions and regional alliances to enhance policy effectiveness without completely eroding state control. Technological advancements and digital diplomacy will play crucial roles in reshaping sovereignty, enabling states to protect their interests while participating in a more interconnected and interdependent global system.
Global governance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com