A motion of thanks is a formal expression of gratitude typically presented after a significant speech or event, often in parliamentary or organizational settings. It acknowledges the efforts and contributions of individuals or groups, fostering a culture of appreciation and respect. Discover how crafting an effective motion of thanks can enhance your communication and diplomatic skills by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
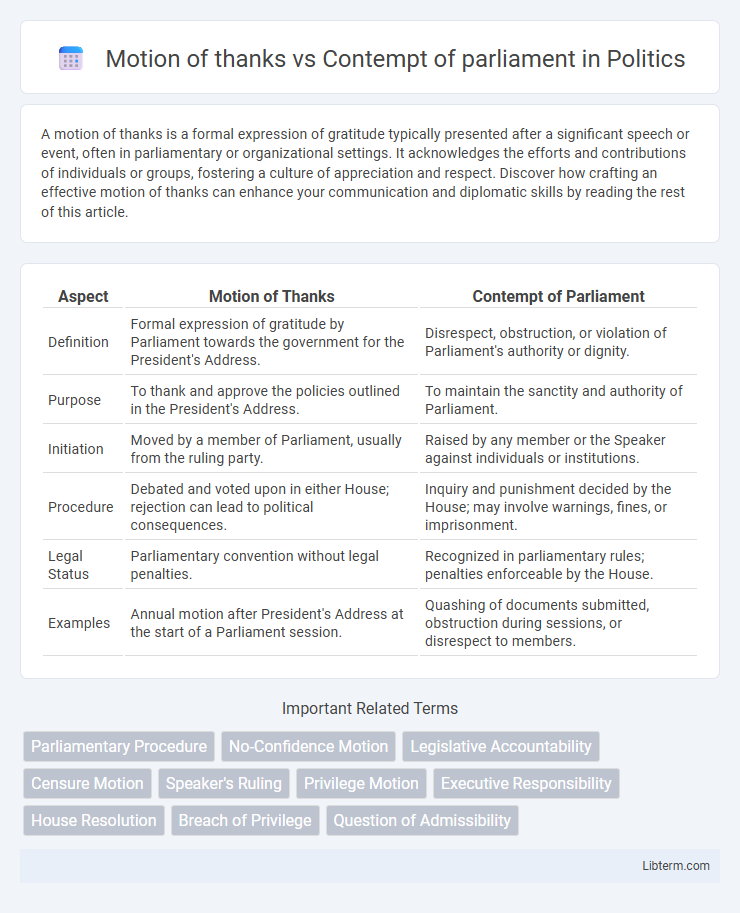
| Aspect | Motion of Thanks | Contempt of Parliament |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal expression of gratitude by Parliament towards the government for the President's Address. | Disrespect, obstruction, or violation of Parliament's authority or dignity. |
| Purpose | To thank and approve the policies outlined in the President's Address. | To maintain the sanctity and authority of Parliament. |
| Initiation | Moved by a member of Parliament, usually from the ruling party. | Raised by any member or the Speaker against individuals or institutions. |
| Procedure | Debated and voted upon in either House; rejection can lead to political consequences. | Inquiry and punishment decided by the House; may involve warnings, fines, or imprisonment. |
| Legal Status | Parliamentary convention without legal penalties. | Recognized in parliamentary rules; penalties enforceable by the House. |
| Examples | Annual motion after President's Address at the start of a Parliament session. | Quashing of documents submitted, obstruction during sessions, or disrespect to members. |
Introduction to Motion of Thanks and Contempt of Parliament
The Motion of Thanks is a formal expression of gratitude by the parliament towards the President for the Address outlining the government's policies and programmes, serving as a key moment for legislative debate on the administration's agenda. Contempt of Parliament refers to any action or conduct that obstructs or impedes the parliament's functions, disrespects its authority, or disregards its privileges, ensuring the institution's dignity and effectiveness are maintained. Both concepts underscore the interplay between parliamentary accountability and authority, with the Motion of Thanks enabling scrutiny and Contempt provisions safeguarding legislative integrity.
Historical Background of Both Concepts
The Motion of Thanks traces back to British parliamentary traditions where it served as a formal expression of gratitude to the government for the King's or President's address, evolving over centuries as a key democratic practice. Contempt of Parliament has its roots in the medieval English Parliament, designed to uphold the authority and dignity of the legislature by penalizing acts that obstruct parliamentary functions or defy its prerogatives. Both concepts reflect the historical development of parliamentary sovereignty and the balance between executive accountability and legislative authority.
Definition and Purpose of Motion of Thanks
A Motion of Thanks is a formal parliamentary procedure expressing gratitude to the President for the address outlining government policies and priorities, serving as a platform for members to discuss and evaluate the administration's agenda. It aims to foster accountability and support for the government's legislative and policy framework by allowing constructive debate. In contrast, Contempt of Parliament refers to actions or behaviors that obstruct or disrespect the authority and dignity of the legislative body, ensuring the effective functioning and integrity of parliamentary proceedings.
Meaning and Significance of Contempt of Parliament
Contempt of Parliament refers to any act that obstructs or impedes the functioning or authority of the legislative body, including disobedience to parliamentary rules or defiance of its orders. It is significant because it upholds the dignity, autonomy, and effective functioning of Parliament, ensuring members and non-members respect legislative procedures and decisions. Unlike the Motion of Thanks, which is a formal vote expressing gratitude towards the government's address, contempt safeguards the fundamental integrity and authority of parliamentary institutions.
Constitutional Provisions Governing Both
The Motion of Thanks is governed by Article 87(3) of the Indian Constitution, requiring the Lok Sabha to express gratitude for the President's address, and is a key parliamentary procedure for accountability. Contempt of Parliament is based on the inherent powers of the Houses, supported by Articles 105 and 194, empowering them to punish for breach of privilege or contempt to maintain authority and dignity. Both actions reflect constitutional mechanisms ensuring parliamentary discipline and effective functioning within India's legislative framework.
Key Differences Between Motion of Thanks and Contempt of Parliament
Motion of Thanks is a formal expression of gratitude by the parliament towards the government for the President's Address, while Contempt of Parliament refers to acts that obstruct or discredit the functioning of the parliamentary institution. Motion of Thanks is a routine procedure debated annually and aims to endorse or criticize government policies, whereas Contempt of Parliament involves punitive actions against individuals or entities violating parliamentary privileges, which can include disobedience or disrespect. The former is a deliberative process focused on government accountability, and the latter serves as a protective mechanism preserving the authority and dignity of the legislature.
Procedures for Initiating Each Process
A Motion of Thanks is initiated by a member of the legislature who moves a formal expression of gratitude following the President's address, requiring prior notice and usually discussed in both houses of Parliament. In contrast, Contempt of Parliament proceedings begin when a member alleges an act that obstructs the legislature's functioning, typically initiated by a resolution moved by any member and referred to a committee for investigation. Both processes involve specific procedural rules, but while the Motion of Thanks centers on debate and approval, Contempt proceedings focus on inquiry and potential punitive action.
Notable Cases and Examples
The Motion of Thanks on the President's Address has witnessed notable instances such as the 1978 refusal by the opposition to vote, signaling dissent without halting parliamentary proceedings. Contempt of Parliament cases include the 2001 expulsion of MPs for contempt during the telecom scam investigations, illustrating stringent measures to uphold legislative integrity. These examples emphasize the parliamentary mechanisms addressing respect and accountability within India's legislative framework.
Impact on Parliamentary Democracy
Motion of thanks strengthens parliamentary democracy by promoting executive accountability and enabling debate on government policies, fostering transparency and public trust. Contempt of parliament safeguards the institution's authority and privileges, ensuring members and outsiders respect parliamentary procedures and decisions, which protects democratic functions from obstruction or undue influence. Both mechanisms reinforce the balance of power, transparency, and institutional integrity essential for a robust parliamentary democracy.
Conclusion: Relevance in Modern Parliamentary Practice
The motion of thanks and contempt of parliament both serve crucial functions in maintaining legislative accountability and decorum, with the former reflecting approval of government policies and the latter addressing breaches in parliamentary privilege. In modern parliamentary practice, these motions ensure the balance of power between the executive and legislature, reinforcing democratic oversight and discipline. Their continued relevance lies in promoting transparency, safeguarding institutional authority, and fostering responsible governance within parliamentary democracies.
Motion of thanks Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com