Idealist inspires individuals to make a positive impact through volunteering, nonprofit work, and social change opportunities. By connecting You with meaningful projects and organizations, it fosters a community dedicated to driving real-world solutions. Explore the article to discover how Idealist can empower Your journey toward creating lasting change.
Table of Comparison
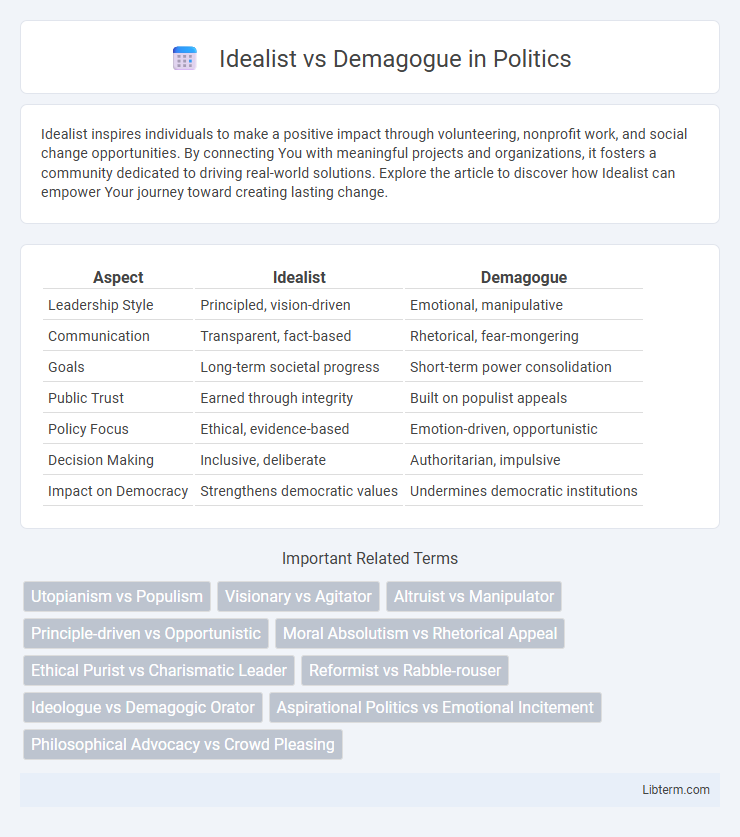
| Aspect | Idealist | Demagogue |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Style | Principled, vision-driven | Emotional, manipulative |
| Communication | Transparent, fact-based | Rhetorical, fear-mongering |
| Goals | Long-term societal progress | Short-term power consolidation |
| Public Trust | Earned through integrity | Built on populist appeals |
| Policy Focus | Ethical, evidence-based | Emotion-driven, opportunistic |
| Decision Making | Inclusive, deliberate | Authoritarian, impulsive |
| Impact on Democracy | Strengthens democratic values | Undermines democratic institutions |
Defining the Idealist and the Demagogue
An idealist pursues principled goals driven by ethical values, envisioning a better future through reasoned policy and inclusive dialogue. A demagogue exploits emotions, fears, and prejudices to manipulate public opinion, often prioritizing personal power over truth and democratic integrity. Understanding these distinctions highlights the contrast between constructive leadership and divisive rhetoric in political discourse.
Core Values: Principles vs. Popularity
Idealists prioritize unwavering adherence to core principles, emphasizing integrity, ethical consistency, and long-term vision over immediate approval. Demagogues manipulate popular opinion by appealing to emotions and desires, often sacrificing foundational values to gain mass support. This fundamental clash between steadfast ideals and transient popularity shapes leadership styles and public trust.
Communication Styles: Inspiration vs. Manipulation
Idealists utilize transparent and empathetic communication to inspire trust and motivate positive change, emphasizing authenticity and shared values. Demagogues rely on emotional manipulation, exaggeration, and fear-mongering to control public opinion and maintain power. The communication style of idealists fosters genuine engagement, while demagogues prioritize influence through deception and division.
Leadership Approaches: Visionary vs. Opportunist
Idealist leadership centers on a visionary approach, emphasizing long-term goals, ethical values, and inspiring collective progress through innovation and hope. Demagogues adopt an opportunist leadership style, leveraging emotional appeals, populist rhetoric, and immediate gains to manipulate public sentiment for personal power. This contrast highlights visionary leaders fostering sustainable change, while opportunists prioritize short-term influence over principled direction.
Impact on Society and Culture
Idealists inspire societal progress by promoting visionary principles and ethical values that encourage cooperation, innovation, and cultural enrichment. Demagogues often undermine social cohesion by exploiting fears and prejudices, leading to polarization, misinformation, and erosion of democratic institutions. The cultural impact of idealists typically fosters resilience and inclusivity, while demagogues contribute to division and social instability.
Historical Examples: Icons and Infamous Figures
Idealists such as Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr. championed nonviolent resistance and social justice, inspiring global movements for civil rights and independence. In contrast, demagogues like Adolf Hitler and Joseph McCarthy manipulated public fears and prejudices to seize power, often leading to oppression and conflict. Historical examples illustrate the stark contrast between visionary leaders focused on ethical progress and populist figures exploiting social divisions for authoritarian control.
Public Perception and Influence
Idealists are perceived as visionary leaders who inspire positive change through ethical principles and forward-thinking ideas, often gaining trust and long-term support. Demagogues leverage emotional appeals and populist rhetoric, manipulating public fears and prejudices to achieve immediate influence, often at the cost of social cohesion. Public perception of idealists centers on credibility and hope, while demagogues evoke polarization and distrust.
Navigating Ethics and Morality
Idealists prioritize ethical consistency and moral principles, seeking to uphold universal values even in complex situations while emphasizing integrity and altruism. Demagogues manipulate ethical narratives to gain power, often exploiting fears and prejudices by distorting moral norms for personal or political gain. Navigating ethics and morality requires discerning genuine commitment to principles from manipulative rhetoric to ensure accountability and social justice.
Challenges and Criticisms Faced
Idealists often face challenges related to perceived naivety and impracticality, as critics argue their visions can overlook complex real-world constraints. Demagogues encounter intense scrutiny for manipulative tactics and fostering division, drawing criticism for prioritizing personal power over collective well-being. Both archetypes struggle with maintaining credibility while addressing public demands in volatile political environments.
Relevance in Today’s Political Climate
Idealists offer visionary policies focused on sustainable progress and societal well-being, emphasizing ethics and inclusive dialogue in governance. Demagogues exploit fear and division through populist rhetoric and manipulative tactics, often undermining democratic institutions and social cohesion. In today's polarized political climate, understanding the contrast between idealism and demagoguery is crucial for promoting informed voting and resilient democracies.
Idealist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com