A clerk plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth office operations by managing records, handling correspondence, and supporting administrative tasks efficiently. Their attention to detail and organizational skills contribute significantly to maintaining accurate data and facilitating communication within the workplace. Discover how mastering clerk responsibilities can enhance your career and streamline your daily workflow in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
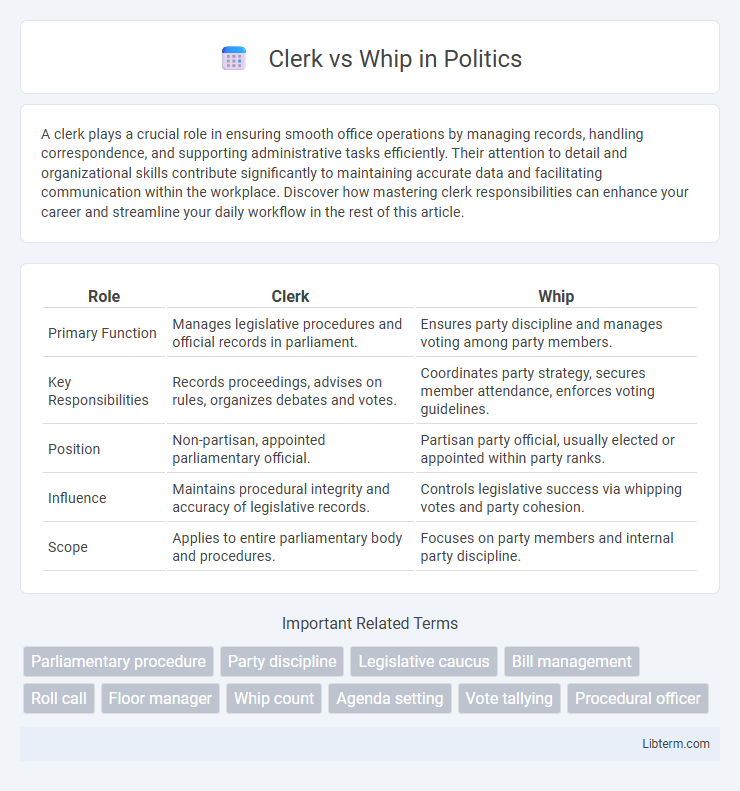
| Role | Clerk | Whip |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages legislative procedures and official records in parliament. | Ensures party discipline and manages voting among party members. |
| Key Responsibilities | Records proceedings, advises on rules, organizes debates and votes. | Coordinates party strategy, secures member attendance, enforces voting guidelines. |
| Position | Non-partisan, appointed parliamentary official. | Partisan party official, usually elected or appointed within party ranks. |
| Influence | Maintains procedural integrity and accuracy of legislative records. | Controls legislative success via whipping votes and party cohesion. |
| Scope | Applies to entire parliamentary body and procedures. | Focuses on party members and internal party discipline. |
Understanding the Roles: Clerk vs Whip
The Clerk manages legislative documentation, records proceedings, and ensures procedural compliance, serving as the administrative backbone of parliamentary functions. The Whip focuses on party discipline, coordinating votes, and maintaining member attendance to secure legislative priorities. Both roles are integral to effective parliamentary operations, with the Clerk handling procedural accuracy and the Whip managing political strategy.
Historical Origins of Clerks and Whips
Clerks and whips both originated in British parliamentary traditions, with clerks emerging in the medieval English Parliament as essential officials responsible for maintaining records and advising on procedural rules. Whips developed later in the 18th century as party enforcers tasked with ensuring member attendance and discipline during votes. The evolution of clerks reflected a focus on administrative continuity, while whips became pivotal in party cohesion and legislative strategy.
Core Responsibilities of a Clerk
The Clerk in legislative bodies manages official records, maintains roll calls, and ensures accurate documentation of proceedings, playing a pivotal role in the legislative workflow. This position oversees the distribution of legislative materials and coordinates communication between members, committees, and administrative staff. The Clerk also facilitates the processing of bills, resolutions, and amendments, ensuring regulatory compliance and procedural accuracy throughout legislative sessions.
Essential Duties of a Whip
A Whip's essential duties include maintaining party discipline, ensuring members attend key votes, and communicating the party leadership's position on legislative matters. They coordinate voting strategies and manage vote counting to secure the passage of bills aligned with party goals. Whips also serve as a vital liaison between party leaders and rank-and-file members, monitoring potential defections and persuading undecided legislators.
Hierarchical Position in Legislative Bodies
The Clerk typically holds an administrative and nonpartisan role responsible for record-keeping and procedural guidance, positioned outside the formal political hierarchy in legislative bodies. The Whip occupies a partisan leadership role, ranking above many members as an essential enforcer of party discipline and vote coordination within the legislature. Hierarchically, Whips are integral to the party leadership team, while Clerks serve as impartial parliamentary officers supporting legislative operations.
Key Skills: Clerk vs Whip
The Clerk requires exceptional organizational skills, meticulous attention to detail, and strong knowledge of parliamentary procedures to manage legislative documentation and ensure accurate record-keeping. The Whip demands superior interpersonal skills, political strategy, and negotiation abilities to maintain party discipline and coordinate voting among party members. Both roles emphasize communication proficiency, but the Clerk focuses on procedural expertise while the Whip prioritizes influence and party cohesion.
Impact on Legislative Process
The Clerk plays a critical role in the legislative process by managing official records, preparing agendas, and ensuring procedural compliance, which facilitates smooth and organized sessions. In contrast, the Whip primarily influences the legislative process through political strategy, mobilizing party members to secure votes and maintain party discipline on key legislation. Together, the Clerk's administrative support and the Whip's political coordination significantly impact the efficiency and outcome of legislative decision-making.
Collaboration and Interaction with Members
The Clerk facilitates collaboration by managing legislative documents and aiding communication between members and committees, ensuring transparent information flow. The Whip fosters interaction by coordinating party members' attendance and voting strategies, maintaining cohesion and discipline within the party ranks. Together, the Clerk's procedural expertise and the Whip's party management create an effective legislative environment promoting member cooperation.
Challenges Faced by Clerks and Whips
Clerks and whips face distinct challenges rooted in their roles within legislative bodies. Clerks encounter difficulties in managing complex legislative documentation, ensuring procedural accuracy, and maintaining impartiality under intense political pressure. Whips struggle with enforcing party discipline, coordinating voting strategies, and navigating intra-party conflicts that can affect legislative outcomes.
Clerk vs Whip: Choosing the Right Role
Clerk and Whip hold distinct responsibilities in legislative processes, with the Clerk managing procedural records and documentation, ensuring legislative accuracy, while the Whip focuses on party discipline, coordinating votes, and maintaining party strategy. Choosing the right role depends on an individual's strengths in organizational detail and legal knowledge for Clerk versus leadership and persuasive communication skills for Whip. Understanding these functional differences optimizes legislative efficiency and political effectiveness within governing bodies.
Clerk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com