A semi-closed primary allows registered party members and independents to vote in a party's primary, while registered members of other parties are excluded. This system balances inclusivity with party control to influence candidate selection. Explore the rest of the article to understand how semi-closed primaries impact your voting options and election outcomes.
Table of Comparison
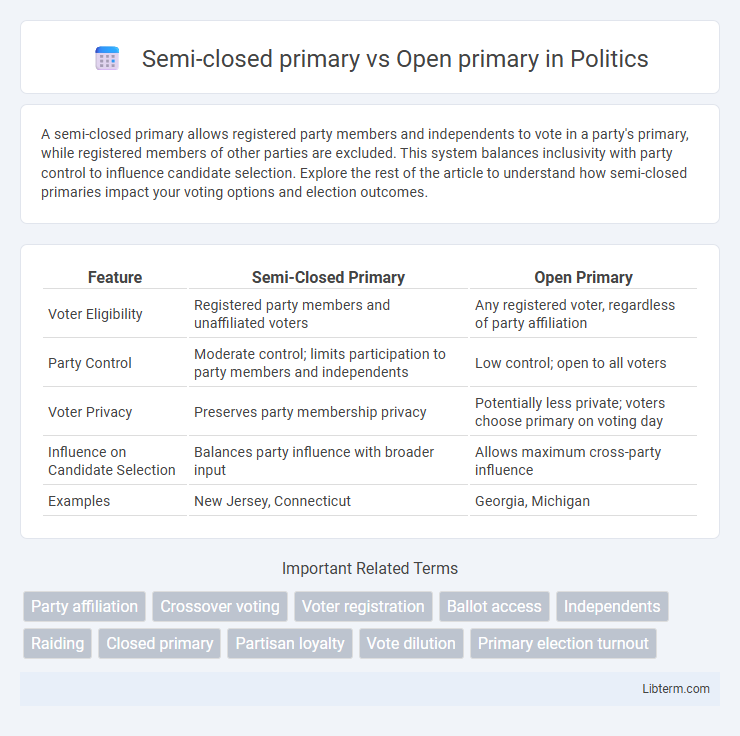
| Feature | Semi-Closed Primary | Open Primary |
|---|---|---|
| Voter Eligibility | Registered party members and unaffiliated voters | Any registered voter, regardless of party affiliation |
| Party Control | Moderate control; limits participation to party members and independents | Low control; open to all voters |
| Voter Privacy | Preserves party membership privacy | Potentially less private; voters choose primary on voting day |
| Influence on Candidate Selection | Balances party influence with broader input | Allows maximum cross-party influence |
| Examples | New Jersey, Connecticut | Georgia, Michigan |
Understanding Primary Election Systems
Semi-closed primary systems allow voters registered with a specific party and unaffiliated voters to participate, balancing party control and voter inclusivity. Open primaries permit all registered voters to choose any party's ballot regardless of affiliation, increasing voter participation but risking cross-party influence. Understanding these systems highlights the trade-offs between party influence and broad voter access in selecting candidates.
What Is a Semi-Closed Primary?
A semi-closed primary allows only registered party members and unaffiliated voters to participate in selecting a party's candidate, balancing inclusivity with party control. This system prevents members of opposing parties from voting in the primary, reducing the risk of strategic cross-party influence. Semi-closed primaries are used by several U.S. states seeking to maintain party integrity while encouraging broader voter participation.
What Is an Open Primary?
An open primary allows voters to participate in any party's primary regardless of their registered party affiliation, providing greater flexibility and inclusiveness in the voting process. Unlike a semi-closed primary where only registered party members and unaffiliated voters can participate in a party's primary, open primaries do not restrict voter choice based on party registration. This system aims to increase voter turnout and encourage cross-party appeal by opening the candidate selection to a broader electorate.
Key Differences Between Semi-Closed and Open Primaries
Semi-closed primaries allow only registered party members and independents to vote, limiting participation to those aligned or unaffiliated, while open primaries permit all registered voters to choose any party's ballot regardless of their party affiliation. Voter privacy differs as semi-closed systems keep party preference confidential but restrict ballot choice, whereas open primaries provide greater flexibility but less party-specific confidentiality. These differences impact party control over candidate selection and voter turnout dynamics within the electoral process.
Voter Eligibility in Semi-Closed Primaries
Semi-closed primaries restrict voter eligibility to registered party members and, in some states, allow unaffiliated voters to participate by choosing a party's ballot, ensuring candidates appeal primarily to their base while expanding inclusivity. This system contrasts with open primaries, which permit all registered voters to participate regardless of party affiliation, potentially encouraging crossover voting. Semi-closed primaries balance party control over candidate selection with limited voter access, influencing electoral strategies and voter engagement.
Voter Participation in Open Primaries
Open primaries allow all registered voters to participate regardless of party affiliation, significantly increasing voter participation rates compared to semi-closed primaries, which restrict voting to registered party members and unaffiliated voters. Research shows open primaries tend to engage more independent and moderate voters, resulting in a broader representation of the electorate. Higher voter turnout in open primaries can influence candidate selection by reflecting a wider range of voter preferences beyond strict party lines.
Pros and Cons of Semi-Closed Primaries
Semi-closed primaries allow registered party members and independents to participate, increasing voter turnout while maintaining a degree of party control over candidate selection. This system balances inclusivity with party loyalty, preventing potential exploitation by opposing party members seen in open primaries. However, semi-closed primaries may still limit participation compared to fully open primaries, potentially reducing the diversity of voter input in the candidate nomination process.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Open Primaries
Open primaries allow voters to participate regardless of party affiliation, increasing voter turnout and fostering a more inclusive democratic process. However, they risk party nominees being selected by non-party members, potentially diluting party ideology and weakening party unity. Open primaries also increase the likelihood of strategic voting, where voters cast ballots to influence opposing party outcomes rather than genuinely supporting their preferred candidates.
Impact on Party Dynamics and Election Outcomes
Semi-closed primaries restrict voting to registered party members and unaffiliated voters, which tends to strengthen party cohesion by limiting influence from opposing party members. Open primaries allow any registered voter to participate regardless of party affiliation, often leading to more moderate candidate selections to appeal to a broader electorate. The choice between these systems significantly affects party dynamics by shaping candidate platforms and can influence election outcomes by determining voter turnout and engagement across party lines.
Which Primary System Best Supports Democratic Representation?
Semi-closed primary systems restrict voting to registered party members and independents, promoting party cohesion and reducing crossover voting, which strengthens the representation of core party interests. Open primary systems allow all voters to participate regardless of party affiliation, enhancing inclusiveness and enabling broader democratic representation by reflecting a wider range of voter preferences. Research indicates that semi-closed primaries better support party accountability, while open primaries foster greater voter engagement and ideological diversity in candidate selection.
Semi-closed primary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com