Egalitarianism promotes equal rights and opportunities for all individuals, challenging social hierarchies and systemic inequalities. It emphasizes fairness in wealth distribution, education, and political representation to create a more just society. Explore the rest of this article to understand how egalitarian principles can impact Your community and daily life.
Table of Comparison
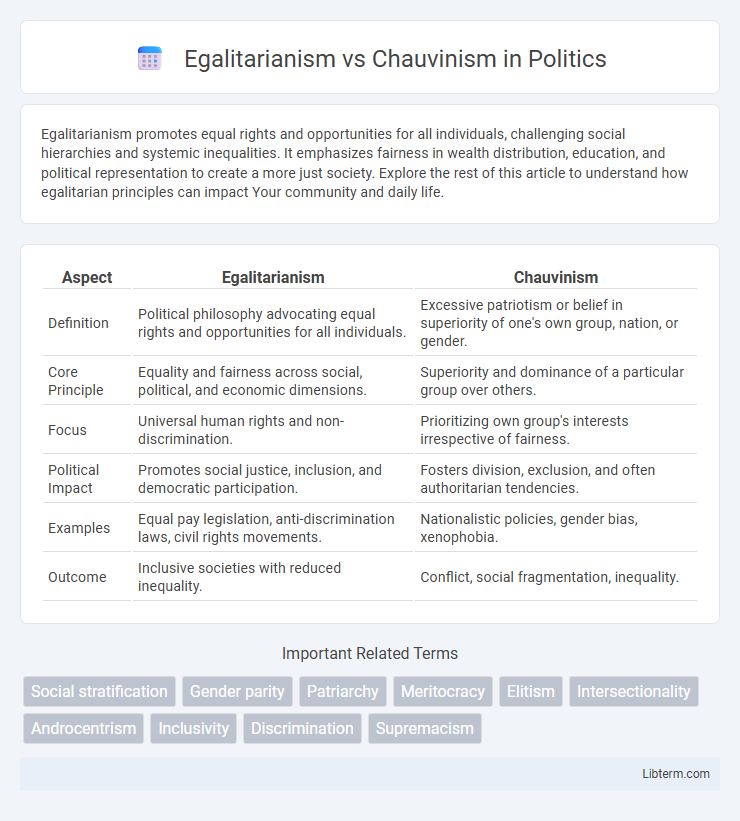
| Aspect | Egalitarianism | Chauvinism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political philosophy advocating equal rights and opportunities for all individuals. | Excessive patriotism or belief in superiority of one's own group, nation, or gender. |
| Core Principle | Equality and fairness across social, political, and economic dimensions. | Superiority and dominance of a particular group over others. |
| Focus | Universal human rights and non-discrimination. | Prioritizing own group's interests irrespective of fairness. |
| Political Impact | Promotes social justice, inclusion, and democratic participation. | Fosters division, exclusion, and often authoritarian tendencies. |
| Examples | Equal pay legislation, anti-discrimination laws, civil rights movements. | Nationalistic policies, gender bias, xenophobia. |
| Outcome | Inclusive societies with reduced inequality. | Conflict, social fragmentation, inequality. |
Introduction to Egalitarianism and Chauvinism
Egalitarianism promotes equal rights, opportunities, and treatment for all individuals regardless of gender, ethnicity, or social status, emphasizing fairness and social justice. Chauvinism, often characterized by an excessive or prejudiced loyalty to one's own group, particularly manifests in male chauvinism, which asserts male superiority and dominance. Understanding these contrasting ideologies highlights the social and psychological foundations that influence gender relations and power dynamics in societies.
Defining Key Concepts: Egalitarianism and Chauvinism
Egalitarianism advocates for equal rights, opportunities, and treatment across all genders, races, and social groups, emphasizing fairness and justice in societal structures. Chauvinism refers to an irrational belief in the superiority of one's own group, often manifesting as aggressive bias or discrimination, particularly in gender or national contexts. Understanding these key concepts highlights the fundamental ideological divide between promoting equality and perpetuating supremacy based on identity factors.
Historical Roots and Evolution
Egalitarianism traces its roots to Enlightenment thinkers like Rousseau and Locke, advocating equal rights and social justice as foundations of modern democracy. Chauvinism originated from aggressive nationalism and gender biases, often linked to 19th-century militarism and imperialism that promoted superiority of one group over others. Over time, egalitarian principles evolved through civil rights movements, while chauvinistic ideologies persisted in various forms, influencing social and political conflicts globally.
Social Impacts of Egalitarianism
Egalitarianism promotes social equality by reducing disparities in wealth, education, and access to opportunities, fostering inclusive communities where diverse groups thrive. Societies embracing egalitarian values experience lower rates of social unrest and higher levels of trust and cooperation among citizens. Enhanced social mobility and equitable resource distribution resulting from egalitarian principles lead to sustainable economic growth and improved overall well-being.
Consequences of Chauvinistic Attitudes
Chauvinistic attitudes foster discrimination, perpetuating inequality and social division by undermining diversity and fair treatment in workplaces and communities. Such biases contribute to hostility, reduced collaboration, and systemic oppression, which can hinder economic growth and social cohesion. The long-term consequences often include diminished mental health, increased conflict, and the marginalization of vulnerable groups.
Gender Perspectives: Equality vs Superiority
Egalitarianism advocates for gender equality, emphasizing equal rights, opportunities, and treatment regardless of gender, grounded in principles of fairness and justice. Chauvinism, in contrast, promotes gender superiority, often manifesting as male dominance and discrimination against women, undermining social equity and inclusiveness. Gender perspectives in egalitarianism highlight empowerment and dismantling stereotypes, while chauvinism perpetuates inequality and reinforces traditional power hierarchies.
Egalitarianism in Politics and Governance
Egalitarianism in politics and governance emphasizes equal rights, opportunities, and treatment for all citizens regardless of race, gender, or socioeconomic status, promoting inclusive decision-making processes. Policies rooted in egalitarian principles often support social welfare programs, equitable access to education, and anti-discrimination laws designed to reduce systemic inequality. This political ideology aims to create a just society where power and resources are distributed fairly, counteracting hierarchical or chauvinistic systems that prioritize certain groups over others.
Chauvinism in Modern Society
Chauvinism in modern society manifests as an aggressive and unquestioning belief in the superiority of one's group, often leading to discrimination and social division. This ideology undermines efforts toward equality by perpetuating biases based on gender, nationality, or ethnicity, resulting in systemic injustice and inequality. Contemporary challenges include combating chauvinistic attitudes through education, policy reforms, and promoting inclusive cultural norms.
Overcoming Chauvinism: Pathways to Egalitarianism
Overcoming chauvinism requires fostering awareness of its deep-rooted biases and promoting inclusive education that highlights equality and respect for all individuals regardless of gender, race, or nationality. Implementing policies that ensure equal opportunities in workplaces and social institutions dismantles systemic favoritism and empowers marginalized groups. Encouraging open dialogues and cultural shifts toward empathy and mutual recognition catalyzes the transition from chauvinistic attitudes to a more egalitarian society.
Conclusion: Striving for an Equitable Society
Striving for an equitable society requires rejecting chauvinism's bias and embracing egalitarianism's principle of equal rights and opportunities for all individuals regardless of gender, race, or social background. Achieving true equity demands systemic reforms that dismantle discriminatory structures and promote inclusive policies fostering fairness and mutual respect. Prioritizing empathy and education encourages societal cohesion, paving the way for sustainable justice and equality.
Egalitarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com