The majority party holds the most seats in a legislative assembly, giving it significant control over the legislative agenda and decision-making processes. This dominance enables the party to influence policies, pass laws, and appoint key leadership positions effectively. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the majority party shapes governance and impacts your political environment.
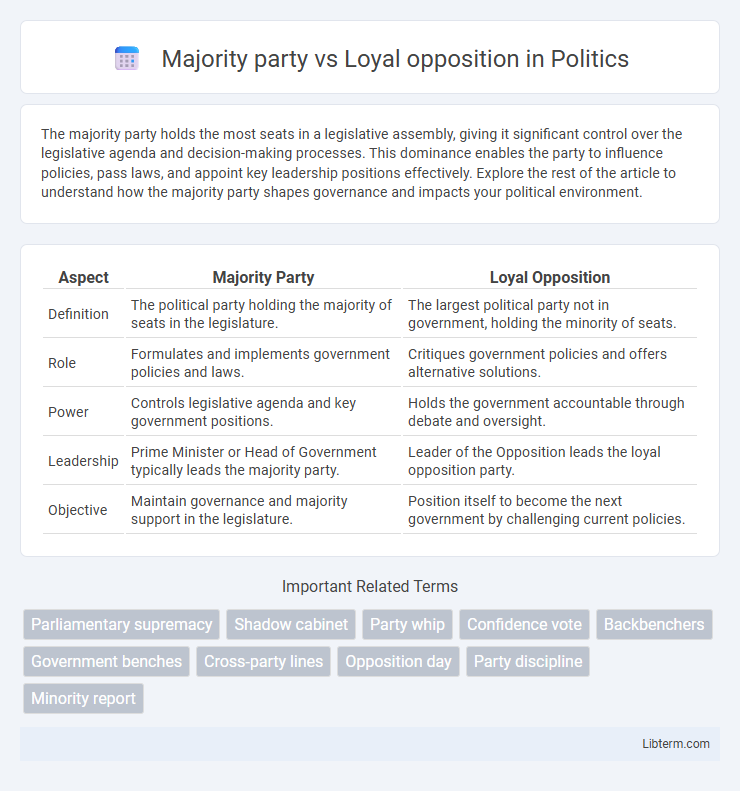
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Majority Party | Loyal Opposition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The political party holding the majority of seats in the legislature. | The largest political party not in government, holding the minority of seats. |
| Role | Formulates and implements government policies and laws. | Critiques government policies and offers alternative solutions. |
| Power | Controls legislative agenda and key government positions. | Holds the government accountable through debate and oversight. |
| Leadership | Prime Minister or Head of Government typically leads the majority party. | Leader of the Opposition leads the loyal opposition party. |
| Objective | Maintain governance and majority support in the legislature. | Position itself to become the next government by challenging current policies. |
Understanding the Majority Party: Roles and Responsibilities
The majority party holds the primary responsibility for setting the legislative agenda and controlling the flow of bills in the government. Its roles include appointing committee chairs, managing debates, and ensuring party discipline during votes to effectively implement policies. Understanding these functions is crucial to grasp how the majority party influences governance and policy-making processes.
Defining the Loyal Opposition in Democratic Systems
The loyal opposition in democratic systems refers to the political party or group that does not hold the majority of seats but remains committed to democratic principles by challenging and scrutinizing the policies of the majority party. This opposition plays a crucial role in ensuring governmental accountability and fostering healthy political debate without undermining the legitimacy of the ruling party. By offering alternative policies and holding the majority accountable, the loyal opposition strengthens the democratic process and prevents the concentration of power.
Historical Evolution of Majority Party and Loyal Opposition
The historical evolution of the majority party and loyal opposition traces back to the development of parliamentary democracy in 17th-century England, where the majority party formed the government while the loyal opposition provided a critical yet supportive role. Over time, this dual structure became a fundamental principle in Westminster-style democracies, ensuring political stability by balancing governance with accountability. The loyal opposition evolved from being a mere dissenting group to an institutionalized entity responsible for scrutinizing government policies and presenting alternative solutions.
Importance of Balance: Majority Rule vs. Constructive Dissent
The balance between the majority party and the loyal opposition is crucial for a healthy democracy, ensuring that majority rule is tempered by constructive dissent that holds power accountable. Majority rule enables efficient governance and policy implementation, while the loyal opposition provides critical scrutiny, alternative perspectives, and safeguards against authoritarianism. This dynamic fosters transparency, promotes diverse viewpoints, and strengthens legislative decision-making, ultimately supporting democratic integrity and responsiveness.
Legislative Powers of the Majority Party
The majority party in a legislative body wields significant power to shape policy agendas, control committee chairmanships, and influence the legislative calendar. This dominance allows the majority party to prioritize bills, manage debates, and facilitate or obstruct legislation through voting strength. The ability to organize legislative procedures and discipline party members further consolidates the majority party's authority in lawmaking processes.
Oversight Functions of the Loyal Opposition
The Loyal Opposition plays a crucial role in democratic governance by performing oversight functions that ensure the majority party remains accountable and transparent. Through mechanisms such as questioning government policies, scrutinizing legislative proposals, and investigating administrative actions, the opposition helps prevent abuses of power and promotes good governance. This persistent examination of the majority party's decisions safeguards democratic principles and strengthens institutional checks and balances.
Impact on Policy-Making: Collaboration or Confrontation
The majority party holds the power to set legislative agendas and pass policies efficiently, often driving initiatives aligned with their platform. Loyal opposition plays a critical role by scrutinizing majority proposals, offering alternative policies, and representing minority viewpoints to ensure balanced governance. The dynamic between cooperation and confrontation shapes the effectiveness of policy-making, influencing legislative outcomes and democratic accountability.
Democratic Stability: Safeguarding Checks and Balances
The majority party plays a crucial role in governance by setting legislative agendas and forming the government, while the loyal opposition ensures democratic stability through rigorous oversight and accountability mechanisms. Effective checks and balances are maintained as the loyal opposition scrutinizes the majority party's decisions, preventing abuse of power and promoting transparency. This dynamic fosters a healthy political environment where differing views contribute to policy refinement and uphold the rule of law.
Challenges Facing Majority Parties and Loyal Oppositions
Majority parties face challenges such as maintaining party unity amid diverse member interests and managing the pressure of delivering on campaign promises while governing effectively. Loyal oppositions struggle with limited access to resources and influence, making it difficult to present viable alternatives and hold the majority accountable. Both must navigate the complexities of public opinion, media scrutiny, and internal factionalism to sustain their political relevance and effectiveness.
Future Trends: Strengthening Democratic Institutions
Future trends indicate that the dynamic between majority parties and loyal opposition will increasingly emphasize transparency, accountability, and constructive debate to strengthen democratic institutions. Advancements in digital platforms enable greater citizen engagement, promoting inclusive policymaking and reinforcing checks and balances. Institutional reforms are expected to enhance the capacity of opposition parties to effectively scrutinize government actions, ensuring resilient and vibrant democracies.
Majority party Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com