A deliberative parliament serves as the cornerstone of democratic governance, where elected representatives engage in thoughtful discussion and decision-making on public policies. It fosters transparency, accountability, and inclusive debate, ensuring that diverse viewpoints shape legislation. Explore the article to understand how your voice influences the legislative process through this vital institution.
Table of Comparison
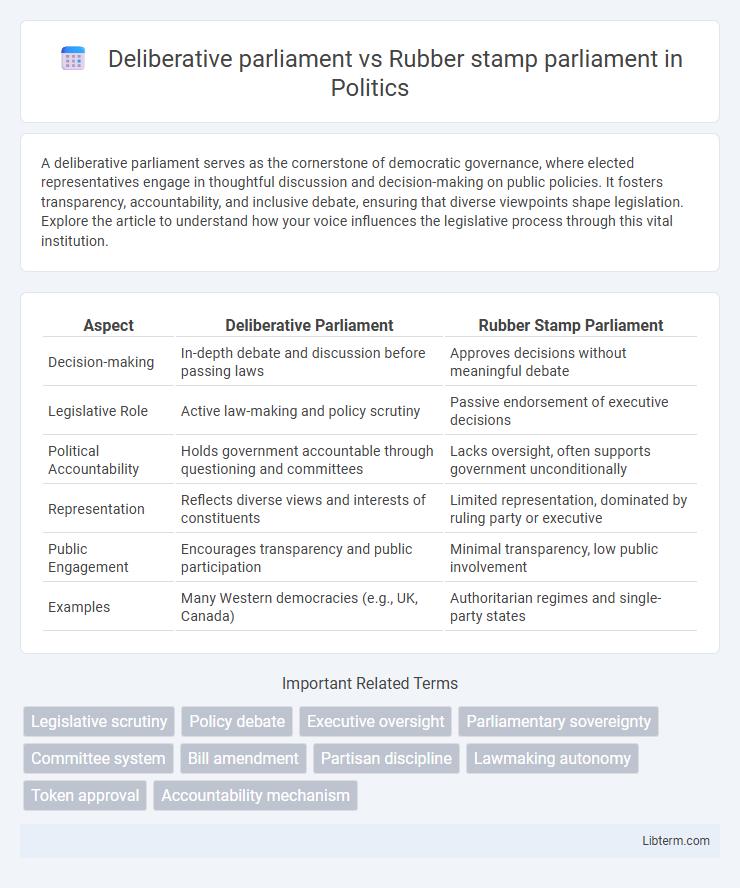
| Aspect | Deliberative Parliament | Rubber Stamp Parliament |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-making | In-depth debate and discussion before passing laws | Approves decisions without meaningful debate |
| Legislative Role | Active law-making and policy scrutiny | Passive endorsement of executive decisions |
| Political Accountability | Holds government accountable through questioning and committees | Lacks oversight, often supports government unconditionally |
| Representation | Reflects diverse views and interests of constituents | Limited representation, dominated by ruling party or executive |
| Public Engagement | Encourages transparency and public participation | Minimal transparency, low public involvement |
| Examples | Many Western democracies (e.g., UK, Canada) | Authoritarian regimes and single-party states |
Introduction to Parliamentary Models
Deliberative parliaments engage in critical debate, thorough examination of legislation, and active participation of members to ensure sound decision-making based on diverse viewpoints. Rubber stamp parliaments primarily approve decisions made by the executive branch with little to no meaningful discussion, serving as a formal endorsement rather than a forum for legislative scrutiny. Understanding these parliamentary models is essential for analyzing the effectiveness and democratic nature of legislative processes worldwide.
Defining Deliberative Parliaments
Deliberative parliaments prioritize thorough discussion, critical debate, and informed decision-making, emphasizing transparency and accountability in legislative processes. Members actively engage in examining diverse viewpoints, ensuring policies reflect comprehensive analysis rather than mere approval. This contrasts sharply with rubber stamp parliaments, where the legislative body merely endorses decisions made by executive authorities without meaningful scrutiny.
Characteristics of Rubber Stamp Parliaments
Rubber stamp parliaments primarily function as formal institutions that approve decisions made by the executive branch without meaningful debate or opposition. These parliaments often lack independent legislative power, with sessions characterized by unanimous votes and minimal scrutiny of government policies. Their main characteristic is to legitimize predetermined outcomes, undermining democratic processes and checks and balances.
Historical Evolution of Parliamentary Functions
The historical evolution of parliamentary functions reveals a transformation from purely "rubber stamp" parliaments, which pass laws without debate, to deliberative parliaments characterized by robust discussion, scrutiny, and representation. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many colonial and authoritarian regimes maintained rubber stamp parliaments primarily endorsing executive decisions. Modern democratic systems emphasize the deliberative role, ensuring legislative oversight, accountability, and diverse stakeholder engagement in policy-making processes.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Deliberative parliaments engage in thorough debate, considering diverse viewpoints and evidence before reaching decisions, ensuring policies are well-analyzed and representative of public interests. In contrast, rubber stamp parliaments simply approve decisions made by dominant authorities without meaningful discussion, limiting transparency and accountability in the decision-making process. This fundamental difference impacts the quality of legislation, with deliberative bodies contributing to more informed and democratic outcomes.
Impact on Democratic Governance
Deliberative parliaments enhance democratic governance by fostering informed debate, accountability, and diverse representation, which leads to more transparent and effective policy-making. Rubber stamp parliaments undermine democracy by merely approving decisions without scrutiny, eroding checks and balances and reducing public trust in political institutions. Strong deliberative processes are crucial for ensuring responsive governance and safeguarding democratic principles.
Role of Political Parties and Leadership
Deliberative parliaments feature active roles for political parties and leadership in shaping policy through debate, negotiation, and coalition-building, fostering transparency and accountability in governance. In contrast, rubber stamp parliaments have political parties and leadership largely controlled by executive authority, resulting in limited independent decision-making and primarily endorsing predetermined policies. The effectiveness of legislative function strongly depends on the autonomy and influence of political parties within the parliamentary framework.
Public Participation and Transparency
A deliberative parliament encourages extensive public participation through open debates, committee hearings, and consultations, ensuring transparency by providing accessible records and live broadcasts of sessions. In contrast, a rubber stamp parliament limits citizen input, often approving decisions without meaningful discussion, resulting in reduced transparency and diminished accountability to the public. Effective public participation and transparent processes are crucial indicators distinguishing deliberative parliaments from rubber stamp bodies.
Case Studies: Global Examples
The United Kingdom's Parliament exemplifies a deliberative parliament where diverse political parties engage in robust debates, scrutinizing legislation thoroughly before approval. In contrast, North Korea's Supreme People's Assembly functions primarily as a rubber stamp parliament, where decisions made by the ruling party are swiftly endorsed with minimal opposition or discourse. Case studies from India and South Africa highlight hybrid systems, where deliberative processes coexist with dominant party influences, affecting legislative accountability and democratic governance.
Future Trends and Reform Pathways
Future trends in parliamentary reform emphasize enhancing deliberative capacities through digital technologies, such as e-participation platforms and real-time data analytics, which promote transparent decision-making and informed debate. Reform pathways advocate for institutional changes including strengthened committee systems, increased public engagement, and improved legislative scrutiny to transform rubber stamp parliaments into deliberative ones. Empirical studies highlight that countries adopting these reforms experience higher policy legitimacy, better governance outcomes, and increased citizen trust in democratic institutions.
Deliberative parliament Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com