State initiatives play a crucial role in driving local economic growth and improving public services by addressing community-specific challenges through targeted policies. These programs often focus on education, infrastructure, healthcare, and environmental sustainability to enhance residents' quality of life. Explore the rest of the article to discover how state initiatives can directly impact your community and opportunities.
Table of Comparison
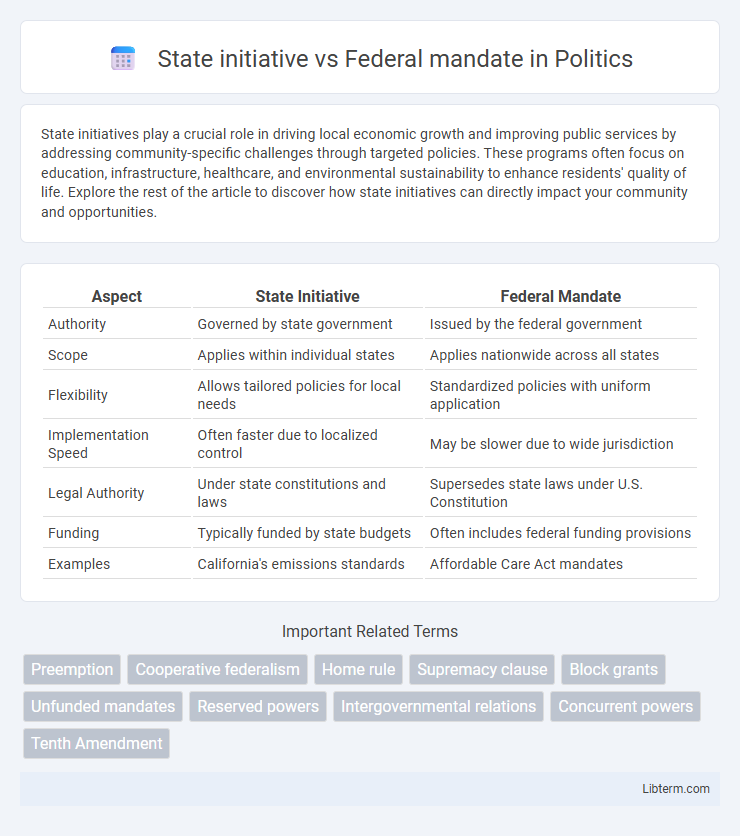
| Aspect | State Initiative | Federal Mandate |
|---|---|---|
| Authority | Governed by state government | Issued by the federal government |
| Scope | Applies within individual states | Applies nationwide across all states |
| Flexibility | Allows tailored policies for local needs | Standardized policies with uniform application |
| Implementation Speed | Often faster due to localized control | May be slower due to wide jurisdiction |
| Legal Authority | Under state constitutions and laws | Supersedes state laws under U.S. Constitution |
| Funding | Typically funded by state budgets | Often includes federal funding provisions |
| Examples | California's emissions standards | Affordable Care Act mandates |
Defining State Initiatives
State initiatives are legislative actions or referendums developed and approved within individual states to address specific local issues, bypassing federal involvement. These initiatives allow residents to directly propose, approve, or reject laws, reflecting unique state priorities and policies. Unlike federal mandates, state initiatives provide tailored solutions that respond to the cultural, economic, and political context of the state.
Understanding Federal Mandates
Federal mandates are legally binding requirements imposed by the national government on state and local governments, often tied to funding conditions or compliance standards. These mandates ensure uniformity in areas such as environmental regulation, civil rights, and public health, compelling states to adhere to specific federal policies regardless of local preferences. Understanding the legal and financial impact of federal mandates is crucial for states navigating autonomy challenges and resource allocation.
Key Differences: State vs Federal Authority
State initiatives allow individual states to create laws and policies tailored to local needs, exercising sovereignty in areas like education, health, and transportation. Federal mandates require states to comply with nationwide regulations established by the federal government, often backed by constitutional authority such as the Supremacy Clause. The primary difference lies in the source of authority: states have autonomous control unless overridden by federal law, which ensures uniformity across all states.
Historical Context of State and Federal Roles
State initiatives have historically reflected localized governance aimed at addressing region-specific needs, while federal mandates originate from the Constitution's allocation of powers to ensure nationwide uniformity. The balance of authority evolved through landmark events such as the New Deal, which expanded federal influence during economic crises, and civil rights movements that necessitated federal intervention to enforce equality. This dynamic tension continues to shape policy-making, with states pushing initiatives to assert autonomy and the federal government employing mandates to maintain national standards.
Advantages of State Initiatives
State initiatives offer the advantage of allowing localized policy-making tailored to the specific needs and values of individual populations, fostering innovation through experimentation with diverse approaches. These initiatives enable more rapid response to emerging issues compared to slower, uniform federal mandates, promoting greater citizen engagement and accountability at the local level. Such autonomy supports flexible governance that can adapt to regional economic, social, and environmental conditions more effectively than blanket federal regulations.
Challenges Posed by Federal Mandates
Federal mandates often create challenges for states by imposing uniform requirements that may not align with local priorities or capacities, leading to increased administrative and financial burdens. States struggle to comply with mandates without adequate federal funding, forcing reallocation of resources from other critical areas. This disconnect can result in legal disputes, implementation delays, and reduced policy effectiveness across diverse jurisdictions.
Case Studies: State Initiative Successes
California's renewable energy standards demonstrate the impact of state initiatives, achieving 60% clean energy by 2030 ahead of federal targets. Massachusetts' healthcare reforms expanded coverage and reduced costs through state-level innovation without waiting for federal mandates. Oregon's progressive climate policies cut greenhouse gas emissions by 25% since 2005, showcasing effective localized action driving national momentum.
Case Studies: Federal Mandate Impact
Federal mandates such as the Clean Air Act and the Affordable Care Act have driven nationwide policy compliance, significantly shaping state-level implementation strategies and resource allocation. Case studies reveal that federal mandates often create uniform standards, compelling states to adjust local governance and funding priorities to meet national objectives. The impact of these mandates highlights challenges in balancing state autonomy with federal requirements, often leading to legal disputes and varied levels of state compliance.
Balancing State Flexibility with Federal Oversight
State initiatives allow for tailored policies that address specific regional needs, promoting innovation and local responsiveness. Federal mandates ensure uniform standards and protect national interests, preventing disparities in critical areas such as healthcare, education, and environmental regulation. Balancing these approaches requires clear delineation of authority, collaborative frameworks, and mechanisms for accountability to maintain both state flexibility and effective federal oversight.
Future Trends in State-Federal Collaboration
Future trends in state-federal collaboration emphasize increasing integration of technology and data sharing to address public health, climate change, and infrastructure challenges. States are adopting more flexible policies while aligning with federal mandates to enhance responsiveness and innovation in governance. Enhanced intergovernmental partnerships and funding models are expected to drive cooperative solutions to complex societal issues.
State initiative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com