Consensus is a powerful tool for achieving agreement and cooperation within groups by ensuring all members contribute their perspectives and concerns. It fosters stronger collaboration, improved decision-making, and lasting commitment to the outcomes. Discover how mastering consensus techniques can enhance your teamwork and drive success in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
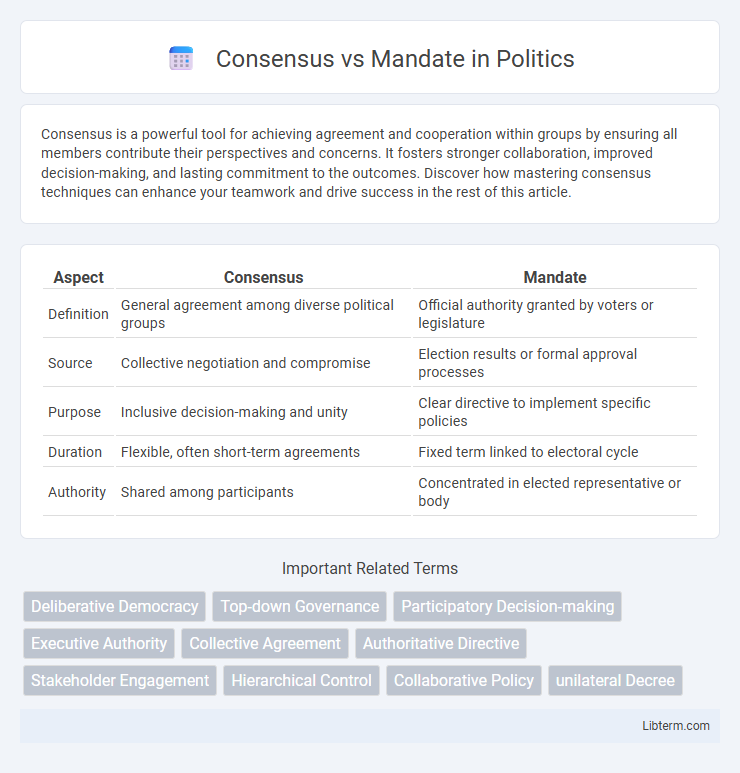
| Aspect | Consensus | Mandate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | General agreement among diverse political groups | Official authority granted by voters or legislature |
| Source | Collective negotiation and compromise | Election results or formal approval processes |
| Purpose | Inclusive decision-making and unity | Clear directive to implement specific policies |
| Duration | Flexible, often short-term agreements | Fixed term linked to electoral cycle |
| Authority | Shared among participants | Concentrated in elected representative or body |
Understanding Consensus and Mandate: Key Definitions
Consensus is a collaborative decision-making process where all parties reach general agreement, emphasizing mutual respect and shared goals, while mandate refers to an authoritative command or instruction given by a higher authority, often requiring compliance without negotiation. Understanding consensus involves recognizing its foundation in collective input and voluntary cooperation, whereas a mandate centers on directive power and obligation. Effective leadership balances these concepts by fostering consensus to encourage participation and using mandates to ensure decisive action when necessary.
Historical Context of Consensus and Mandate
The historical context of consensus traces back to ancient democratic practices where group decisions were made collectively to ensure unity and social cohesion, prominently seen in early Greek city-states and tribal councils. Mandate historically originates from the Roman legal system and medieval governance, where authority was granted through formal orders or commissions from a higher power, emphasizing hierarchical control and legitimacy. These contrasting origins highlight consensus as a cooperative process while mandate reflects an imposed directive grounded in legal or authoritative endorsement.
The Role of Consensus in Decision-Making
Consensus plays a crucial role in decision-making by fostering collective agreement among all participants, ensuring that diverse perspectives are valued and integrated into the final outcome. This inclusive approach enhances cooperation, reduces conflict, and promotes commitment to shared goals, which often leads to more sustainable and effective decisions. Unlike mandates, which rely on authoritative directives, consensus emphasizes collaboration and mutual understanding, strengthening team dynamics and long-term success.
Mandate: Centralized Authority and Its Impacts
Mandate refers to the authority granted to a centralized power to make decisions and enforce policies without requiring broad agreement from all stakeholders. This centralized authority enables swift decision-making and consistent policy implementation but can also lead to reduced participation and potential resistance from those excluded in the process. The impact of a mandate-based system often includes streamlined governance and clear accountability, yet risks centralized control that may overlook diverse perspectives and needs.
Benefits of Consensus-Based Approaches
Consensus-based approaches foster collaboration and collective ownership, leading to more sustainable and widely accepted decisions. This method enhances group cohesion by ensuring all voices are heard, which reduces conflicts and increases satisfaction among participants. Empirical studies show consensus processes result in higher commitment to implementation compared to mandate-driven directives.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Mandates
Mandates often face resistance due to limited stakeholder buy-in, leading to reduced compliance and increased conflict within organizations. The lack of flexibility in mandates can hinder innovation and adaptability to changing circumstances, resulting in suboptimal outcomes. Enforcement of mandates requires significant resources, which can strain organizational capacity and generate resentment among affected parties.
Practical Examples: Consensus vs Mandate in Action
Consensus in action is exemplified by team meetings where all members discuss and agree on project timelines, ensuring collective buy-in and collaboration. Mandate is demonstrated when a company CEO directs the marketing team to launch a campaign by a specific date, emphasizing top-down decision-making and swift execution. In government, consensus is seen in bipartisan legislation passed through negotiation, while mandates appear as executive orders enforcing policies without legislative approval.
When to Choose Consensus over Mandate
Consensus is preferable when team collaboration, diverse input, and shared ownership of decisions are critical for project success and long-term commitment. It fosters open communication, aligns stakeholders' interests, and enhances buy-in, especially in complex or innovative environments where adaptability is essential. Choosing consensus over mandate reduces resistance, increases trust, and leverages collective intelligence to achieve more sustainable outcomes.
The Impact of Organizational Culture on Decision Methods
Organizational culture profoundly influences the effectiveness of consensus and mandate decision-making methods, with collaborative cultures favoring consensus for increased employee engagement and innovation. In contrast, hierarchical cultures rely on mandates to ensure swift execution and clear accountability, especially in high-stakes environments. Understanding these cultural dynamics enables leaders to align decision strategies with organizational values, enhancing overall performance and adaptability.
Striking a Balance: Integrating Consensus and Mandate
Striking a balance between consensus and mandate involves integrating collaborative decision-making with authoritative directives to optimize organizational effectiveness. Consensus fosters inclusive participation and shared ownership, enhancing commitment and reducing resistance, while mandates ensure swift execution and clear accountability during critical situations. Combining these approaches strengthens strategic alignment, promotes adaptability, and drives cohesive action within complex environments.
Consensus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com